Related Research Articles

Gunter Annex is a United States Air Force installation located in the North-northeast suburbs of Montgomery, Alabama. The base is named after former Montgomery mayor William Adams Gunter. Until 1992 it was known as Gunter Air Force Base or Gunter Air Force Station. It has been a military training base since its opening in 1940.

Dothan Regional Airport is a public airport in Dale County, Alabama, United States, seven miles northwest of Dothan, a city mostly in Houston County.

Pryor Field Regional Airport is a public airport located three miles (5 km) northeast of the central business district of Decatur and south of Athens, in Limestone County, Alabama, United States. It is owned by Decatur/Athens Airport Authority.

Tuscaloosa National Airport is 3.5 miles northwest of Tuscaloosa, in Tuscaloosa County, Alabama. The airport is owned and operated by the City of Tuscaloosa. The FAA's National Plan of Integrated Airport Systems for 2019–2023 categorized the airport as a general aviation facility. The City of Tuscaloosa changed the name of the airport that had formerly operated under the name Tuscaloosa Regional Airport, in March 2019, to reflect the FAA's official designation as a national airport, one of only 89 in the nation.
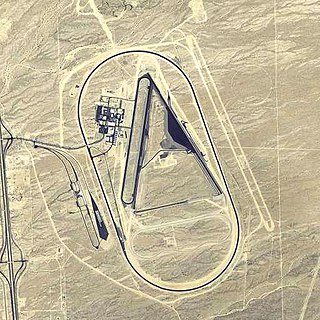
Yucca Army Airfield is a former military airfield located about 1 mile (1.6 km) west of Yucca, in Mohave County, Arizona, United States. It is on the east side of Interstate 40, 25 miles (40 km) south of Kingman. It is now used as a private facility owned by Fiat Chrysler Automobiles named Chrysler Arizona Proving Grounds.
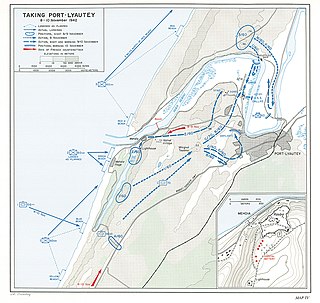
The Battle of Port Lyautey began on 8 November 1942 for the city of Port Lyautey, today known as Kenitra, in French Morocco. The battle ended with its capture and occupation by American troops, overrunning French forces after more than two days of fierce fighting.

Greenville Air Force Base is a former United States Air Force base in Greenville, Mississippi. It was closed as a military installation in December 1966 and redeveloped into Mid-Delta Regional Airport.

Stuttgart Army Airfield is a former World War II military airfield, located 7 miles north of Stuttgart, Arkansas. It operated as an advanced pilot training school for the United States Army Air Forces from 1942 until 1945.

George Field is a former World War II military airfield, located 5 miles east-northeast of Lawrenceville, Illinois. It operated as an advanced pilot training school for the United States Army Air Forces from 1942 until 1945.
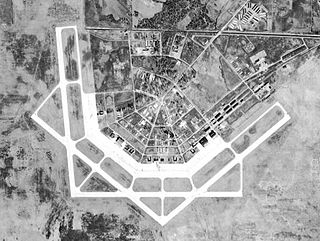
Courtland Army Airfield is a former United States Army facility located two nautical miles northeast of the central business district of Courtland, a town in Lawrence County, Alabama, United States.
Danville Auxiliary Field is a former facility of the United States Army Air Forces located in Danville, Alabama. Constructed after 1941 as an auxiliary to the nearby Courtland Army Air Field, it was turned into Danville Airport following the war, and was eventually closed between 1986 and 1989. No trace of the airfield remains.
Trinity Auxiliary Field is a former facility of the United States Army Air Forces located in Trinity, Alabama. Constructed after 1941 as an auxiliary to the nearby Courtland Army Air Field, it was turned back into farmland after the war.
Bay Auxiliary Field is a former facility of the United States Army Air Forces located in Courtland, Alabama. Constructed after 1941 as an auxiliary to the nearby Courtland Army Air Field, it was converted back into farmland after the war.
Furniss Auxiliary Field is a former facility of the United States Army Air Forces located in Orrville, Alabama. Constructed after 1941 as an auxiliary to the nearby Craig Field, it was turned back into farmland after the war.
Mollette Auxiliary Field is a former facility of the United States Army Air Forces located in Orrville, Alabama. Constructed after 1941 as an auxiliary to the nearby Craig Field, it was turned back into farmland after the war.
Passmore Auxiliary Field is a former facility of the United States Army Air Forces located in Prattville, Alabama. Constructed after 1941 as an auxiliary to the nearby Maxwell Field, it was turned back into farmland after the war.
Troy Auxiliary Field is a former facility of the United States Army Air Forces located in Troy, Alabama. Constructed after 1942 as an auxiliary to the nearby Maxwell Field, it was turned into Troy Municipal Airport after the war.

