An earthquake – also called a quake, tremor, or temblor – is the shaking of the Earth's surface resulting from a sudden release of energy in the lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those so weak they cannot be felt, to those violent enough to propel objects and people into the air, damage critical infrastructure, and wreak destruction across entire cities. The seismic activity of an area is the frequency, type, and size of earthquakes experienced over a particular time. The seismicity at a particular location in the Earth is the average rate of seismic energy release per unit volume.

A tsunami is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and underwater explosions above or below water all have the potential to generate a tsunami. Unlike normal ocean waves, which are generated by wind, or tides, which are in turn generated by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun, a tsunami is generated by the displacement of water from a large event.

Southern California is a geographic and cultural region that generally comprises the southern portion of the U.S. state of California. It includes the Los Angeles metropolitan area as well as the Inland Empire. The region generally contains ten of California's 58 counties: Los Angeles, San Diego, Orange, Riverside, San Bernardino, Kern, Ventura, Santa Barbara, San Luis Obispo, and Imperial counties.

Earthquakes are caused by movements within the Earth's crust and uppermost mantle. They range from weak events detectable only by seismometers, to sudden and violent events lasting many minutes which have caused some of the greatest disasters in human history. Below, earthquakes are listed by period, region or country, year, magnitude, cost, fatalities, and number of scientific studies.

The Hawaiian Islands are an archipelago of eight major volcanic islands, several atolls, and numerous smaller islets in the North Pacific Ocean, extending some 1,500 miles from the island of Hawaiʻi in the south to northernmost Kure Atoll. Formerly called the Sandwich Islands by Europeans, the present name for the archipelago is derived from the name of its largest island, Hawaiʻi.

The Great Hanshin Earthquake occurred on January 17, 1995, at 05:46:53 JST in the southern part of Hyōgo Prefecture, Japan, including the region known as Hanshin. It measured 6.9 on the moment magnitude scale and had a maximum intensity of 7 on the JMA Seismic Intensity Scale. The tremors lasted for approximately 20 seconds. The focus of the earthquake was located 17 km beneath its epicenter, on the northern end of Awaji Island, 20 km away from the center of the city of Kobe.

The 1964 Alaskan earthquake, also known as the Great Alaskan earthquake and Good Friday earthquake, occurred at 5:36 PM AKST on Good Friday, March 27, 1964. Across south-central Alaska, ground fissures, collapsing structures, and tsunamis resulting from the earthquake caused about 131 deaths.

The San Jose Earthquakes are an American professional soccer club based in San Jose, California. The Earthquakes compete in Major League Soccer (MLS) as a member of the Western Conference. Originally as the San Jose Clash, the franchise began play in 1996 as one of the charter members of the league. The Earthquakes took part in the first game in MLS history, defeating D.C. United 1–0. The Earthquakes have won two MLS Cup titles and two Supporters' Shields. In 2002, the team played in its first CONCACAF Champions Cup, making it to the quarterfinals. The team holds a fierce rivalry with the LA Galaxy known as the California Clásico.

The Great Kantō earthquake also known in Japanese as Kantō daishinsai (関東大震災) struck the Kantō Plain on the main Japanese island of Honshū at 11:58:32 JST on Saturday, September 1, 1923. Varied accounts indicate the duration of the earthquake was between four and ten minutes. Extensive firestorms and a fire whirl added to the death toll.

The 1755 Lisbon earthquake, also known as the Great Lisbon earthquake, impacted Portugal, the Iberian Peninsula, and Northwest Africa on the morning of Saturday, 1 November, Feast of All Saints, at around 09:40 local time. In combination with subsequent fires and a tsunami, the earthquake almost completely destroyed Lisbon and adjoining areas. Seismologists estimate the Lisbon earthquake had a magnitude of 7.7 or greater on the moment magnitude scale, with its epicenter in the Atlantic Ocean about 200 km west-southwest of Cape St. Vincent, a cape in Algarve region, and about 290 km southwest of Lisbon.

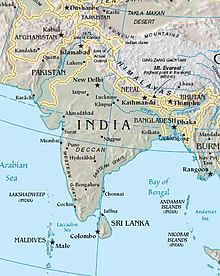
The 2001 Gujarat earthquake, also known as the Bhuj earthquake, occurred on 26 January at . The epicentre was about 9 km south-southwest of the village of Chobari in Bhachau Taluka of Kutch (Kachchh) District of Gujarat, India.

On 26 December 2004, at 07:58:53 local time (UTC+7), a major earthquake with a magnitude of 9.2–9.3 struck with an epicentre off the west coast of northern Sumatra, Indonesia. The undersea megathrust earthquake, known by the scientific community as the Sumatra–Andaman earthquake, was caused by a rupture along the fault between the Burma plate and the Indian plate, and reached a Mercalli intensity of IX in some areas.
The Richter scale, also called the Richter magnitude scale, Richter's magnitude scale, and the Gutenberg–Richter scale, is a measure of the strength of earthquakes, developed by Charles Richter in collaboration with Beno Gutenberg, and presented in Richter's landmark 1935 paper, where he called it the "magnitude scale". This was later revised and renamed the local magnitude scale, denoted as ML or ML .

At 05:12 AM Pacific Standard Time on Wednesday, April 18, 1906, the coast of Northern California was struck by a major earthquake with an estimated moment magnitude of 7.9 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of XI (Extreme). High-intensity shaking was felt from Eureka on the North Coast to the Salinas Valley, an agricultural region to the south of the San Francisco Bay Area. Devastating fires soon broke out in San Francisco and lasted for several days. More than 3,000 people died, and over 80% of the city was destroyed. The event is remembered as the deadliest earthquake in the history of the United States. The death toll remains the greatest loss of life from a natural disaster in California's history and high on the lists of American disasters.

The following is a summary of significant earthquakes during the 21st century. In terms of fatalities, the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake was the most destructive event with 227,898 confirmed fatalities, followed by the 2010 Haiti earthquake with about 160,000 fatalities, the 2008 Sichuan earthquake with 87,587 fatalities, the 2005 Kashmir earthquake suffered by Pakistan with 87,351 fatalities, and the 2023 Turkey–Syria earthquakes with at least 59,488 fatalities.

On 11 March 2011, at 14:46 JST, a 9.0–9.1 undersea megathrust earthquake occurred in the Pacific Ocean, 72 km (45 mi) east of the Oshika Peninsula of the Tōhoku region. It lasted approximately six minutes and caused a tsunami. It is sometimes known in Japan as the "Great East Japan Earthquake", among other names. The disaster is often referred to by its numerical date, 3.11.
A potent magnitude 6.6 Mw intraplate aftershock occurred at 17:16 JST (08:16 UTC) on 11 April, in the Hamadōri region of Fukushima, Japan. With a shallow focus of 13 km (8.1 mi), the earthquake was centred inland about 36 km (22 mi) west of Iwaki, causing widespread strong to locally severe shaking. It was one of many aftershocks to follow the 11 March Tōhoku earthquake, and the strongest to have its epicentre located inland.