
The Ho Chi Minh Trail, also called Annamite Range Trail was a logistical network of roads and trails that ran from North Vietnam to South Vietnam through the kingdoms of Laos and Cambodia. The system provided support, in the form of manpower and materiel, to the Viet Cong and the People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN), during the Vietnam War. Construction for the network began following the North Vietnamese invasion of Laos in July 1959. At the time it was believed to be the main supply route, however it later transpired that the Sihanouk Trail which ran through Cambodia was handling significantly more material.
Yankee Station was a fixed coordinate off the coast of Vietnam where U.S. Navy aircraft carriers and support ships operated in open waters over a nine-year period during the Vietnam War. The location was used primarily by aircraft carriers of Task Force 77 to launch strikes over North Vietnam. While the coordinate's official designation was "Point Yankee", it was universally referred to as Yankee Station. Carriers conducting air operations at Yankee Station were said to be "on the line" and statistical summaries were based on days on the line. Yankee Station was initially located at 16° 00′ N, 110° 00′ E, however with a massive increase in operations over North Vietnam in 1966 the station was moved about 145 miles (230 km) northwest to 17° 30′ N, 108° 30′ E, placing it about 90 miles (145 km) from the North Vietnamese shore.

Operation Rolling Thunder was a gradual and sustained aerial bombardment campaign conducted by the United States (U.S.) 2nd Air Division, U.S. Navy, and Republic of Vietnam Air Force (RVNAF) against North Vietnam, China and North Korea from 2 March 1965 until 2 November 1968, during the Vietnam War.

Operation Linebacker II, sometimes referred to as the Christmas bombings and, in Vietnam, Dien Bien Phu in the air, was a strategic bombing campaign conducted by the United States against targets in North Vietnam from 18 December to 29 December 1972, during the Vietnam War. More than 20,000 tons of ordnance was dropped on military and industrial areas in Hanoi and Haiphong and at least 1,624 civilians were killed. The operation was the final major military operation carried out by the U.S. during the conflict, and the largest bombing campaign involving heavy bombers since World War II.
During Operation Arc Light from 1965 to 1973, the United States Air Force deployed B-52 Stratofortresses from bases in the U.S. Territory of Guam to provide battlefield air interdiction during the Vietnam War. This included strikes at enemy bases, supply routes, and behind the lines troop concentrations, as well as occasionally providing close air support directly to ground combat operations in Vietnam.

Operation Commando Hunt was a covert U.S. Seventh Air Force and U.S. Navy Task Force 77 aerial interdiction campaign that took place during the Vietnam War. The operation began on 15 November 1968 and ended on 29 March 1972. The objective of the campaign was to prevent the transit of People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN) personnel and supplies on the logistical corridor known as the Ho Chi Minh Trail that ran from southwestern North Vietnam through the southeastern portion of the Kingdom of Laos and into South Vietnam.

Operation Linebacker was the codename of a U.S. Seventh Air Force and U.S. Navy Task Force 77 air interdiction campaign conducted against North Vietnam from 9 May to 23 October 1972, during the Vietnam War.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the Vietnam War:

Military Assistance Command, Vietnam – Studies and Observations Group (MACV-SOG) was a highly classified, multi-service United States special operations unit which conducted covert unconventional warfare operations before and during the Vietnam War.

Tan Son Nhut Air Base (1955–1975) was a Republic of Vietnam Air Force (RVNAF) facility. It was located near the city of Saigon in southern Vietnam. The United States used it as a major base during the Vietnam War (1959–1975), stationing Army, Air Force, Navy, and Marine units there. Following the Fall of Saigon, it was taken over as a Vietnam People's Air Force (VPAF) facility and remains in use today.

The Nakhon Phanom Royal Thai Navy Base (NKP), formerly Nakhon Phanom Royal Thai Air Force Base, is a Royal Thai Navy facility used for riverine patrols along the Mekong River. It is approximately 587 km (365 mi) northeast of Bangkok, 14.5 km (9.0 mi) west of Nakhon Phanom city in Nakhon Phanom Province in the northeastern region of Thailand, and 411 km (255 mi) from Hanoi in Vietnam. The Mekong River is NKP's border with Laos. The airfield at NKP is jointly used as a civilian airport.

Takhli Royal Thai Air Force Base is a Royal Thai Air Force (RTAF) facility in central Thailand, approximately 144 miles (240 km) northwest of Bangkok in Takhli District, Nakhon Sawan Province.
Ubon Royal Thai Air Force Base is a Royal Thai Air Force (RTAF) facility located near the city of Ubon Ratchathani, in Ubon Ratchathani Province. It is approximately 488 km northeast of Bangkok. The Laos border is about 60 kilometres (37 mi) directly east. The facility is also used as a civil airport.
U-Tapao Royal Thai Navy Airfield is a military airfield of the Royal Thai Navy (RTN) approximately 140 kilometres (87 mi) southeast of Bangkok in the Ban Chang District of Rayong Province near Sattahip on the Gulf of Thailand. It is serves as the home of the RTN First Air Wing.
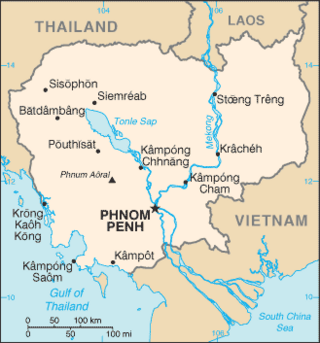
The Sihanouk Trail was a logistical supply system in Cambodia used by the People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN) and its Viet Cong (VC) guerrillas during the Vietnam War (1960–1975). Between 1966 and 1970, this system operated in the same manner and served the same purposes as the much better known Ho Chi Minh trail which ran through the southeastern portion of the Kingdom of Laos. The name is of American derivation, since the North Vietnamese considered the system integral to the supply route mentioned above. U.S. attempts to interdict this system began in 1969.

Forward air controllers (FACs) played a significant part in the Vietnam War from the very start. Largely relegated to airborne duty by the constraints of jungled terrain, FACs began operations as early as 1962. Using makeshift propeller-driven aircraft and inadequate radio nets, they became so essential to air operations that the overall need for FACs would not be completely satisfied until 1969. The FAC's expertise as an air strike controller also made him an intelligence source, munitions expert, communication specialist, and above all, the on-scene commander of the strike forces and the start of any subsequent combat search and rescue if necessary.
Senior Master Sergeant James J. "Jim" Stanford instituted forward air control techniques for directing air strikes during the Vietnam War and the Laotian Civil War. Despite his Combat Controller activities being restricted by his lack of a pilot's license, no access to military aircraft, and a ban on using rocketry to mark targets for strikes, Stanford flew 218 combat missions in Laos. Although his duties were abruptly ended by a decision by General William W. Momyer, Stanford had demonstrated the necessity for forward air control in Laos; his successors were the Raven Forward Air Controllers. The resulting air campaigns would drop about the same tonnage of bombs on Laos as were dropped during the entirety of World War II. After serving 24 years in the U.S. Air Force, Stanford transitioned to an allied civilian job in airfield management for a further 20-year career. He died on 25 August 2012 as a result of surgery.