Chico Army Airfield auxiliary fields were a number of airfields used during World War II to support the Chico Army Airfield. On September 11, 1941, the US Army rented from the City of Chico a small 1930's airport that sat on 160 acres (0.65 km2) of land. The Airfield was five miles (8.0 km) north of the city center. The Army built up the small airport into the Chico Army Airfield. From the Chico Army Airfield operated the: United States Army Air Corps's Army Air Forces Basic Flying School, the Army Air Force Pilot School, the 10th Base Headquarters an Air Base Squadron and the 433rd Army Air Force Base Unit or Combat Crew Training Station of Fighter. To support the training of the many pilots, Chico Army Airfield operated a number of auxiliary airfields. Some auxiliary fields were no more than a landing strip runway, others were other operation airfield that supported the training at the Chico Army Airfield.

Victorville Army Airfield auxiliary fields were four airfields used during World War II to support the Victorville Army Airfield pilot training near Victorville, California, and Adelanto, California. After the war the Victorville Army Airfield was renamed George Air Force Base on January 13, 1948. The airfields were built in 1941 by the United States Army Air Corps just before the war. Victorville Army Airfield covered 2,200-acre in the Mojave Desert. The US Army held a groundbreaking ceremony on 12 July 1941. The base, called Victorville Army Flying School, was ready to use before the attack on Pearl Harbor on December 7, 1941. The Army built four runways in a triangle configuration, with one runway down the middle of the triangle. Seven hangars were built to support operation. On April 23, 1943, the base was renamed Victorville Army Airfield.

Merced Army Air Field auxiliary fields were built to support pilot training at the Merced Army Air Field. In 1940 the US Army wanted to build near Merced, California a 30,000 per year basic pilot training base. The former city of Cuba, Merced County, California near the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway rail line was chosen at 37°22′50″N120°34′05″W at an elevation of 181 feet (55 m) for the main base, in Atwater, California. United States Army Air Corps leased the land from the City of Merced on 16 June 1941. Building the airbase school started on 8 July 1941 and opened on 20 September 1941 as a sub-base of Army Air Forces Western Flying Training Command at Moffett Field. First called Air Corps Basic Flying School, Merced. The US Army moved part of the: 98th Bombardment Group, 539th School Squadrons, 540th School Squadrons, 541st School Squadrons, the 90th Air Base Squadron, and the 340th Material Squadron at Moffett Field to the new base in November 1941. The Air Corps Basic Flying School was renamed the Merced Army Flying School on 7 April 1942. To support the training auxiliary fields near the Merced Army Flying School were to be built for the flight training program. Merced Army Flying School was renamed the Merced Army Air Field in May 1943 and became part of the Western Flying Training Command.
References
- ↑ "WW2 Military Airfields including Auxiliaries and Support fields Alabama - California". Airfieldsdatabase.com. Archived from the original on 27 September 2016. Retrieved 25 October 2015.