Related Research Articles

Bishkek, formerly Pishpek and Frunze, is the capital and largest city of Kyrgyzstan. Bishkek is also the administrative centre of the Chüy Region. The region surrounds the city, although the city itself is not part of the region but rather a region-level unit of Kyrgyzstan. Bishkek is situated near the border with Kazakhstan and has a population of 1,074,075, as of 2021. Bishkek is the primate city of Kyrgyzstan—it is the sole metropolis in the country, and about 17% of all inhabitants of the country live in Bishkek's metropolitan area.

Kyrgyzstan, officially the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Asia, lying in the Tian Shan and Pamir mountain ranges. Bishkek is the capital and largest city of the country. Kyrgyzstan is bordered by Kazakhstan to the north, Uzbekistan to the west, Tajikistan to the south, and China to the east and southeast. Ethnic Kyrgyz make up the majority of the country's 7 million people, followed by significant minorities of Uzbeks and Russians.

The Los Angeles Aqueduct system, comprising the Los Angeles Aqueduct and the Second Los Angeles Aqueduct, is a water conveyance system, built and operated by the Los Angeles Department of Water and Power. The Owens Valley aqueduct was designed and built by the city's water department, at the time named The Bureau of Los Angeles Aqueduct, under the supervision of the department's Chief Engineer William Mulholland. The system delivers water from the Owens River in the eastern Sierra Nevada mountains to Los Angeles.

The Chu is a river in Northern Kyrgyzstan and Southern Kazakhstan. Of its total length of 1,067 kilometres (663 mi), the first 115 kilometres are in Kyrgyzstan, then for 221 kilometres the river is the border between Kyrgyzstan and Kazakhstan and the last 731 kilometres are in Kazakhstan. It is one of the longest rivers in Kyrgyzstan and in Kazakhstan. It has a drainage basin of 62,500 square kilometres (24,100 sq mi).
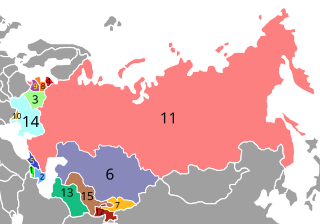
The post-Soviet states, also referred to as the former Soviet Union (FSU) or the former Soviet republics, are the independent sovereign states that emerged/re-emerged out of the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. Prior to their independence, they existed as Union Republics, which were the top-level constituents of the Soviet Union. There are 15 post-Soviet states in total: Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Estonia, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Latvia, Lithuania, Moldova, Russia, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Ukraine, and Uzbekistan. Each of these countries succeeded their respective Union Republics: the Armenian SSR, the Azerbaijan SSR, the Byelorussian SSR, the Estonian SSR, the Georgian SSR, the Kazakh SSR, the Kirghiz SSR, the Latvian SSR, the Lithuanian SSR, the Moldavian SSR, the Russian SFSR, the Tajik SSR, the Turkmen SSR, the Ukrainian SSR, and the Uzbek SSR. In Russia, the term "near abroad" is sometimes used to refer to the post-Soviet states other than Russia.

The Naryn rises in the Tian Shan mountains in Kyrgyzstan, Central Asia, flowing west through the Fergana Valley into Uzbekistan. Here it merges with the Kara Darya to form the Syr Darya. It is 807 kilometres (501 mi) long and its basin area is 59,100 square kilometres (22,800 sq mi). It has an annual flow of 13.7 cubic kilometres (11,100,000 acre⋅ft).

The Supreme Council is the unicameral parliament of the Kyrgyz Republic. It was known as the Supreme Soviet of the Kirghiz Soviet Socialist Republic until 1991.

Millerton Lake is an artificial lake near the town of Friant, about 15 mi (24 km) north of downtown Fresno, California, United States. The reservoir was created by the construction of 319 ft high Friant Dam on the San Joaquin River which, with the lake, serves as much of the county line between Fresno County to the south and Madera County to the north.

Toktogul Dam is a hydroelectric and irrigation dam on the Naryn River in the Jalal-Abad Province of Kyrgyzstan. It is concrete gravity dam with height of 215 metres (705 ft) and length of 292.5 metres (960 ft). It is a part of the Naryn-Syr Darya cascade. It is named after Toktogul Satilganov.

