
The following is a list of pagi (the Latin term glossing Old High German gowe , corresponding to English shire ) of the Frankish duchy of Alamannia (Swabia).

The following is a list of pagi (the Latin term glossing Old High German gowe , corresponding to English shire ) of the Frankish duchy of Alamannia (Swabia).
In Alamannia under Frankish suzerainty (8th century), each pagus was ruled by a count (Gaugraf ) who in turn responded to the duke of Alamannia. Many of the names of these territories survive in modern toponymy.
The county of Raetia Curiensis was absorbed into Alamannia in the early 10th century, as Burchard II at the time of the proclamation of the duchy also held the title of count of Raetia Curiensis. It comprised the Ringowe (Rheingau; Bregenz), named for the Rhine, and Retia proper.
At the time of its formation in the 10th century, the younger stem duchy comprised the following provinces (pagi, gowe ): [1]
The territory between Alamannia and Upper Burgundy was known as Argowe (Aargau, Lenzburg) named for the Aare river). The pertinence of this territory to either Alamannia or Upper Burgundy was disputed.
Counties of the kingdom of Upper Burgundy:

The Alemanni were a confederation of Germanic tribes on the Upper Rhine River. First mentioned by Cassius Dio in the context of the campaign of Caracalla of 213, the Alemanni captured the Agri Decumates in 260, and later expanded into present-day Alsace, and northern Switzerland, leading to the establishment of the Old High German language in those regions, by the eighth century named Alamannia.

The Duchy of Lorraine, originally Upper Lorraine, was a duchy now included in the larger present-day region of Lorraine in northeastern France. Its capital was Nancy.

Swabia is a cultural, historic and linguistic region in southwestern Germany. The name is ultimately derived from the medieval Duchy of Swabia, one of the German stem duchies, representing the territory of Alemannia, whose inhabitants interchangeably were called Alemanni or Suebi.

Alamannia or Alemannia was the kingdom established and inhabited by the Alemanni, a Germanic tribal confederation, after they broke through the Roman limes in 213. The Alemanni expanded from the Main River basin during the 3rd century, raiding Roman provinces and settling on the left bank of the Rhine River beginning in the 4th century.

Gau is a Germanic term for a region within a country, often a former or current province. It was used in the Middle Ages, when it can be seen as roughly corresponding to an English shire. The administrative use of the term was revived as a subdivision during the period of Nazi Germany in 1933–1945. It still appears today in regional names, such as the Rheingau or Allgäu.
Sundgau is a geographical territory in the southern Alsace region, on the eastern edge of France. The name is derived from Alemannic German Sunt-gowe, denoting an Alemannic county in the Old High German period. The principal city and historical capital is Altkirch.

The Duchy of Swabia was one of the five stem duchies of the medieval German Kingdom. It arose in the 10th century in the southwestern area that had been settled by Alemanni tribes in Late Antiquity.

The Kingdom of Upper Burgundy was a Frankish dominion established in 888 by the Welf king Rudolph I of Burgundy on the territory of former Middle Francia. It grew out of the Carolingian margraviate of Transjurane Burgundy southeast of ('beyond') the Jura Mountains together with the adjacent County of Burgundy (Franche-Comté) in the northwest. The adjective 'upper' refers to its location further up the Rhône river, as distinct from Lower Burgundy and also from the Duchy of Burgundy west of the Saône river. Upper Burgundy was reunited with the Kingdom of Lower Burgundy in 933 to form the Kingdom of Burgundy, later known as Kingdom of Arles or Arelat.
The Rammachgau was a Gau in southern Germany in present-day Baden-Württemberg. The Rammachgau was located in northern Upper Swabia.
The Duchy of Alsace was a large political subdivision of the Frankish Empire during the last century and a half of Merovingian rule. It corresponded to the territory of Alsace and was carved out of southern Austrasia in the last decade of the reign of Dagobert I, probably to stabilise the southern reaches of Austrasia against Alemannia and Burgundy. By the late Middle Ages, the region was considered part of Swabia.
The Conradines or Conradiner were a dynasty of Franconian counts and dukes in the 8th to 11th Century, named after Duke Conrad the Elder and his son King Conrad I of Germany.

The Romansh people are a Romance ethnic group, the speakers of the Romansh language, native to the Swiss canton of Grisons (Graubünden).

The Belfort Gap or Burgundian Gate is the area of relatively flat terrain between the Vosges Mountains to the north and the Jura Mountains to the south. It marks the watershed between the drainage basins of the River Rhine to the east and the River Rhône to the west, part of the European Watershed between the North Sea and the Mediterranean Sea. It is also the boundary between the historic regions of Burgundy to the west and Alsace to the east, and as such has marked the Franco-German border for long periods of its history.
Ufgau was a historical county (gowe) of the duchy of Franconia, along the Oos River and the lower Murg, delimited to the south by the counties of Albgau and Ortenau. It was part of the bishopric of Speyer. Modern cities located in the territory of Ufgau include Baden-Baden, Rastatt and Karlsruhe.
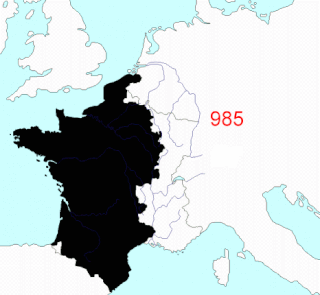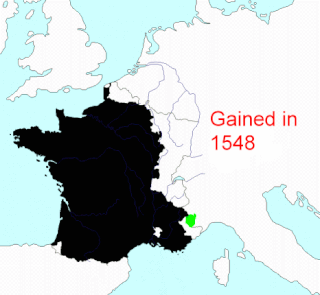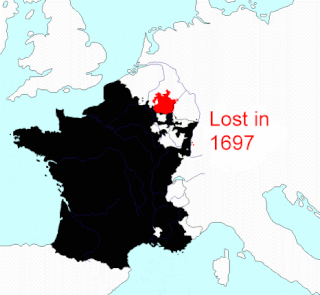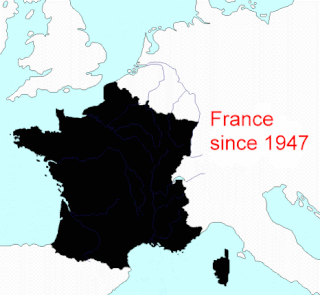
This article describes the process by which the territorial extent of metropolitan France came to be as it is since 1947. The territory of the French State is spread throughout the world. Metropolitan France is that part which is in Europe.

Raetia Curiensis was an early medieval province in Central Europe, named after the preceding Roman province of Raetia prima which retained its Romansh culture during the Migration Period, while the adjacent territories in the north were largely settled by Alemannic tribes. The administrative capital was Chur in the present Swiss canton of Grisons.

The County of Flanders was a historic territory in the Low Countries.

The Thurgau was a pagus of the Duchy of Alamannia in the early medieval period. A County of Thurgau existed from the 13th century until 1798. Parts of Thurgau were acquired by the Old Swiss Confederacy during the early 15th century, and the entire county passed to the Confederacy as a condominium in 1460.

The Province of Alsace was an administrative region of the Kingdom of France and one of the many provinces formed in the late 1600s. In 1648, the Landgraviate of Upper-Alsace was absorbed into the Kingdom of France and subsequently became the Province of Alsace, which it remain an integral part of for almost 150 years. In 1790, as a result of the Decree dividing France into departments, the province was disestablished and split into three departments: Bas-Rhin, Haut-Rhin, and part of Moselle.