
Spilomelinae is a very species-rich subfamily of the lepidopteran family Crambidae, the crambid snout moths. With 4,132 described species in 340 genera worldwide, it is the most speciose group among pyraloids.

Anacampsis is a worldwide genus of moth with most found in the nearctic and neotropical regions. It is in the family Gelechiidae. The larvae feed on a range of deciduous trees and shrubs in a rolled or folded leaf, or spun shoot.

Acrobasis is a genus of moths of the family Pyralidae.

Udea is a genus of snout moths in the subfamily Spilomelinae of the family Crambidae. The genus was erected by Achille Guenée in 1845. The currently known 214 species are present on all continents except Antarctica. About 41 species are native to Hawaii.
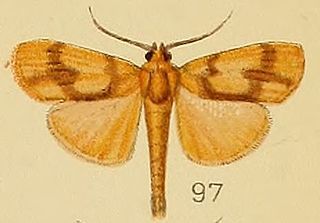
Ulopeza is a genus of moths of the family Crambidae. It was described by Philipp Christoph Zeller in 1852.

Patania is a genus of moths of the family Crambidae described by Moore in 1888.
Piletocera is a genus of moths of the family Crambidae. The genus was first described by Julius Lederer in 1863.

Scoparia is a grass moth genus of subfamily Scopariinae. Some authors have assigned the synonymous taxon Sineudonia to the snout moth family (Pyralidae), where all grass moths were once also included, but this seems to be in error.

Trichophysetis is a genus of moths of the family Crambidae.

Titanio is a genus of moths of the family Crambidae.

The Epipaschiinae are a subfamily of snout moths. Almost 600 species are known today, which are found mainly in the tropics and subtropics. Some occur in temperate regions, but the subfamily is apparently completely absent from Europe, at least as native species. A few Epipaschiinae are crop pests that may occasionally become economically significant.

Ancylosis is a genus of snout moth. It was described by Philipp Christoph Zeller in 1839, and is known from South Africa, Uzbekistan, Spain, Turkmenistan, Lebanon, Algeria, Tunisia, Russia, Israel, Palestine, Tinos, Australia, Seychelles, Afghanistan, the United States, Iraq, Namibia, Kazakhstan, Iran, Mauritius, Mozambique, Sarepta, Argentina, Sri Lanka, and Aden.

Euzophera is a genus of snout moths. It was described by Philipp Christoph Zeller in 1867.
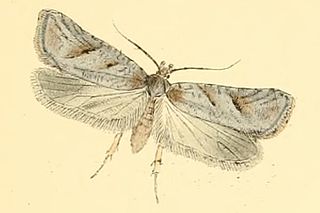
Exaeretia is a moth genus of the superfamily Gelechioidea. It is placed in the family Depressariidae, which is often – particularly in older treatments – considered a subfamily of Oecophoridae or included in the Elachistidae.

Sciota is a genus of snout moths. It was described by George Duryea Hulst in 1888.
Lepidogma atomalis is a species of snout moth in the genus Lepidogma. It was described by Hugo Theodor Christoph in 1887 and is known from Turkey.
Lepidogma violescens is a species of snout moth in the genus Lepidogma. It was described by Harrison Gray Dyar Jr. in 1914 and is known from Panama.
Lepidogma megaloceros is a species of snout moth in the genus Lepidogma. It was described by Edward Meyrick in 1934, and is known from the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Lepidogma obatralis is a species of snout moth in the genus Lepidogma. It was described by Hugo Theodor Christoph in 1877 and is known from Turkmenistan.

Xyloryctidae is a family of moths contained within the superfamily Gelechioidea described by Edward Meyrick in 1890. Most genera are found in the Indo-Australian region. While many of these moths are tiny, some members of the family grow to a wingspan of up to 66 mm, making them giants among the micromoths.













