Related Research Articles

Day trading is a form of speculation in securities in which a trader buys and sells a financial instrument within the same trading day, so that all positions are closed before the market closes for the trading day to avoid unmanageable risks and negative price gaps between one day's close and the next day's price at the open. Traders who trade in this capacity are generally classified as speculators. Day trading contrasts with the long-term trades underlying buy-and-hold and value investing strategies. It is made easier using day trading software. Day trading is similar to swing trading, in which positions are held for a few days.
In financial services, a broker-dealer is a natural person, company or other organization that engages in the business of trading securities for its own account or on behalf of its customers. Broker-dealers are at the heart of the securities and derivatives trading process.
The Depository Trust & Clearing Corporation (DTCC) is an American post-trade financial services company providing clearing and settlement services to the financial markets. It performs the exchange of securities on behalf of buyers and sellers and functions as a central securities depository by providing central custody of securities.
Front running, also known as tailgating, is the prohibited practice of entering into an equity (stock) trade, option, futures contract, derivative, or security-based swap to capitalize on advance, nonpublic knowledge of a large ("block") pending transaction that will influence the price of the underlying security. In essence, it means the practice of engaging in a Personal Securities Transaction in advance of a transaction in the same security for a client's account. Front running is considered a form of market manipulation in many markets. Cases typically involve individual brokers or brokerage firms trading stock in and out of undisclosed, unmonitored accounts of relatives or confederates. Institutional and individual investors may also commit a front running violation when they are privy to inside information. A front running firm either buys for its own account before filling customer buy orders that drive up the price, or sells for its own account before filling customer sell orders that drive down the price. Front running is prohibited since the front-runner profits from nonpublic information, at the expense of its own customers, the block trade, or the public market.
Algorithmic trading is a method of executing orders using automated pre-programmed trading instructions accounting for variables such as time, price, and volume. This type of trading attempts to leverage the speed and computational resources of computers relative to human traders. In the twenty-first century, algorithmic trading has been gaining traction with both retail and institutional traders. It is widely used by investment banks, pension funds, mutual funds, and hedge funds that may need to spread out the execution of a larger order or perform trades too fast for human traders to react to. A study in 2019 showed that around 92% of trading in the Forex market was performed by trading algorithms rather than humans.
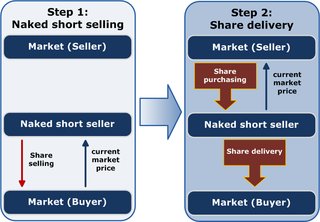
Naked short selling, or naked shorting, is the practice of short-selling a tradable asset of any kind without first borrowing the asset from someone else or ensuring that it can be borrowed. When the seller does not obtain the asset and deliver it to the buyer within the required time frame, the result is known as a "failure to deliver" (FTD). The transaction generally remains open until the asset is acquired and delivered by the seller, or the seller's broker settles the trade on their behalf.
Direct market access (DMA) is a term used in financial markets to describe electronic trading facilities that give investors wishing to trade in financial instruments a way to interact with the order book of an exchange. Normally, trading on the order book is restricted to broker-dealers and market making firms that are members of the exchange. Using DMA, investment companies and other private traders use the information technology infrastructure of sell side firms such as investment banks and the market access that those firms possess, but control the way a trading transaction is managed themselves rather than passing the order over to the broker's own in-house traders for execution. Today, DMA is often combined with algorithmic trading giving access to many different trading strategies. Certain forms of DMA, most notably "sponsored access", have raised substantial regulatory concerns because of the possibility of a malfunction by an investor to cause widespread market disruption.
Regulation National Market System is a US financial regulation promulgated and described by the United States Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) as "a series of initiatives designed to modernize and strengthen the National Market System for equity securities". The Reg NMS is intended to assure that investors receive the best (NBBO) price executions for their orders by encouraging competition in the marketplace. Some contend that the rule has contributed to the rise of high-frequency trading, which is sometimes regarded as controversial.

In finance, a dark pool is a private forum for trading securities, derivatives, and other financial instruments. Liquidity on these markets is called dark pool liquidity. The bulk of dark pool trades represent large trades by financial institutions that are offered away from public exchanges like the New York Stock Exchange and the NASDAQ, so that such trades remain confidential and outside the purview of the general investing public. The fragmentation of electronic trading platforms has allowed dark pools to be created, and they are normally accessed through crossing networks or directly among market participants via private contractual arrangements. Generally, dark pools are not available to the public, but in some cases, they may be accessed indirectly by retail investors and traders via retail brokers.
An electronic trading platform is a piece of computer software that allows users to place orders for financial products over a network with a financial intermediary. These products include products such as stocks, bonds, currencies, commodities, and derivatives. The first widespread electronic trading platform was Nasdaq. The availability of such trading platforms to the public has encouraged a surge in retail investing.
Lightspeed Trading, LLC offers an electronic trading platform to trade financial assets including common stocks, preferred stocks, futures contracts, exchange-traded funds, options, mutual funds, and fixed income investments. It also provides margin lending, and cash management services.
High-frequency trading (HFT) is a type of algorithmic financial trading characterized by high speeds, high turnover rates, and high order-to-trade ratios that leverages high-frequency financial data and electronic trading tools. While there is no single definition of HFT, among its key attributes are highly sophisticated algorithms, co-location, and very short-term investment horizons. HFT can be viewed as a primary form of algorithmic trading in finance. Specifically, it is the use of sophisticated technological tools and computer algorithms to rapidly trade securities. HFT uses proprietary trading strategies carried out by computers to move in and out of positions in seconds or fractions of a second.

