
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower. Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4,500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined and also more than nuclear power. Hydropower can provide large amounts of low-carbon electricity on demand, making it a key element for creating secure and clean electricity supply systems. A hydroelectric power station that has a dam and reservoir is a flexible source, since the amount of electricity produced can be increased or decreased in seconds or minutes in response to varying electricity demand. Once a hydroelectric complex is constructed, it produces no direct waste, and almost always emits considerably less greenhouse gas than fossil fuel-powered energy plants. However, when constructed in lowland rainforest areas, where part of the forest is inundated, substantial amounts of greenhouse gases may be emitted.

Kárahnjúkar Hydropower Plant, officially called Fljótsdalur Power Station is a hydroelectric power plant in Fljótsdalshérað municipality in eastern Iceland, designed to produce 4,600 gigawatt-hours (17,000 TJ) annually for Alcoa's Fjarðaál aluminum smelter 75 kilometres (47 mi) to the east in Reyðarfjörður. With the installed capacity of 690 megawatts (930,000 hp), the plant is the largest power plant in Iceland. The project, named after the nearby Kárahnjúkar mountains, involves damming the rivers Jökulsá á Dal and Jökulsá í Fljótsdal with five dams, creating three reservoirs. Water from the reservoirs is diverted through 73 kilometres (45 mi) of underground water tunnels and down a 420-metre (1,380 ft) vertical penstock towards a single underground power station. The smelter became fully operational in 2008 and the hydropower project was completed in 2009.

The Dez Dam, formerly known as Mohammad-Reza Shah Pahlavi Dam, before 1979 Revolution, is an arch dam on the Dez River in the southwestern province of Khuzestan, Iran. It is about 23 km from Andimeshk city. It was built between 1959 and 1963 during the rule of Mohammad Reza Pahlavi,the last Shah of Iran, with contacting an Italian consortium and is owned by the Khuzestan Water & Power Authority. The dam is 203 metres (666 ft) high, making it one of the highest in the country, and has a reservoir capacity of 3,340,000,000 m3 (2,710,000 acre⋅ft). At the time of construction the Dez Dam was Iran's biggest development project. The primary purpose of the dam is hydroelectric power production and irrigation. It has an associated 520 MW power station and its reservoir helps irrigate up to 80,500 ha of farmland. US$42 million of the cost to construct the dam came from the World Bank.

The Nam Theun 2 Hydropower Project, or simply NT2, is a hydroelectric dam on the Nam Theun River in Laos. Commercial operation of the plant began in April 2010. The scheme diverts water from the Nam Theun, a tributary of the Mekong River, to the Xe Bang Fai River, enabling a generation capacity of 1,075 MW, from a 350 m (1,148 ft) difference in elevation between the reservoir and the power station.
The Atatürk Dam, originally the Karababa Dam, is the third largest dam in the world and it is a zoned rock-fill dam with a central core on the Euphrates River on the border of Adıyaman Province and Şanlıurfa Province in the Southeastern Anatolia Region of Turkey. Built both to generate electricity and to irrigate the plains in the region, it was renamed in honour of Mustafa Kemal Atatürk (1881–1938), the founder of the Turkish Republic. The construction began in 1983 and was completed in 1990. The dam and the hydroelectric power plant, which went into service after the upfilling of the reservoir was completed in 1992, are operated by the State Hydraulic Works (DSİ). The reservoir created behind the dam, called Atatürk Reservoir, is the third largest in Turkey.

The Karun-3 dam is a hydroelectric dam on the Karun river located in the province of Khuzestan, Iran. It was built to help meet Iran's energy demands as well as provide seasonal flood control. The Karun river has the highest discharge slits and seasonal flooding in Iran.
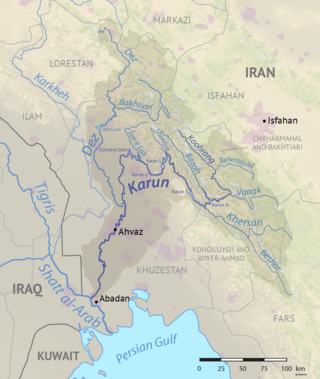
The Karun is the Iranian river with the highest water flow, and the country's only navigable river. It is 950 km (590 mi) long. The Karun rises in the Zard Kuh mountains of the Bakhtiari district in the Zagros Range, receiving many tributaries, such as the Dez and the Kuhrang. It passes through the capital of the Khuzestan Province of Iran, the city of Ahvaz, before emptying to its mouth into Arvand Rud.

