
Linear algebra is the branch of mathematics concerning linear equations such as:

Numerical analysis is the study of algorithms that use numerical approximation for the problems of mathematical analysis. It is the study of numerical methods that attempt to find approximate solutions of problems rather than the exact ones. Numerical analysis finds application in all fields of engineering and the physical sciences, and in the 21st century also the life and social sciences like economics, medicine, business and even the arts. Current growth in computing power has enabled the use of more complex numerical analysis, providing detailed and realistic mathematical models in science and engineering. Examples of numerical analysis include: ordinary differential equations as found in celestial mechanics, numerical linear algebra in data analysis, and stochastic differential equations and Markov chains for simulating living cells in medicine and biology.

In mathematics, a partial differential equation (PDE) is an equation which computes a function between various partial derivatives of a multivariable function.

Monte Carlo methods, or Monte Carlo experiments, are a broad class of computational algorithms that rely on repeated random sampling to obtain numerical results. The underlying concept is to use randomness to solve problems that might be deterministic in principle. The name comes from the Monte Carlo Casino in Monaco, where the primary developer of the method, physicist Stanislaw Ulam, was inspired by his uncle's gambling habits.

Computational physics is the study and implementation of numerical analysis to solve problems in physics. Historically, computational physics was the first application of modern computers in science, and is now a subset of computational science. It is sometimes regarded as a subdiscipline of theoretical physics, but others consider it an intermediate branch between theoretical and experimental physics — an area of study which supplements both theory and experiment.
In mathematics and science, a nonlinear system is a system in which the change of the output is not proportional to the change of the input. Nonlinear problems are of interest to engineers, biologists, physicists, mathematicians, and many other scientists since most systems are inherently nonlinear in nature. Nonlinear dynamical systems, describing changes in variables over time, may appear chaotic, unpredictable, or counterintuitive, contrasting with much simpler linear systems.
An inverse problem in science is the process of calculating from a set of observations the causal factors that produced them: for example, calculating an image in X-ray computed tomography, source reconstruction in acoustics, or calculating the density of the Earth from measurements of its gravity field. It is called an inverse problem because it starts with the effects and then calculates the causes. It is the inverse of a forward problem, which starts with the causes and then calculates the effects.
Structural analysis is a branch of solid mechanics which uses simplified models for solids like bars, beams and shells for engineering decision making. Its main objective is to determine the effect of loads on the physical structures and their components. In contrast to theory of elasticity, the models used in structure analysis are often differential equations in one spatial variable. Structures subject to this type of analysis include all that must withstand loads, such as buildings, bridges, aircraft and ships. Structural analysis uses ideas from applied mechanics, materials science and applied mathematics to compute a structure's deformations, internal forces, stresses, support reactions, velocity, accelerations, and stability. The results of the analysis are used to verify a structure's fitness for use, often precluding physical tests. Structural analysis is thus a key part of the engineering design of structures.
Computational science, also known as scientific computing, technical computing or scientific computation (SC), is a division of science that uses advanced computing capabilities to understand and solve complex physical problems. This includes
Numerical methods for partial differential equations is the branch of numerical analysis that studies the numerical solution of partial differential equations (PDEs).
Computational mechanics is the discipline concerned with the use of computational methods to study phenomena governed by the principles of mechanics. Before the emergence of computational science as a "third way" besides theoretical and experimental sciences, computational mechanics was widely considered to be a sub-discipline of applied mechanics. It is now considered to be a sub-discipline within computational science.
Numerical continuation is a method of computing approximate solutions of a system of parameterized nonlinear equations,
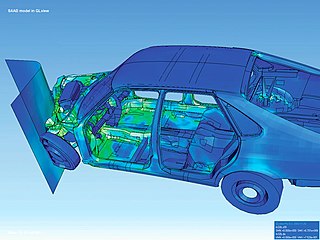
The finite element method (FEM) is a popular method for numerically solving differential equations arising in engineering and mathematical modeling. Typical problem areas of interest include the traditional fields of structural analysis, heat transfer, fluid flow, mass transport, and electromagnetic potential.
The following is a timeline of scientific computing, also known as computational science.
The following is a timeline of numerical analysis after 1945, and deals with developments after the invention of the modern electronic computer, which began during Second World War. For a fuller history of the subject before this period, see timeline and history of mathematics.
This is a timeline of key developments in computational mathematics.
Probabilistic numerics is an active field of study at the intersection of applied mathematics, statistics, and machine learning centering on the concept of uncertainty in computation. In probabilistic numerics, tasks in numerical analysis such as finding numerical solutions for integration, linear algebra, optimization and simulation and differential equations are seen as problems of statistical, probabilistic, or Bayesian inference.