This article may require cleanup to meet Wikipedia's quality standards. The specific problem is: unnecessary details, citations, and copyediting.(October 2023) |
 Jey Oil Refining Company site located in Isfahan at night | |
| Company type | Public stock. Public Company |
|---|---|
| Industry | Oil, Betumen |
| Founded | 2003 |
| Headquarters | , |
Key people | Majid Azami (CEO) Mehdi Sanaee Far (COO) Behzad Poorahmadi (Member of the Board) MohammadReza Sadri Esfahani (Member of the Board) Hadi Amirshaghaghi (ContentsMember of the Board) |
| Products | |
| Parent | Naftiran Intertrade |
| Subsidiaries | Hamyar Jey Co.- Milad Co.-Asia Gostar Co.-Jey Corner Pars Co.-Azad Chemical Co. |
| Website | jeyoil |
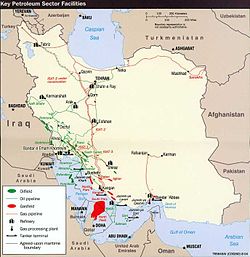
The Oil Refinery Jey or the Oil Refining Company Jey has been established in 2003; with the investment of Oil Industry Personnel Pension Fund, [1] with a nominal capacity of 1'800'000 tons as the largest producer of bituminous units in the Middle East. [2]