A glycogen storage disease is a metabolic disorder caused by a deficiency of an enzyme or transport protein affecting glycogen synthesis, glycogen breakdown, or glucose breakdown, typically in muscles and/or liver cells.

Phosphoglucomutase is an enzyme that transfers a phosphate group on an α-D-glucose monomer from the 1 to the 6 position in the forward direction or the 6 to the 1 position in the reverse direction.

Lysosomal storage diseases are a group of over 70 rare inherited metabolic disorders that result from defects in lysosomal function. Lysosomes are sacs of enzymes within cells that digest large molecules and pass the fragments on to other parts of the cell for recycling. This process requires several critical enzymes. If one of these enzymes is defective due to a mutation, the large molecules accumulate within the cell, eventually killing it.

Sphingolipidoses are a class of lipid storage disorders or degenerative storage disorders caused by deficiency of an enzyme that is required for the catabolism of lipids that contain ceramide, also relating to sphingolipid metabolism. The main members of this group are Niemann–Pick disease, Fabry disease, Krabbe disease, Gaucher disease, Tay–Sachs disease and metachromatic leukodystrophy. They are generally inherited in an autosomal recessive fashion, but notably Fabry disease is X-linked recessive. Taken together, sphingolipidoses have an incidence of approximately 1 in 10,000, but substantially more in certain populations such as Ashkenazi Jews. Enzyme replacement therapy is available to treat mainly Fabry disease and Gaucher disease, and people with these types of sphingolipidoses may live well into adulthood. The other types are generally fatal by age 1 to 5 years for infantile forms, but progression may be mild for juvenile- or adult-onset forms.

Inborn errors of carbohydrate metabolism are inborn error of metabolism that affect the catabolism and anabolism of carbohydrates.

Coarse facial features is a constellation of facial features that are present in many inborn errors of metabolism.
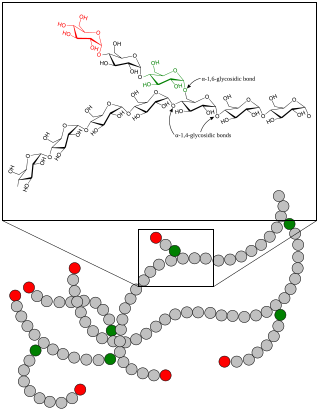
Glycogen phosphorylase, liver form (PYGL), also known as human liver glycogen phosphorylase (HLGP), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PYGL gene on chromosome 14. This gene encodes a homodimeric protein that catalyses the cleavage of alpha-1,4-glucosidic bonds to release glucose-1-phosphate from liver glycogen stores. This protein switches from inactive phosphorylase B to active phosphorylase A by phosphorylation of serine residue 14. Activity of this enzyme is further regulated by multiple allosteric effectors and hormonal controls. Humans have three glycogen phosphorylase genes that encode distinct isozymes that are primarily expressed in liver, brain and muscle, respectively. The liver isozyme serves the glycemic demands of the body in general while the brain and muscle isozymes supply just those tissues. In glycogen storage disease type VI, also known as Hers disease, mutations in liver glycogen phosphorylase inhibit the conversion of glycogen to glucose and results in moderate hypoglycemia, mild ketosis, growth retardation and hepatomegaly. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011].