Combinatorics is an area of mathematics primarily concerned with counting, both as a means and as an end to obtaining results, and certain properties of finite structures. It is closely related to many other areas of mathematics and has many applications ranging from logic to statistical physics and from evolutionary biology to computer science.
Discrete mathematics is the study of mathematical structures that can be considered "discrete" rather than "continuous". Objects studied in discrete mathematics include integers, graphs, and statements in logic. By contrast, discrete mathematics excludes topics in "continuous mathematics" such as real numbers, calculus or Euclidean geometry. Discrete objects can often be enumerated by integers; more formally, discrete mathematics has been characterized as the branch of mathematics dealing with countable sets. However, there is no exact definition of the term "discrete mathematics".
In graph theory, the girth of an undirected graph is the length of a shortest cycle contained in the graph. If the graph does not contain any cycles, its girth is defined to be infinity. For example, a 4-cycle (square) has girth 4. A grid has girth 4 as well, and a triangular mesh has girth 3. A graph with girth four or more is triangle-free.

In mathematics and computer science, graph theory is the study of graphs, which are mathematical structures used to model pairwise relations between objects. A graph in this context is made up of vertices which are connected by edges. A distinction is made between undirected graphs, where edges link two vertices symmetrically, and directed graphs, where edges link two vertices asymmetrically. Graphs are one of the principal objects of study in discrete mathematics.

In abstract algebra, a cyclic group or monogenous group is a group, denoted Cn, that is generated by a single element. That is, it is a set of invertible elements with a single associative binary operation, and it contains an element g such that every other element of the group may be obtained by repeatedly applying the group operation to g or its inverse. Each element can be written as an integer power of g in multiplicative notation, or as an integer multiple of g in additive notation. This element g is called a generator of the group.
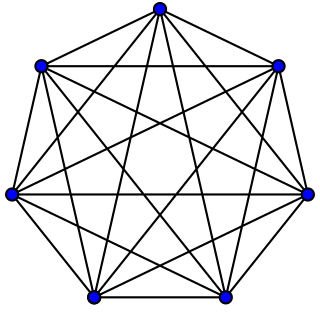
In the mathematical field of graph theory, a complete graph is a simple undirected graph in which every pair of distinct vertices is connected by a unique edge. A complete digraph is a directed graph in which every pair of distinct vertices is connected by a pair of unique edges.
In mathematics, connectedness is used to refer to various properties meaning, in some sense, "all one piece". When a mathematical object has such a property, we say it is connected; otherwise it is disconnected. When a disconnected object can be split naturally into connected pieces, each piece is usually called a component.

In the mathematical field of graph theory, a bipartite graph is a graph whose vertices can be divided into two disjoint and independent sets and , that is, every edge connects a vertex in to one in . Vertex sets and are usually called the parts of the graph. Equivalently, a bipartite graph is a graph that does not contain any odd-length cycles.

In discrete mathematics, particularly in graph theory, a graph is a structure consisting of a set of objects where some pairs of the objects are in some sense "related". The objects are represented by abstractions called vertices and each of the related pairs of vertices is called an edge. Typically, a graph is depicted in diagrammatic form as a set of dots or circles for the vertices, joined by lines or curves for the edges.
In mathematics, an incidence matrix is a logical matrix that shows the relationship between two classes of objects, usually called an incidence relation. If the first class is X and the second is Y, the matrix has one row for each element of X and one column for each mapping from X to Y. The entry in row x and column y is 1 if the vertex x is part of the mapping that corresponds to y, and 0 if it is not. There are variations; see below.

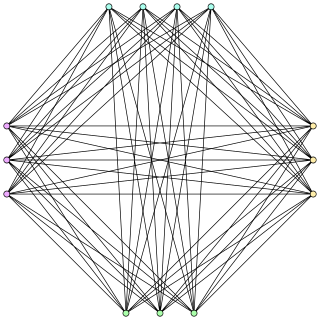
In the mathematical field of graph theory, a complete bipartite graph or biclique is a special kind of bipartite graph where every vertex of the first set is connected to every vertex of the second set.
Extremal graph theory is a branch of combinatorics, itself an area of mathematics, that lies at the intersection of extremal combinatorics and graph theory. In essence, extremal graph theory studies how global properties of a graph influence local substructure. Results in extremal graph theory deal with quantitative connections between various graph properties, both global and local, and problems in extremal graph theory can often be formulated as optimization problems: how big or small a parameter of a graph can be, given some constraints that the graph has to satisfy? A graph that is an optimal solution to such an optimization problem is called an extremal graph, and extremal graphs are important objects of study in extremal graph theory.

In graph theory, the degree of a vertex of a graph is the number of edges that are incident to the vertex; in a multigraph, a loop contributes 2 to a vertex's degree, for the two ends of the edge. The degree of a vertex is denoted or . The maximum degree of a graph is denoted by , and is the maximum of 's vertices' degrees. The minimum degree of a graph is denoted by , and is the minimum of 's vertices' degrees. In the multigraph shown on the right, the maximum degree is 5 and the minimum degree is 0.
In the mathematical field of algebraic graph theory, the degree matrix of an undirected graph is a diagonal matrix which contains information about the degree of each vertex—that is, the number of edges attached to each vertex. It is used together with the adjacency matrix to construct the Laplacian matrix of a graph: the Laplacian matrix is the difference of the degree matrix and the adjacency matrix.

Frank Harary was an American mathematician, who specialized in graph theory. He was widely recognized as one of the "fathers" of modern graph theory. Harary was a master of clear exposition and, together with his many doctoral students, he standardized the terminology of graphs. He broadened the reach of this field to include physics, psychology, sociology, and even anthropology. Gifted with a keen sense of humor, Harary challenged and entertained audiences at all levels of mathematical sophistication. A particular trick he employed was to turn theorems into games—for instance, students would try to add red edges to a graph on six vertices in order to create a red triangle, while another group of students tried to add edges to create a blue triangle. Because of the theorem on friends and strangers, one team or the other would have to win.
The Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series A and Series B, are mathematical journals specializing in combinatorics and related areas. They are published by Elsevier. Series A is concerned primarily with structures, designs, and applications of combinatorics. Series B is concerned primarily with graph and matroid theory. The two series are two of the leading journals in the field and are widely known as JCTA and JCTB.

In mathematics, and more specifically in graph theory, a directed graph is a graph that is made up of a set of vertices connected by directed edges, often called arcs.
N = 4 supersymmetric Yang–Mills (SYM) theory is a relativistic conformally invariant Lagrangian gauge theory describing the interactions of fermions via gauge field exchanges. In D=4 spacetime dimensions, N=4 is the maximal number of supersymmetries or supersymmetry charges.