
The Craniidae are a family of brachiopods, the only surviving members of the subphylum Craniiformea. They are the only members of the order Craniida, the monotypic suborder Craniidina, and the superfamily Cranioidea; consequently, the latter two taxa are at present redundant and rarely used.There are three living genera within Craniidae: Neoancistrocrania, Novocrania, and Valdiviathyris. As adults, craniids either live freely on the ocean floor or, more commonly, cement themselves onto a hard object with all or part of the ventral valve.

Strophomenida is an extinct order of articulate brachiopods which lived from the lower Ordovician period to the mid Carboniferous period. Strophomenida is part of the extinct class Strophomenata, and was the largest known order of brachiopods, encompassing over 400 genera. Some of the largest and heaviest known brachiopod species belong to this class. Strophomenids were among the most diverse and abundant brachiopods during the Ordovician, but their diversity was strongly impacted at the Late Ordovician mass extinction. Survivors rediversified into new morphologies in the Silurian, only to be impacted once again at the Late Devonian mass extinction. However, they still survived till the mid Carboniferous.

Brachiopods, phylum Brachiopoda, are a phylum of trochozoan animals that have hard "valves" (shells) on the upper and lower surfaces, unlike the left and right arrangement in bivalve molluscs. Brachiopod valves are hinged at the rear end, while the front can be opened for feeding or closed for protection. Two major categories are traditionally recognized, articulate and inarticulate brachiopods. The word "articulate" is used to describe the tooth-and-groove structures of the valve-hinge which is present in the articulate group, and absent from the inarticulate group. This is the leading diagnostic skeletal feature, by which the two main groups can be readily distinguished as fossils. Articulate brachiopods have toothed hinges and simple, vertically oriented opening and closing muscles. Conversely, inarticulate brachiopods have weak, untoothed hinges and a more complex system of vertical and oblique (diagonal) muscles used to keep the two valves aligned. In many brachiopods, a stalk-like pedicle projects from an opening near the hinge of one of the valves, known as the pedicle or ventral valve. The pedicle, when present, keeps the animal anchored to the seabed but clear of sediment which would obstruct the opening.

The origin of the brachiopods is uncertain; they either arose from reduction of a multi-plated tubular organism, or from the folding of a slug-like organism with a protective shell on either end. Since their Cambrian origin, the phylum rose to a Palaeozoic dominance, but dwindled during the Mesozoic.
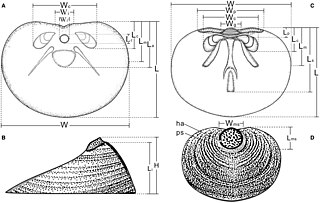
Acrotretides (Acrotretida) are an extinct order of linguliform brachiopods in the class Lingulata. Acrotretida contains 8 families within the sole superfamily Acrotretoidea. They lived from the Lower Cambrian to the Middle Devonian, rapidly diversifying during the middle Cambrian. In the upper Cambrian, linguliforms reached the apex of their diversity: acrotretides and their relatives the lingulides together comprised nearly 70% of brachiopod genera at this time. Though acrotretides continued to diversify during the Ordovician, their proportional dominance declined, as rhynchonelliforms took on a larger role in brachiopod faunas.

Rhynchonelliformea is a major subphylum and clade of brachiopods. It is roughly equivalent to the former class Articulata, which was used previously in brachiopod taxonomy up until the 1990s. These so-called articulated brachiopods have many anatomical differences relative to "inarticulate" brachiopods of the subphyla Linguliformea and Craniformea. Articulates have hard calcium carbonate shells with tongue-and-groove hinge articulations and separate sets of simple opening and closing muscles.

Pentamerida is an order of biconvex, impunctate shelled, articulate brachiopods that are found in marine sedimentary rocks that range from the Middle Cambrian through the Devonian.

Gigantoproductus giganteus is an extinct species of brachiopods in the family Monticuliferidae, known only from its fossil remains. It was a marine invertebrate found on the seabed in shallow seas. It evolved during the Carboniferous period and it is believed to be the largest brachiopod that has ever existed.

