Related Research Articles

Earthquakes are caused by movements within the Earth's crust and uppermost mantle. They range from weak events detectable only by seismometers, to sudden and violent events lasting many minutes which have caused some of the greatest disasters in human history. Below, earthquakes are listed by period, region or country, year, magnitude, cost, fatalities, and number of scientific studies.

The 1999 İzmit earthquake had a moment magnitude of 7.6 and struck Kocaeli Province, Turkey on 17 August. Between 17,127 and 18,373 people died as a result, and the damage was estimated at US$6.5 billion. It was named for the epicenter's proximity to the northwestern city of İzmit. The earthquake occurred at 03:01 local time at a shallow depth of 15 km (9.3 mi). A maximum Mercalli intensity of X (Extreme) was observed. The earthquake lasted for 37 seconds, causing seismic damage, and is widely remembered as one of the deadliest natural disasters in modern Turkish history.

This list of 20th-century earthquakes is a list of earthquakes of magnitude 6 and above that occurred in the 20th century. Sone smaller events which nevertheless had a significant impact are also included. After 1900 most earthquakes have some degree of instrumental records and this means that the locations and magnitudes are more reliable than for earlier events.
Abhaya Malla was the second Malla king of Nepal and a son of Aridev Malla. He succeeded his father in 1216 and died during the 1255 earthquake which wiped out a third of the population of the Kathmandu Valley.
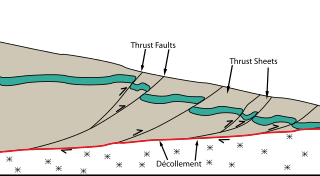
The Main Himalayan Thrust (MHT) is a décollement under the Himalaya Range. This thrust fault follows a NW-SE strike, reminiscent of an arc, and gently dips about 10 degrees towards the north, beneath the region. It is the largest active continental megathrust fault in the world.
In 1954, the state of Nevada was struck by a series of earthquakes that began with three magnitude 6.0+ events in July and August that preceded the Mw 7.1–7.3 mainshock and M 6.9 aftershock, both on December 12. All five earthquakes are among the largest in the state, and the largest since the Cedar Mountain earthquake of 1932 and Pleasant Valley event in 1915. The earthquake was felt throughout much of the western United States.

An earthquake occurred off the coast of the Alaska Peninsula on July 28, 2021, at 10:15 p.m. local time. The large megathrust earthquake had a moment magnitude of 8.2 according to the United States Geological Survey (USGS). A tsunami warning was issued by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) but later cancelled. The mainshock was followed by a number of aftershocks, including three that were of magnitude 5.9, 6.1 and 6.9 respectively.
References
- ↑ Dixit, Kunda (13 January 2016). "Stirred, not shaken". Nepali Times . Retrieved 26 October 2016.
The last one in 1255 killed one-third of the Valley's population, including King Abhaya Malla.
- ↑ "Comments for the 1255 earthquake". National Geophysical Data Center . Retrieved 28 April 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "Historical Earthquakes in Nepal". Disaster Preparedness Network Nepal . Retrieved 12 August 2015.
- ↑ "Comments for the 1833 earthquake". National Geophysical Data Center . Retrieved 28 April 2015.
- ↑ "Comments for the 1869 earthquake". National Geophysical Data Center . Retrieved 28 April 2015.
- ↑ "Comments for the 1916 earthquake". National Geophysical Data Center . Retrieved 28 April 2015.
- ↑ "Comments for the 1934 earthquake". National Geophysical Data Center . Retrieved 28 April 2015.
- ↑ "Comments for the 1966 earthquake". National Geophysical Data Center . Retrieved 28 April 2015.
- ↑ "Comments for the 1980 earthquake". National Geophysical Data Center . Retrieved 28 April 2015.
- ↑ "Comments for the 1988 earthquake". National Geophysical Data Center . Retrieved 28 April 2015.
- ↑ "M7.9 – 29 km ESE of Lamjung, Nepal". United States Geological Survey. 25 April 2015. Retrieved 28 April 2015.
- ↑ "M 5.7 – 21 km E of Dipayal, Nepal". United States Geological Survey. 8 November 2022.
- ↑ "6 killed as 6.3-magnitude earthquake hits Nepal; strong tremors felt in Delhi, neighbouring areas". The Times of India . 9 November 2022.
- ↑ "Scores killed by powerful earthquake in Nepal". The Guardian. Reuters. 2023-11-03. ISSN 0261-3077 . Retrieved 2023-11-04.
- ↑ "M 5.7 – 46 km E of Dailekh, Nepal". United States Geological Survey. 3 November 2023. Retrieved 7 November 2023.