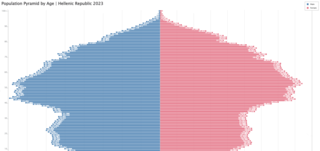
The Demographics of Greece refer to the demography of the population that inhabits the Greek peninsula. The population of Greece was estimated by the United Nations to be 10,445,365 in 2021.

Pakistan is a multilingual country with over 70 languages spoken as first languages. The majority of Pakistan's languages belong to the Indo-Iranian group of the Indo-European language family.
Bihari languages are a group of the Indo-Aryan languages. The Bihari languages are mainly spoken in the Indian states of Bihar, Jharkhand, Uttar Pradesh, and West Bengal, and also in Nepal. The most widely spoken languages of the Bihari group are Bhojpuri, Magahi and Maithili.

A multitude of languages have always been spoken in Canada. Prior to Confederation, the territories that would become Canada were home to over 70 distinct languages across 12 or so language families. Today, a majority of those indigenous languages are still spoken; however, most are endangered and only about 0.6% of the Canadian population report an indigenous language as their mother tongue. Since the establishment of the Canadian state, English and French have been the co-official languages and are, by far, the most-spoken languages in the country.
A minority language is a language spoken by a minority of the population of a territory. Such people are termed linguistic minorities or language minorities. With a total number of 196 sovereign states recognized internationally and an estimated number of roughly 5,000 to 7,000 languages spoken worldwide, the vast majority of languages are minority languages in every country in which they are spoken. Some minority languages are simultaneously also official languages, such as Irish in Ireland or the numerous indigenous languages of Bolivia. Likewise, some national languages are often considered minority languages, insofar as they are the national language of a stateless nation.
Kenya is a multilingual country. The two official languages of Kenya, Swahili and English, are widely spoken as lingua francas; however, including second-language speakers, Swahili is more widely spoken than English. Swahili is a Bantu language native to East Africa and English is inherited from British colonial rule.

Peru has many languages in use, with its official languages being Spanish, Quechua and Aymara. Spanish has been in the country since it began being taught in the time of José Pardo instead of the country's Native languages, especially the languages in the Andes. In the beginning of the 21st century, it was estimated that in this multilingual country, about 50 very different and popular languages are spoken: which reduces to 44 languages if dialects are considered variants of the same language. The majority of these languages are Indigenous, but the most common language is Spanish, the main language that about 94.4% of the population speaks. Spanish is followed by the country's Indigenous languages, especially all types of Quechua and Aymara (1.7%), who also have co-official status according to Article 48 of the Constitution of Peru, as well as the languages of the Amazon and the Peruvian Sign Language. In urban areas of the country, especially the coastal region, most people are monolingual and only speak Spanish, while in many rural areas of the country, especially in the Amazon, multilingual populations are prevalent.

The Republic of Vanuatu has the world's highest linguistic density per capita. Despite being a country with a population of less than 300,000, Vanuatu is home to 138 indigenous Oceanic languages.

Afghanistan is a linguistically diverse nation, with upwards of 40 distinct languages. However, Dari and Pashto are two of the most prominent languages in the country, and have shared official status under various governments of Afghanistan. Dari, as a shared language between multiple ethnic groups in the country, has served as a historical lingua franca between different linguistic groups in the region and is the most widely understood language in the country.

The official language of Greece is Greek, spoken by 99% of the population. In addition, a number of non-official, minority languages and some Greek dialects are spoken as well. The most common foreign languages learned by Greeks are English, German, French and Italian.

Thailand is home to 51 living indigenous languages and 24 living non-indigenous languages, with the majority of people speaking languages of the Southwestern Tai family, and the national language being Central Thai. Lao is spoken along the borders with the Lao PDR, Karen languages are spoken along the border with Myanmar, Khmer is spoken near Cambodia and Malay is spoken in the south near Malaysia. Sixty-two 'domestic' languages are officially recognized, and international languages spoken in Thailand, primarily by international workers, expatriates and business people, include Burmese, Karen, English, Chinese, Japanese, and Vietnamese, among others.

The geographical distribution of speakers of Macedonian refers to the total number of native speakers of Macedonian, an East South Slavic language that serves as the official language of North Macedonia. Estimates of the number of native and second language speakers of Macedonian varies; the number of native speakers in the country ranges from 1,344,815 according to the 2002 census in North Macedonia to 1,476,500 per linguistic database Ethnologue in 2016. Estimates of the total number of speakers in the world include 3.5 million people. Macedonian is studied and spoken as a second language by all ethnic minorities in the country.

The Tharu or Tharuhat languages are any of the Indo-Aryan languages spoken by the Tharu people of the Terai region in Nepal, and neighboring regions of Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh and Bihar in India.

The Warumungu language is spoken by the Warumungu people in Australia's Northern Territory. In addition to spoken language, the Warumungu have a highly developed sign language.

The Punjabi dialects and languages or Greater Punjabi are a series of dialects and languages spoken around the Punjab region of Pakistan and India with varying degrees of official recognition. They have sometimes been referred to as the Greater Punjabi macrolanguage. Punjabi may also be considered as a pluricentric language with more than one standard variety.
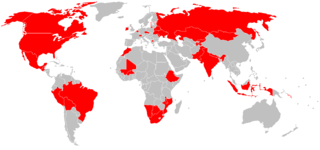
Many countries, through the use of censuses, enumerate their populations by languages and by their level of competence in using those languages.













