Related Research Articles

The Pequot are a Native American people of Connecticut. The modern Pequot are members of the federally recognized Mashantucket Pequot Tribe, four other state-recognized groups in Connecticut including the Eastern Pequot Tribal Nation, or the Brothertown Indians of Wisconsin. They historically spoke Pequot, a dialect of the Mohegan-Pequot language, which became extinct by the early 20th century. Some tribal members are undertaking revival efforts.
Scouting in Connecticut has experienced many organizational changes since 1910. With only eight counties, Connecticut has had 40 Boy Scout Councils since the Scouting movement began in 1910. In 1922, 17 Boy Scout Councils existed in Connecticut, but currently only four exist. The Girl Scouts of the USA has had at least 53 Girl Scout Councils in Connecticut since their program began in 1912. Today there is one, Girl Scouts of Connecticut, which assumed operation on October 1, 2007.

Moodus is a village in the town of East Haddam, Connecticut, United States. The village is the basis of a census-designated place (CDP) of the same name. The population of the CDP was 1,982 as of the census of 2020.

Uncas was a sachem of the Mohegans who made the Mohegans the leading regional Indian tribe in lower Connecticut, through his alliance with the New England colonists against other Indian tribes.

The Pequot War was an armed conflict that took place in 1636 and ended in 1638 in New England, between the Pequot tribe and an alliance of the colonists from the Massachusetts Bay, Plymouth, and Saybrook colonies and their allies from the Narragansett and Mohegan tribes. The war concluded with the decisive defeat of the Pequot. At the end, about 700 Pequots had been killed or taken into captivity. Hundreds of prisoners were sold into slavery to colonists in Bermuda or the West Indies; other survivors were dispersed as captives to the victorious tribes.

The Quinnipiac River is a 45.5-mile (73.2 km) long river in the New England region of the United States, located entirely in the state of Connecticut.
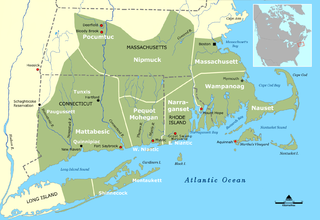
The Niantic are a tribe of Algonquian-speaking American Indians who lived in the area of Connecticut and Rhode Island during the early colonial period. They were divided into eastern and western groups due to intrusions by the more numerous and powerful Pequots. The Western Niantics were subject to the Pequots and lived just east of the mouth of the Connecticut River, while the Eastern Niantics became very close allies to the Narragansetts. It is likely that the name Nantucket is derived from the tribe's endonym, Nehantucket.

The Algonquian are one of the most populous and widespread North American native language groups. They historically were prominent along the Atlantic Coast and in the interior regions along Saint Lawrence River and around the Great Lakes. This grouping consists of the peoples who speak Algonquian languages.

Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands include Native American tribes and First Nation bands residing in or originating from a cultural area encompassing the northeastern and Midwest United States and southeastern Canada. It is part of a broader grouping known as the Eastern Woodlands. The Northeastern Woodlands is divided into three major areas: the Coastal, Saint Lawrence Lowlands, and Great Lakes-Riverine zones.

The Eastern Algonquian languages constitute a subgroup of the Algonquian languages. Prior to European contact, Eastern Algonquian consisted of at least 17 languages, whose speakers collectively occupied the Atlantic coast of North America and adjacent inland areas, from what are now the Maritimes of Canada to North Carolina. The available information about individual languages varies widely. Some are known only from one or two documents containing words and phrases collected by missionaries, explorers or settlers, and some documents contain fragmentary evidence about more than one language or dialect. Many of the Eastern Algonquian languages were greatly affected by colonization and dispossession. Miꞌkmaq and Malecite-Passamaquoddy have appreciable numbers of speakers, but Western Abenaki and Lenape (Delaware) are each reported to have fewer than 10 speakers after 2000.
The Mohegan are an Algonquian Native American tribe historically based in present-day Connecticut. Today the majority of the people are associated with the Mohegan Indian Tribe, a federally recognized tribe living on a reservation in the eastern upper Thames River valley of south-central Connecticut. It is one of two federally recognized tribes in the state, the other being the Mashantucket Pequot, whose reservation is in Ledyard, Connecticut. There are also three state-recognized tribes: the Schaghticoke, Paugusett, and Eastern Pequot.

Bigelow Hollow State Park is public recreation area in the town of Union, Connecticut, in the Quinebaug Highlands. The state park's 516 acres (209 ha) border Nipmuck State Forest on the east and west and Mashapaug Lake on the north. The park and forest are located in a large hollow or depression approximately 700' below the surrounding ridgelines. They are managed by the Connecticut Department of Energy and Environmental Protection.
The Podunk were an Indigenous people who spoke an Algonquian Quiripi language and lived primarily in what is now known as Hartford County, Connecticut, United States. English colonists adopted use of a Nipmuc dialect word for the territory of this people.

The Blue-Blazed Hiking Trail system, managed by the Connecticut Forest & Park Association (CFPA), and the related trail systems documented in the two-volume 19th Edition of the "Connecticut Walk Book" comprise over 800 miles of hiking trails in Connecticut.

The Aspetuck Valley Trail is a 5.9-mile (9.5 km) Blue-Blazed hiking trail in the Aspetuck River Valley area of Fairfield County in the towns of Newtown, Easton and Redding Connecticut.

The Quinebaug Trail is a 8.1-mile (13.0 km) Connecticut hiking trail and is one of the Blue-Blazed hiking trails maintained by the Connecticut Forest and Park Association.
The Wangunk or Wongunk were an Indigenous people from central Connecticut. They had three major settlements in the areas of the present-day towns of Portland, Middletown, and Wethersfield. They also used lands in other parts of what were later organized by English settlers as Middlesex and Hartford counties. Some sources call the Wangunk the Mattabessett, or Mattabesch, but Wangunk is the name used by scholars and by contemporary Wangunk descendants.
References
Citations
- ↑ Harper, Douglas. "Connecticut". Online Etymology Dictionary . Retrieved 2006-11-28.
- ↑ Campbell (1997), p. 11.
- ↑ Afable, Patricia O. and Madison S. Beeler (1996). "Place Names", in "Languages", ed. Ives Goddard. Vol. 17 of Handbook of North American Indians, ed. William C. Sturtevant. Washington, D.C.: Smithsonian Institution, pg. 193
- ↑ Skinner, Charles Montgomery (1969) "Moodus Noises" Myths & Legends of Our Own Land Singing Tree Press, Detroit, Michigan, page 266 OCLC 19933; reprinted from the fifth edition of 1896 of J.B. Lippincott Company.
Sources
- Bright, William (2004). Native American Placenames of the United States. Norman: University of Oklahoma Press. ISBN 080613576X.
- Campbell, Lyle (1997). American Indian Languages: The Historical Linguistics of Native America. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0195094271.