Paterinata is an extinct class of linguliform brachiopods which lived from the lower Cambrian ("Tommotian") to the Upper Ordovician (Hirnantian). It contains the single order Paterinida and the subfamily Paterinoidea. Despite being some of the earliest brachiopods to appear in the fossil record, paterinides stayed as a relatively subdued and low-diversity group even as other brachiopods diversified later in the Cambrian and Ordovician. Paterinides are notable for their high degree of convergent evolution with rhynchonelliform (articulate) brachiopods, which have a similar set of muscles and hinge-adjacent structures.

Trimerellida is an extinct order of craniate brachiopods, containing the sole superfamily Trimerelloidea and the families Adensuidae, Trimerellidae, and Ussuniidae. Trimerellidae was a widespread family of warm-water brachiopods ranging from the Middle Ordovician to the late Silurian (Ludlow). Adensuidae and Ussuniidae are monogeneric families restricted to the Ordovician of Kazakhstan. Most individuals were free-living, though some clustered into large congregations similar to modern oyster reefs.

Argyrotheca is a genus of very small to minute lampshells. All species share a large pedicel opening, one ridge on the inside of the pedunculate valve, pits in a diamond pattern on the inside of both valves, and without radial ridges that end in tubercles. It occurs in depths between 6 and 1300 m. It is known since the latest Cretaceous.

Productida is an extinct order of brachiopods in the extinct class Strophomenata. Members of Productida first appeared during the Silurian. They represented the most abundant group of brachiopods during the Permian period, accounting for 45-70% of all species. The vast majority of species went extinct during the Permian-Triassic extinction event, though a handful survived into the Early Triassic. Many productids are covered in hollow tubular spines, which are characteristic of the group. A number of functions for the spines have been proposed, including as a defensive mechanism against predators.

Siphonotretida is an extinct order of linguliform brachiopods in the class Lingulata. The order is equivalent to the sole superfamily Siphonotretoidea, itself containing the sole family Siphonotretidae. Siphonotretoids were originally named as a superfamily of Acrotretida, before being raised to their own order.

Kutorginates (Kutorginata) are an extinct class of early rhynchonelliform ("articulate") brachiopods. The class contains only a single order, Kutorginida (kutorginides). Kutorginides were among the earliest rhynchonelliforms, restricted to the lower-middle part of the Cambrian Period.

The orthotetides (Orthotetida) are an extinct order of brachiopods in the class Strophomenata. Though not particularly diverse or abundant relative to strophomenides (Strophomenida) or productides (Productida), orthotetides were nevertheless the longest-lasting order of strophomenates, surviving from the Middle Ordovician (“Llanvirn”) up until the Late Permian. Externally, many orthotetides are difficult to distinguish from strophomenides. Most fundamental differences between the two orders are internal: orthotetides have more elaborate cardinal processes and a greater diversity of shell microstructure.
Crurithyris is an extinct genus of brachiopod belonging to the order Spiriferida and family Ambocoeliidae.

Linoproductidae is an extinct family of brachiopods which lived during the Carboniferous and Permian periods. The family was widespread across marine habitats, with fossils having been found on all continents except Antarctica. Members of this family commonly lack dorsal spines, and are characterized in possessing a distinct trail and deep corpus cavity.

Productidae is an extinct family of brachiopods which lived from the Upper Devonian to Upper Permian periods in marine environments. It is the most diversified family in the suborder Productidina, with some 100 genera.

Echinoconchidae is an extinct family of brachiopods which lived from the Lower Carboniferous to Upper Permian periods in marine habitats. Currently, four subfamilies are assigned to it, though the evolutionary relationships between them and the family Productidae have been heavily debated for the better part of the 20th Century.

Antiquatonia is an extinct genus of brachiopod belonging to the order Productida and family Productidae. Specimens have been found in Carboniferous beds across many continents, suggesting the genus had a cosmopolitan distribution. Species level taxonomy of Antiquatonia is in need of revision.



















