The Persians are a Western Iranian ethnic group who comprise the majority of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian.

The Persian Gulf, sometimes called the Arabian Gulf, is a mediterranean sea in West Asia. The body of water is an extension of the Indian Ocean located between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula. It is connected to the Gulf of Oman in the east by the Strait of Hormuz. The Shatt al-Arab river delta forms the northwest shoreline.

The history of Iran is intertwined with Greater Iran, a sociocultural region spanning from Anatolia to the Indus River and from the Caucasus to the Persian Gulf. Central to this area is modern-day Iran, which covers the bulk of the Iranian plateau.

The Kingdom of Ormus was located in the eastern side of the Persian Gulf and extended as far as Bahrain in the west at its zenith. The Kingdom was established in the 11th century initially as a dependency of the Kerman Seljuk Sultanate, and later as an autonomous tributary of the Salghurid Turkmens and the Ilkhanates. In its last phase Ormus became a client state of the Portuguese Empire in the East. Most of its territory was eventually annexed by the Safavid Empire in the 17th century. It bordered Laristan, with whom it was regularly at odds with.
Persian War may refer to:

ʿAjam is an Arabic word for a non-Arab, especially a Persian. It was historically used as a pejorative—figuratively ascribing muteness to those whose native language is not Arabic—during and after the Muslim conquest of Iran. Since the early Muslim conquests, it has been adopted in various non-Arabic languages, such as Turkish, Azerbaijani, Chechen, Kurdish, Malay, Sindhi, Urdu, Bengali, Punjabi, Kashmiri, and Swahili. Today, the terms ʿAjam and ʿAjamī continue to be used to refer to anyone or anything Iranian, particularly in the Arab countries of the Persian Gulf. Communities speaking the Persian language in the Arab world exist among the Iraqis, the Kuwaitis, and the Bahrainis, in addition to others. A number of Arabs with Iranian heritage may have the surname ʿAjamī (عجمي), which has the same meaning as the original word.
The culture of Iran or culture of Persia is among the most influential in the world. Iran (Persia) is widely considered to be one of the cradles of civilization. Due to its dominant geopolitical position in the world, it has heavily influenced peoples and cultures situated of Southern Europe Eastern Europe to the west; Central Asia to the north; and South Asia, East Asia, and Southeast Asia to the east. Iranian history has had a significant influence on the world through art, architecture, poetry, science and technology, medicine, philosophy, and engineering.

The Persian Gulf naming dispute concerns the gulf known historically and internationally as the Persian Gulf, after Persia is involved in an ongoing naming dispute. In connection with the emergence of pan-Arabism and Arab nationalism in the 1960s, the usage of the toponym "Arabian Gulf" as well as just "Gulf" increased.
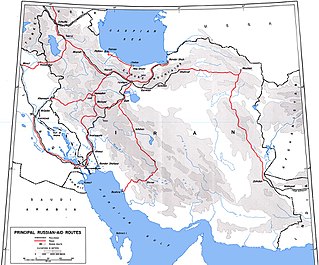
The Persian Corridor was a supply route through Iran into Soviet Azerbaijan by which British aid and American Lend-Lease supplies were transferred to the Soviet Union during World War II. Of the 17.5 million long tons of US Lend-Lease aid provided to the Soviet Union, 7.9 million long tons (45%) were sent through Iran.

Relations between the Grand Duchy of Moscow and the Persian Empire (Iran) officially commenced in 1521, with the Safavids in power. Past and present contact between Russia and Iran have long been complicatedly multi-faceted; often wavering between collaboration and rivalry. The two nations have a long history of geographic, economic, and socio-political interaction. Mutual relations have often been turbulent, and dormant at other times.

Greater Iran or Greater Persia, also called the Iranosphere or the Persosphere, is an expression that denotes a wide socio-cultural region comprising parts of West Asia, the Caucasus, Central Asia, South Asia, and East Asia —all of which have been affected, to some degree, by the Iranian peoples and the Iranian languages.
The military history of Iran has been relatively well-documented, with thousands of years' worth of recorded history. Largely credited to its historically unchanged geographical and geopolitical condition, the modern-day Islamic Republic of Iran has had a long and checkered military culture and history; ranging from triumphant and unchallenged ancient military supremacy, affording effective superpower status for its time; to a series of near-catastrophic defeats, most notably including the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon as well as the Asiatic nomadic tribes at the northeastern boundary of the lands traditionally home to the Iranian peoples.

The Iranian Navy traditionally located in the shallow waters of the Persian Gulf, has always been the smallest of the country's military forces. An Iranian navy in one form or another has existed since Achaemenid times in 500 BC. The Phoenician navy played an important role in the military efforts of the Persians in late antiquity in protecting and expanding trade routes along the Persian Gulf and Indian Ocean. With the Pahlavi dynasty in the 20th century that Iran began to consider building a strong navy to project its strength into the Persian Gulf and Indian Ocean. In more recent years, the country has engaged in domestic ship building industries in response to the western-backed Iraqi invasion of Iran, which left it without suppliers during an invasion.
Anti-Iranian sentiment or Iranophobia, also called anti-Persian sentiment or Persophobia, refers to feelings and expressions of hostility, hatred, discrimination, or prejudice towards Iran, the Iranian government, or Iranian people on the basis of an irrational disdain for their national and cultural affiliation. The opposite phenomenon, in which one holds notable feelings of love or interest towards Iranian people for the same reasons, is known as Iranophilia or Persophilia.
The Persian Gulf Command was a United States Army service command established in December 1943 to facilitate the supply of US lend-lease war material to the Soviet Union, through the "Persian Corridor".
Iran and Georgia have had relations for thousands of years. Eastern and Southern Georgia had been under intermittent Persian suzerainty for many centuries up to the early course of the 19th century, while western Georgia had been under its suzerainty for much shorter periods of time throughout history. Georgia especially rose to importance from the time of the Persian Safavids.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Iran:

The Ottoman–Persian Wars or Ottoman–Iranian Wars were a series of wars between Ottoman Empire and the Safavid, Afsharid, Zand, and Qajar dynasties of Iran through the 16th–19th centuries. The Ottomans consolidated their control of what is today Turkey in the 15th century, and gradually came into conflict with the emerging neighboring Iranian state, led by Ismail I of the Safavid dynasty. The two states were arch rivals, and were also divided by religious grounds, the Ottomans being staunchly Sunni and the Safavids being Shia. A series of military conflicts ensued for centuries during which the two empires competed for control over eastern Anatolia, the Caucasus, and Iraq.

The Anglo-Soviet invasion of Iran or Anglo-Soviet invasion of Persia was the joint invasion of the neutral Imperial State of Iran by the United Kingdom and the Soviet Union in August 1941. The two powers announced that they would stay until six months after the end of the war with their mutual enemy, Nazi Germany, which turned out to be 2 March 1946. On that date the British began to withdraw, while the Soviet Union delayed until May, initially citing "threats to Soviet security", followed by the Iran crisis of 1946.

The Imperial State of Iran, officially known in English as the Imperial State of Persia until 1935, and commonly referred to as Pahlavi Iran, was the Iranian state under the rule of the Pahlavi dynasty. The Pahlavi dynasty was created in 1925 and lasted until 1979, when it was ousted as part of the Islamic Revolution, which ended the Iranian monarchy and established the current Islamic Republic of Iran.