Matchbook FX was an internet-based electronic communication network for trading currency online in the Spot-FX or foreign exchange market. It operated between 1999 and 2002.

The May 6, 2010, flash crash, also known as the crash of 2:45 or simply the flash crash, was a United States trillion-dollar flash crash which started at 2:32 p.m. EDT and lasted for approximately 36 minutes.

Virtu Financial is an American company that provides financial services, trading products and market making services. Virtu provides product suite including offerings in execution, liquidity sourcing, analytics and broker-neutral, multi-dealer platforms in workflow technology and two-sided quotations and trades in equities, commodities, currencies, options, fixed income, and other securities on over 230 exchanges, markets, and dark pools. Virtu uses proprietary technology to trade large volumes of securities. The company went public on the Nasdaq in 2015.

Investors Exchange (IEX) is a stock exchange based in the United States. It was founded in 2012 in order to mitigate the effects of high-frequency trading. IEX was launched as a national securities exchange in September 2016. On October 24, 2017, IEX received regulatory approval from the SEC to list companies. IEX listed its first public company, Interactive Brokers, on October 5, 2018. The exchange said that companies would be able to list for free for the first five years, before a flat annual rate of $50,000. On September 23, 2019 it announced it was exiting its listing business.

Interactive Brokers LLC (IB) is an American multinational brokerage firm. It operates the largest electronic trading platform in the U.S. by number of daily average revenue trades. The company brokers stocks, options, futures, EFPs, futures options, forex, bonds, and funds.

Securities market participants in the United States include corporations and governments issuing securities, persons and corporations buying and selling a security, the broker-dealers and exchanges which facilitate such trading, banks which safe keep assets, and regulators who monitor the markets' activities. Investors buy and sell through broker-dealers and have their assets retained by either their executing broker-dealer, a custodian bank or a prime broker. These transactions take place in the environment of equity and equity options exchanges, regulated by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), or derivative exchanges, regulated by the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC). For transactions involving stocks and bonds, transfer agents assure that the ownership in each transaction is properly assigned to and held on behalf of each investor.
Jump Trading LLC is a proprietary trading firm with a focus on algorithmic and high-frequency trading strategies. The firm has over 700 employees in Chicago, New York, Austin, London, Tel Aviv, Singapore, Shanghai, Bristol, Gurgaon, Gandhnagar, Sydney, Amsterdam, Hong Kong, and Paris and is active in futures, options, cryptocurrency, and equities markets worldwide.
Stake is an Australian financial services company headquartered in Sydney, Australia. It was founded in 2016 by Matt Liebowitz and Dan Silver. Stake predominately offers low-cost brokerage services to retail investors in Australia, New Zealand, Brazil and the United Kingdom.
References
- ↑ Release, Press (2022-03-18). "Score Priority Rebrands to Lime Financial". Traders Magazine. Retrieved 2022-05-03.
- ↑ "Finam and WhoTrades – New Arrivals to Social and Forex Trading | Finance Magnates". Financial and Business News | Finance Magnates. Retrieved 2022-04-25.
- ↑ Inc, WhoTrades (2015-04-06). "Broker-Dealer WhoTrades, Inc. Acquires Just2Trade & LowTrades Brands". GlobeNewswire News Room. Retrieved 2022-04-25.
- ↑ "WhoTrades - Apps on Google Play". play.google.com. Retrieved 2022-04-25.
- ↑ "New name and updated branding are next steps in the company's journey to transform into a destination for traders". markets.businessinsider.com. Retrieved 2022-05-03.
- ↑ "2021 Outlook: Tony Huck, Score Priority". Markets Media. 2021-01-08. Retrieved 2022-05-03.
- ↑ Release, Press (2020-12-02). "Score Priority Acquires Lightspeed's HFT Assets". Traders Magazine. Retrieved 2022-04-25.
- ↑ "Score Priority Corp. Integrates with Sterling Trader® Pro". www.businesswire.com. 2021-06-17. Retrieved 2022-04-25.
- ↑ "Score Priority Review". Investopedia. Retrieved 2022-05-03.
- ↑ Lyudvig, Anna (2021-08-03). "Lugene Forte: New CEO of Score Priority Sets High Goals". Traders Magazine. Retrieved 2022-04-25.
- ↑ "Score Priority Rebrands to Lime Financial, Expands Access to the Financial Markets for More Traders, Investors and Developers". www.businesswire.com. 2022-03-17. Retrieved 2022-04-25.
- ↑ NYSE Floor Talk: Lime Financial , retrieved 2022-05-03