The ovipositor is a tube-like organ used by some animals, especially insects, for the laying of eggs. In insects, an ovipositor consists of a maximum of three pairs of appendages. The details and morphology of the ovipositor vary, but typically its form is adapted to functions such as preparing a place for the egg, transmitting the egg, and then placing it properly. For most insects, the organ is used merely to attach the egg to some surface, but for many parasitic species, it is a piercing organ as well.

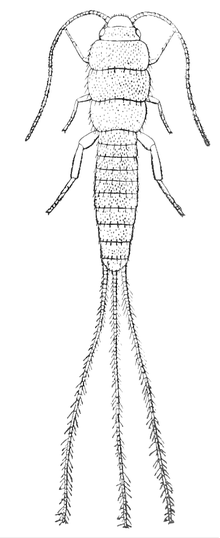
Thysanura is the now deprecated name of what was, for over a century, recognised as an order in the class Insecta. The two constituent groups within the former order, the Archaeognatha and the Zygentoma, share several characteristics, such as of having three long caudal filaments, the lateral ones being the cerci, while the one between (telson) is a medial cerciform appendage, specifically an epiproct. They are also both wingless, and have bodies covered with fine scales, rather like the scales of the practically unrelated Lepidoptera. In the late 20th century, it was recognized that the two suborders were not sister taxa, therefore Thysanura was paraphyletic, and the two suborders were each raised to the status of an independent monophyletic order, with Archaeognatha sister taxon to the Dicondylia, including the Zygentoma.

The Pterygota are a subclass of insects that includes all winged insects and the orders that are secondarily wingless.

Lepisma is a genus of primitive insects in the order Zygentoma and the family Lepismatidae.

The name Apterygota is sometimes applied to a subclass of small, agile insects, distinguished from other insects by their lack of wings in the present and in their evolutionary history; notable examples are the silverfish, the firebrat, and the jumping bristletails. Their first known occurrence in the fossil record is during the Devonian period, 417–354 million years ago. The group Apterygota is not a clade; it is paraphyletic, and not universally recognized. As defined, the group contains two separate clades of wingless insects: Archaeognatha comprises jumping bristletails, while Zygentoma comprises silverfish and firebrats. The Zygentoma are in the clade Dicondylia with winged insects, a clade that includes all other insects, while Archaeognatha is sister to this lineage.

The Archaeognatha are an order of apterygotes, known by various common names such as jumping bristletails. Among extant insect taxa they are some of the most evolutionarily primitive; they appeared in the Middle Devonian period at about the same time as the arachnids. Specimens that closely resemble extant species have been found as both body and trace fossils in strata from the remainder of the Paleozoic Era and more recent periods. For historical reasons an alternative name for the order is Microcoryphia.

Lepismatidae is a family of primitive wingless insects with about 190 described species. This family contains the two most familiar members of the order Zygentoma: the silverfish and the firebrat. It is one of five families in the order Zygentoma.

Zygentoma are an order in the class Insecta, and consist of about 550 known species. The Zygentoma include the so-called silverfish or fishmoths, and the firebrats. A conspicuous feature of the order are the three long caudal filaments. The two lateral filaments are cerci, and the medial one is an epiproct or appendix dorsalis. In this they resemble the Archaeognatha, although the cerci of Zygentoma, unlike in the latter order, are nearly as long as the epiproct.

Ctenolepisma is a genus of primitive insects in the order Zygentoma, closely related to the silverfish and firebrat but less reliant on human habitation, some species being found both indoors and outdoors and some found exclusively outdoors. The genus is distributed nearly worldwide in warm regions. Australia lacks native Ctenolepisma, but is home to introduced species.

Ctenolepisma lineatum is a species of insect of the order Zygentoma. It is similar to the closely related silverfish but can be distinguished by being rather stouter and less shiny with all appendages noticeably longer. The abdomen is often marked with dark brown lines and the species is sometimes called four-lined silverfish.
A silverfish is a wingless insect in the order Zygentoma. The same name can be applied to many species in the order as a whole, which comprises the families the Lepismatidae, Nicoletiidae, Lepidotrichidae, Maindroniidae and Protrinemuridae.