The construction industry of Iran is divided into two main sections. The first is government infrastructure projects, which are central for the cement industry. The second is the housing industry. In recent years, the construction industry has been thriving due to an increase in national and international investment to the extent that it is now the largest in the Middle East region. The Central Bank of Iran indicate that 70 percent of the Iranians own homes, with huge amounts of idle money entering the housing market. Iran has three shopping malls among the largest shopping malls in the world. Iran Mall is the largest shopping mall in the world, located in Tehran. The annual turnover in the construction industry amounts to US$38.4 billion. The real estate sector contributed to 5% of GDP in 2008. Statistics from March 2004 to March 2005 put the number of total Iranian households at 15.1 million and the total number of dwelling units at 13.5 million, signifying a demand for at least 5.1 million dwelling units. Every year there is a need for 750,000 additional units as young couples embark on married life. At present, 2000 units are being built every day although this needs to increase to 2740 units. Iran's construction market will expand to $154.4 billion in 2016 from $88.7 billion in 2013.

Iran has the Third largest oil reserves and the 2nd largest natural gas reserves in the world. The nation is a member of OPEC, and generates approximately 50% of state revenue through oil exports.

The Koohrang is a river originating in the Zagros mountains of western Iran, which joins the Beheštābād river to form the Karun, Iran's largest river. A series of tunnels have been built since the 1950s to redirect some of the Kuhrang's water toward the Zayandeh River to meet the demands of increased population in Esfahan and Yazd provinces.

The Karun-4 Dam is an arch dam on the Karun River located 180 km southwest of Shahr-e-Kord in the province of Chaharmahal and Bakhtiari, Iran. The Karun has the highest discharge of all the Iranian rivers. Its construction is aimed at generating hydroelectric power supply of 2,107 million kWh annually and controlling floods in the upper Karun.

The Shahid Abbaspour Dam, formerly known as Great Reza Shah Kabir Dam before the 1979 Revolution, is a large arch dam providing hydroelectricity from the Karun River; it is located about 50 kilometres (31 mi) northeast of Masjed Soleiman, in the province of Khuzestan, Iran, and originally completed in 1976. The dam was the first of a series of dams planned for development on the Karun River.
Water supply and sanitation in Iran has witnessed some important improvements, especially in terms of increased access to urban water supply, while important challenges remain, particularly concerning sanitation and service provision in rural areas. Institutionally, the Ministry of Energy is in charge of policy and provincial companies are in charge of service provision.

The Masjed Soleyman Dam is a dam in Iran on the Karun river. It is 177 metres (581 ft) high, has an installed capacity of 2,000 MW, and its reservoir holds 261,000,000 cubic metres (212,000 acre⋅ft) of water. The dam is a rock-fill structure with a vertical clay-core. The dam was built by Iran Water and Power Resources Development Co. and completed in 2002. The power station was built in two 1,000-MW stages. The first stage was complete in 2003 and the second in September 2007. The dam was named after the town of Masjed-Soleyman, about 25 kilometres (16 mi) away. The spillway gates are believed to be the largest of their kind in the world.

Shahid Rajaee Dam, also known as the Soleyman Tangeh Dam, is an arch dam on the Tajan River, located about 38 km (24 mi) south of Sari in Mazandaran Province, Iran. The dam was built for hydroelectric power production, flood control and to provide water for industrial and agricultural use. Construction on the dam began in 1987 and it was complete in 1997. In 2000 the power plant portion of the project was given to Iran Water & Power Resources Development Co. from the Mazandaran Regional Water Authority. An earthquake halted the project in 2002 but the power plant was completed in 2007.

Upper Gotvand Dam, or simply the Gotvand Dam, is an embankment dam on the Karun River about 12 km (7.5 mi) northeast of Gotvand in Khuzestan Province, Iran. It currently has an installed capacity of 1,000 MW with another 1,000 MW in the works for a second phase. Studies for the Karun River began in the 1960s and specific designs on the Upper Gotvand were presented in 1967, 1975 and 1982. After the design and location were chosen, a further study was carried out in 1997, the same year preliminary construction began. The river was diverted by April 2003 and excavation began soon thereafter. After completion of the dam, impounding of its reservoir began on 30 July 2011 during a ceremony attended by Iranian President Mahmood Ahmadinejad. The first generator of phase one was commissioned on 5 May 2012, two more by 18 September 2012 and the final in November 2012. Ahmadinejad was again present for the dam's inauguration on 22 April 2013. Phase 2 is estimated to be complete in 2015 and the dam is going to become one of Iran's largest power stations and is already its tallest earth-fill dam.
Energy in Sudan describes energy and electricity production, consumption and imports in Sudan. The chief sources of energy in 2010 were wood and charcoal, hydroelectric power, and oil. Sudan is a net energy exporter. Primary energy use in Sudan was 179 TWh and 4 TWh per million persons in 2008.

Shahid Kazemi Dam is a clay core dam on the Zarrineh River in the Zagros Mountains range, located near Bukan in West Azarbaijan Province, Iran.






















