Related Research Articles
uniq is a utility command on Unix, Plan 9, Inferno, and Unix-like operating systems which, when fed a text file or standard input, outputs the text with adjacent identical lines collapsed to one, unique line of text.

In computing, ls is a command to list computer files and directories in Unix and Unix-like operating systems. It is specified by POSIX and the Single UNIX Specification.

In Unix-like and some other operating systems, the pwd command writes the full pathname of the current working directory to the standard output.
basename is a standard computer program on Unix and Unix-like operating systems. When basename is given a pathname, it will delete any prefix up to the last slash ('/') character and return the result. basename is described in the Single UNIX Specification and is primarily used in shell scripts.

uname is a computer program in Unix and Unix-like computer operating systems that prints the name, version and other details about the current machine and the operating system running on it.

The command chown, an abbreviation of change owner, is used on Unix and Unix-like operating systems to change the owner of file system files and directories. Unprivileged (regular) users who wish to change the group membership of a file that they own may use chgrp.

tr is a command in Unix, Plan 9, Inferno, and Unix-like operating systems. It is an abbreviation of translate or transliterate, indicating its operation of replacing or removing specific characters in its input data set.

wc is a command in Unix, Plan 9, Inferno, and Unix-like operating systems. The program reads either standard input or a list of computer files and generates one or more of the following statistics: newline count, word count, and byte count. If a list of files is provided, both individual file and total statistics follow.

cksum is a command in Unix and Unix-like operating systems that generates a checksum value for a file or stream of data. The cksum command reads each file given in its arguments, or standard input if no arguments are provided, and outputs the file's 32-bit cyclic redundancy check (CRC) checksum and byte count. The CRC output by cksum is different from the CRC-32 used in zip, PNG and zlib.

df is a standard Unix command used to display the amount of available disk space for file systems on which the invoking user has appropriate read access. df is typically implemented using the statfs or statvfs system calls.
The GNU Core Utilities or coreutils is a package of GNU software containing implementations for many of the basic tools, such as cat, ls, and rm, which are used on Unix-like operating systems.
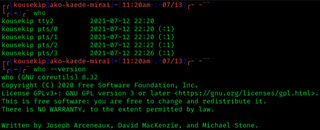
The standard Unix command who displays a list of users who are currently logged into the computer.

rm is a basic command on Unix and Unix-like operating systems used to remove objects such as computer files, directories and symbolic links from file systems and also special files such as device nodes, pipes and sockets, similar to the del command in MS-DOS, OS/2, and Microsoft Windows. The command is also available in the EFI shell.

env is a shell command for Unix and Unix-like operating systems. It is used to either print a list of environment variables or run another utility in an altered environment without having to modify the currently existing environment. Using env, variables may be added or removed, and existing variables may be changed by assigning new values to them.
In computing, sleep is a command in Unix, Unix-like and other operating systems that suspends program execution for a specified time.
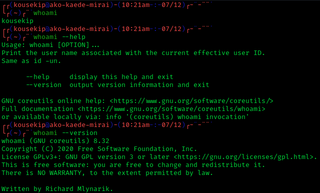
In computing, whoami is a command found on most Unix-like operating systems, Intel iRMX 86, every Microsoft Windows operating system since Windows Server 2003, and on ReactOS. It is a concatenation of the words "Who am I?" and prints the effective username of the current user when invoked.
sum is a legacy utility available on some Unix and Unix-like operating systems. This utility outputs a 16-bit checksum of each argument file, as well as the number of blocks they take on disk. Two different checksum algorithms are in use. POSIX abandoned sum in favor of cksum.

In Unix and Unix-like operating systems, printf is a shell builtin that formats and outputs text like the same-named C function.

cat is a standard Unix utility that reads files sequentially, writing them to standard output. The name is derived from its function to (con)catenate files . It has been ported to a number of operating systems.