
Mentha is a genus of plants in the family Lamiaceae. The exact distinction between species is unclear; it is estimated that 13 to 24 species exist. Hybridization occurs naturally where some species' ranges overlap. Many hybrids and cultivars are known.

Mentha aquatica is a perennial flowering plant in the mint family Lamiaceae. It grows in moist places and is native to much of Europe, northwest Africa and southwest Asia.

Alisma plantago-aquatica, also known as European water-plantain, common water-plantain or mad-dog weed, is a perennial flowering aquatic plant widespread across most of Europe and Asia, and apparently spread elsewhere in both the Old and New World.

The diving bell spider or water spider is the only species of spider known to live almost entirely under water. It is the only member of the genus Argyroneta. When out of the water, the spider ranges in colour from mid to dark brown, although the hairs on the abdomen give it a dark grey, velvet-like appearance. It is native to freshwater habitats in Europe and Asia.

Ipomoea aquatica, widely known as water spinach, is a semi-aquatic, tropical plant grown as a vegetable for its tender shoots. I. aquatica is generally believed to have been first domesticated in Southeast Asia. It is widely cultivated in Southeast Asia, East Asia, and South Asia. It grows abundantly near waterways and requires little to no care.

Phalaris aquatica, known by the common names bulbous canary-grass and Harding grass, is a species of grass in the genus Phalaris of the family Poaceae.

Aquatica is a 705000sq ft water theme park in Kochpukur, under Bhangar 2 cd block of Baruipur sub division, South 24 pgs district, Greater Kolkata, India. The theme park was started in 1999. It is one of the largest water amusement parks in and around Kolkata, as well as eastern India. It is quite a popular destination on the day of Holi. Recently another water theme park, Wet 'O' Wild, has come up adjacent to Nicco Park in the Salt Lake City area.

SeaWorld San Antonio is a 250-acre (100 ha) marine mammal park, oceanarium and animal theme park in the Westover Hills District of San Antonio, Texas, on the city's west side. It is the largest of the three parks in the SeaWorld chain owned and operated by SeaWorld Parks & Entertainment. It is also one of the world's largest marine-life theme parks focused on conservation, education and animal rescue. It is a member of the Alliance of Marine Mammal Parks and Aquariums (AMMPA) and is accredited by the Association of Zoos and Aquariums (AZA).

Pachira aquatica is a tropical wetland tree in the mallow family Malvaceae, native to Central and South America where it grows in swamps. It is known by its common names Malabar chestnut, French peanut, Guiana chestnut, Provision tree, Saba nut, Monguba (Brazil), Pumpo (Guatemala) and is commercially sold under the names Money tree and Money plant. This tree is sometimes sold with a braided trunk and is commonly grown as a houseplant, although more commonly what is sold as a "Pachira aquatica" houseplant is in fact a similar species, P. glabra.

Nyssa aquatica, commonly called the water tupelo, cottongum, wild olive, large tupelo, tupelo-gum, or water-gum, is a large, long-lived tree in the tupelo genus (Nyssa) that grows in swamps and floodplains in the Southeastern United States.
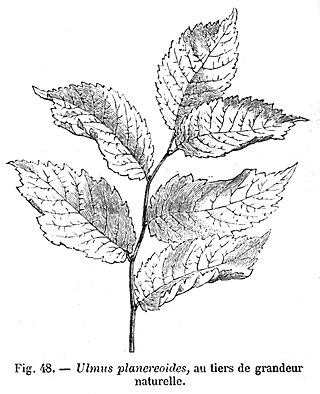
The elm cultivar Ulmus 'Planeroides' [:Planera-like elm] was described by Carrière in the Revue horticole, 1875. It was considered "possibly Ulmus carpinifolia" [:U. minor ] by Green.

Crassula aquatica is a succulent plant known by the common names water pygmyweed, common pygmyweed and just pigmyweed. It is an annual plant of salt marshes, vernal pools, wetlands, and other fresh to brackish water bodies. It is at least partially aquatic, living in areas which are submersed much of the time. It also lives along muddy banks and in tidally-active areas of estuaries.
Montrichardia aquatica is an extinct species of monocot plant in the family Araceae. M. aquatica is related to the living species M. arborescens and M. linifera. The species is solely known from the Middle to Late Paleocene, fossil-rich Cerrejón Formation in La Guajira, northern Colombia.
Aquatica is a chain of water parks owned and operated by SeaWorld Parks & Entertainment. Aquatica parks are operating in Orlando, Florida and San Antonio, Texas.

Ulmus pumila, or 'Poort Bulten,' is a Siberian elm cultivar that hails from Arboretum Poort Bulten in Losser, Netherlands. This tree was for many years mistaken for Planera aquatica or 'water elm' and commercially propagated under that name.
The hybrid elm cultivar Ulmus × hollandica 'Viminalis' [:osier-leaved] was listed by the Späth nursery of Berlin as Ulmus scabraMill. var. viminalis in 1890 and as Ulmus montana viminalis from 1892. Though Späth's catalogues stated that it was "also distributed under the name planera aquatica", it remained in his lists under 'elm' and was accessioned by the Dominion Arboretum, Ottawa, and by the Royal Botanic Garden Edinburgh as an elm cultivar. A similar misidentification occurred in the mid-20th century, when the Siberian elm cultivar Ulmus pumila 'Poort Bulten' was for many years commercially propagated under the name Planera aquatica or 'water elm'. As the leaves of osier or Salix viminalis, however, differ markedly from those of Planera aquatica, being long, thin and tapering at both ends, Spath's name 'Viminalis' for this elm cultivar confirms that its leaves were not Planera-like. The probable explanation for the early distribution name is that Planera was the old name for Zelkova, a close relative of elm with willow-like leaves. It is therefore unlikely that 'Viminalis' was related in any way to the 19th-century elm cultivar Ulmus 'Planeroides'.
Limnochares is a genus of mites in the family Limnocharidae. There are at least two described species in Limnochares.

Pachira glabra is a tropical wetland tree in the mallow family Malvaceae, native to eastern Brazil, where it grows along rivers and other waterways. It is generally known by the nonscientific names Guinea peanut, French peanut, Saba nut, money tree, and lucky tree. It shares many of these common names with Pachira aquatica, the Malabar chestnut, which is quite similar looking, has similar culinary and ornamental uses, and is often confused with P. glabra.

Catabrosa aquatica, called brookgrass, water whorl-grass, water whirlgrass and water hairgrass, is a widespread species of semi-aquatic grass in the genus Catabrosa, native to the most of the non-tropical northern hemisphere, and to southern Chile and Argentina. As its scientific and common names suggest, it prefers to grow in wet areas, such as meadows, stream banks and lake shores.
Sesame Place San Diego is a children's theme park and water park, located in Chula Vista, California. It opened on March 26, 2022, on the former site of Aquatica San Diego. It is the first theme park in the world to open up as a certified autism center by the International Board of Credentialing and Continuing Education Standards (IBCCES). Sesame Place in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, was the first theme park in the world to be a certified autism center.