The Kürpsay Dam is a gravity dam on the river Naryn in Jalal-Abad Region, Kyrgyzstan, downstream from the Toktogul Dam. It is 113 m (371 ft) tall and it creates a 370,000,000 m3 (299,964 acre⋅ft) reservoir of which 27,000,000 m3 (21,889 acre⋅ft) is active for power generation. The installed capacity of the power station is 800 MW. Construction was started in 1976, and the first electricity was supplied in 1981.

A dam failure or dam burst is a catastrophic type of structural failure characterized by the sudden, rapid, and uncontrolled release of impounded water or the likelihood of such an uncontrolled release. Between the years 2000 and 2009 more than 200 notable dam failures happened worldwide.

The Kambar-Ata-2 Hydro Power Plant is a hydroelectric power station on the river Naryn near Kara-Jygach, Toktogul District, Kyrgyzstan. When completed, it will have 3 individual Francis turbine-generators with a nominal output of around 120 MW each which will deliver up to 360 MW of power. The first generator was operational on November 27, 2010. The power plant's dam is 60 m (197 ft) tall and it creates a 70,000,000 m3 (56,750 acre⋅ft) reservoir of which 8,000,000 m3 (6,486 acre⋅ft) is active for power generation.

The Shamaldy-Say Hydro Power Plant is an active hydro power plant on the river Naryn between Tash-Kömür and Shamaldy-Say, in Kyrgyzstan. Completed between 1992 and 1996, it is one of the three hydro power plants on the river Naryn near Tash-Kömür, 14 km downstream from the Tash-Kömür Hydroelectric Power Station. It has 3 individual turbines with a nominal output of around 80 MW and a total nominal capacity of 180 MW. The power plant's dam is 37 m (121 ft) tall and it creates a 41,000,000 m3 (33,239 acre⋅ft) reservoir of which 5,500,000 m3 (4,459 acre⋅ft) is active for power generation.
The Tash-Kömür Hydro Power Plant is a hydroelectric power plant on the river Naryn in Tash-Kömür, Kyrgyzstan. Completed between 1985 and 1987, it is one of the three hydro power plants on the river Naryn near Tash-Kömür, 14 km upstream from the Shamaldy-Say Hydroelectric Power Station. It has 3 individual turbines with a nominal output of around 150 MW and a total nominal capacity of 450 MW. The power plant's dam is 75 m (246 ft) tall and it creates a 140,000,000 m3 (113,500 acre⋅ft) reservoir of which 10,000,000 m3 (8,107 acre⋅ft) is active for power generation.
The Üch-Korgon Hydro Power Plant is an active hydro power plant on the river Naryn in Shamaldy-Say, Kyrgyzstan, upstream from Uchqoʻrgʻon in Uzbekistan. Completed in 1962, it is the oldest of the three hydro power plants on the river Naryn near Tash-Kömür, 25 km downstream from the Shamaldy-Say Hydroelectric Power Station. It has 4 individual turbines with a nominal output of around 45 MW and a total nominal capacity of 180 MW. The power plant's dam is 34 m (112 ft) tall and it creates a 53,000,000 m3 (42,968 acre⋅ft) reservoir of which20,000,000 m3 (16,214 acre⋅ft) is active for power generation.
The Kambar-Ata Dam is a proposed dam on the Naryn River in central Kyrgyzstan. One of six planned to be built on the river, it will become one of the largest dams in the world at approximately 275 metres (902 ft) high and containing about 370 million cubic metres of rock and earth. The Kambar-Ati-1 Hydro Power Plant at the base of the dam will have a capacity of around 2,000 megawatts. The project will be constructed jointly with Russia and possibly Kazakhstan as well.

New Exchequer Dam is a concrete–faced, rock-fill dam on the Merced River in central California in the United States. It forms Lake McClure, which impounds the river for irrigation and hydroelectric power production and has a capacity of more than 1,000,000 acre-feet (1.2 km3). The Merced Irrigation District (MID) operates the dam and was also responsible for its construction.
References
- ↑ "List of major hydroelectric facilities Kyrgyzskoy Republic" (PDF) (in Russian). CA Water. Archived from the original (PDF) on 9 December 2011. Retrieved 24 February 2012.
- ↑ "Water Reservoirs in Kyrgyzstan". Advantour. Retrieved 24 February 2012.
- ↑ "Reservoirs of Kyrgyzstan" (PDF). CA Water. Retrieved 24 February 2012.
- ↑ "Morphometric characteristics of large reservoirs of Kyrgyzstan" (in Russian). Welcome.kg. Retrieved 24 February 2012.