Lepidothrix is a genus of passerine birds in the manakin family Pipridae. Birds in the genus are predominantly found in South America, but one species, the velvety manakin, also ranges into Central America. The females of this genus have green plumage with yellow bellies, as do some of the males. The remaining males have black plumage with white or blue crowns. Some also have yellow bellies or blue rumps.

Maindroniidae is a very small family of silverfish, basal insects belonging to the order Zygentoma. It contains just a single genus, Maindronia, and a handful of species.

The silverfish is a species of small, primitive, wingless insect in the order Zygentoma. Its common name derives from the insect's silvery light grey colour, combined with the fish-like appearance of its movements. The scientific name indicates that the silverfish's diet consists of carbohydrates such as sugar or starches. While the common name silverfish is used throughout the global literature to refer to various species of Zygentoma, the Entomological Society of America restricts use of the term solely for Lepisma saccharinum.

Nicoletiidae is a family of primitive insects belonging to the order Zygentoma. These insects live primarily underground, under detritus, or in caves. A few species are recorded as commensals inside nests of social insects, such as the species Allotrichotriura saevissima which lives inside fire ant nests.Nicoletiidae don’t have eyes as other existing species and they lack pigment. They have medium size, with extended antennae and terminal filaments.Coletinia, a genus of this family, has many characters including a body length that ranges between 10 and 15mm. They may have yellowish pigmentation but most of them are transparent. They have bilayered and very large acrosome, a short nucleus including chromatin being really condensed with tubular invaginations and sperm length and head size classified as short.
Atelurinae is a subfamily of primitive insects belonging to the order Zygentoma. Once considered an independent family, it is now treated as a subfamily within the Nicoletiidae. They are generally found in association with ants or termites, living as inquilines in the hosts' nests. They are typically small, tear-drop or sub-ovoid in body shape, light yellow in color and lacking eyes. The subfamily is quite diverse, with more than 140 described species in about 70 genera; many of the genera are monotypic.
Nicoletia is a genus of silverfish in the family Nicoletiidae. As of 2007, it contains the former members of two other genera.

Lepidotrix is an extinct genus of wingless insect belonging to Zygentoma in the family Lepidotrichidae. There is one described species in Lepidotrix, L. piliferum/pillifera. It is known from specimens found in Eocene aged Baltic amber and Rovno amber. The genus lacks occelli. Its relationship with the extant genus Tricholepidion, which has historically been placed in the same family, is disputed, with some studies finding the two taxa to not be closely related, with Tricholepidion being placed in its own family instead. While often spelled Lepidothrix in historic literature, this is homonymous with a genus of birds, and Lepidotrix was the spelling used in the original publication.

Tricholepidion is a genus of wingless insect belonging to Zygentoma, with only a single described species T. gertschi, native to the northern coast of California in Western North America. It lives under dead bark and in rotting wood of conifers in mesophytic forests. It is alternatively considered the only living member of the family Lepidotrichidae, which also includes Lepidotrix from Eocene aged European amber, or the only member of the family Tricholepidiidae. The taxonomic position of Tricholepidion is uncertain, in some molecular phylogenetics studies it has been recovered as less closely related to flying insects (Pterygota) than the rest of Zygentoma is, rendering Zygentoma paraphyletic. Each compound eye contains ~40 ommatidia, and they have three ocelli. Scales on the body are absent. Unlike Archaeognatha and the other families of Zygentoma, which have three- and sometimes two-segmented tarsi, they have five-segmented tarsi like many winged insects.

Ctenolepisma longicaudatum, generally known as the gray silverfish, long-tailed silverfish or paper silverfish, is a species of Zygentoma in the family Lepismatidae. It was described by the German entomologist Karl Leopold Escherich in 1905 based on specimens collected in South Africa, but is found worldwide as synanthrope in human housings.