
Mount Shasta is a potentially active volcano at the southern end of the Cascade Range in Siskiyou County, California. At an elevation of 14,179 ft (4,322 m), it is the second-highest peak in the Cascades and the fifth-highest in the state. Mount Shasta has an estimated volume of 85 cubic miles, which makes it the most voluminous stratovolcano in the Cascade Volcanic Arc. The mountain and surrounding area are part of the Shasta–Trinity National Forest.

The Lassen volcanic area presents a geological record of sedimentation and volcanic activity in and around Lassen Volcanic National Park in Northern California, U.S. The park is located in the southernmost part of the Cascade Mountain Range in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. Pacific Oceanic tectonic plates have plunged below the North American Plate in this part of North America for hundreds of millions of years. Heat and molten rock from these subducting plates has fed scores of volcanoes in California, Oregon, Washington and British Columbia over at least the past 30 million years, including these in the Lassen volcanic areas.

Mount Jefferson is a stratovolcano in the Cascade Volcanic Arc, part of the Cascade Range in the U.S. state of Oregon. The second highest mountain in Oregon, it is situated within Linn County, Jefferson County, and Marion County and forms part of the Mount Jefferson Wilderness. Due to the ruggedness of its surroundings, the mountain is one of the hardest volcanoes to reach in the Cascades. It is also a popular tourist destination despite its remoteness, with recreational activities including hiking, backpacking, mountaineering, and photography. Vegetation at Mount Jefferson is dominated by Douglas fir, silver fir, mountain hemlock, ponderosa pine, lodgepole pine, and several cedar species. Carnivores, insectivores, bats, rodents, deer, birds, and various other species inhabit the area.

Mount Garibaldi is a dormant stratovolcano in the Garibaldi Ranges of the Pacific Ranges in southwestern British Columbia, Canada. It has a maximum elevation of 2,678 metres and rises above the surrounding landscape on the east side of the Cheakamus River in New Westminster Land District. In addition to the main peak, Mount Garibaldi has two named sub-peaks. Atwell Peak is a sharp, conical peak slightly higher than the more rounded peak of Dalton Dome. Both were volcanically active at different times throughout Mount Garibaldi's eruptive history. The northern and eastern flanks of Mount Garibaldi are obscured by the Garibaldi Névé, a large snowfield containing several radiating glaciers. Flowing from the steep western face of Mount Garibaldi is the Cheekye River, a tributary of the Cheakamus River. Opal Cone on the southeastern flank is a small volcanic cone from which a lengthy lava flow descends. The western face is a landslide feature that formed in a series of collapses between 12,800 and 11,500 years ago. These collapses resulted in the formation of a large debris flow deposit that fans out into the Squamish Valley.

The Garibaldi Volcanic Belt is a northwest–southeast trending volcanic chain in the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains that extends from Watts Point in the south to the Ha-Iltzuk Icefield in the north. This chain of volcanoes is located in southwestern British Columbia, Canada. It forms the northernmost segment of the Cascade Volcanic Arc, which includes Mount St. Helens and Mount Baker. Most volcanoes of the Garibaldi chain are dormant stratovolcanoes and subglacial volcanoes that have been eroded by glacial ice. Less common volcanic landforms include cinder cones, volcanic plugs, lava domes and calderas. These diverse formations were created by different styles of volcanic activity, including Peléan and Plinian eruptions.

An active volcano is a volcano that has erupted during the Holocene, is currently erupting, or has the potential to erupt in the future. A volcano that is not currently erupting but could erupt in the future is known as a dormant volcano. Volcanoes that will not erupt again are known as extinct volcanoes.

Mount Edziza, sometimes called Edziza Mountain or Edziza Peak, is a stratovolcano in Cassiar Land District of northwestern British Columbia, Canada. It is located on the Big Raven Plateau of the Tahltan Highland which extends along the western side of the Stikine Plateau. The mountain has an elevation of 2,786 metres, making it the highest volcano of the Mount Edziza volcanic complex. However, it had an elevation of at least 3,396 metres before its original summit was likely destroyed by a violent, climactic eruption in the geologic past; its current flat summit contains an ice-filled, 2-kilometre (1.2-mile) in diameter crater. Mount Edziza contains several lava domes, cinder cones and lava fields on its flanks, as well as an ice cap that is characterized by several outlet glaciers stretching out to lower altitudes. All sides of the mountain are drained by tributaries of Mess Creek and Kakiddi Creek which are situated within the Stikine River watershed.
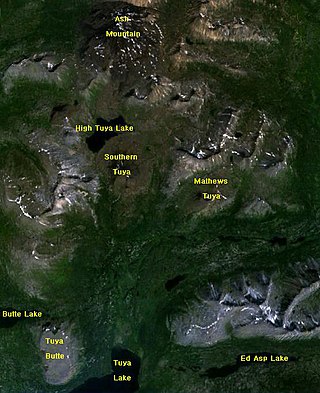
The Tuya volcanic field is a volcanic field of tuyas located in far northern British Columbia, Canada, near the border with the Yukon Territory and focused on the area of the Tuya Range, a subrange of the Stikine Ranges of the Cassiar Mountains, though some vents are in the Kawdy Plateau, the northernmost part of the Stikine Plateau. Several small shield volcanoes, and postglacial lapilli cones and lava flows have been reported in this area. The only nonglacial volcanoes in the field are Gabrielse Cone and the West Tuya lava field.
Tuya Butte is a tuya in the Tuya Range of north-central British Columbia, Canada. It is a bit less isolated from other ranges than neighbouring Mount Josephine. Some of the other volcanoes in the area include South Tuya, Ash Mountain, and Mathews Tuya.

The Spectrum Range, formerly gazetted as the Spectrum Mountains and the Rainbow Mountains, is a small mountain range in Cassiar Land District of northwestern British Columbia, Canada. Located at the southern end of the Tahltan Highland, it borders the Skeena Mountains in the east and the Boundary Ranges of the Coast Mountains in the west. The Spectrum Range is surrounded by the Arctic Lake Plateau in the southwest and the Kitsu Plateau in the northwest, both of which contain volcanic features such as cinder cones. It lies at the southern end of the Mount Edziza volcanic complex which includes the two neighbouring plateaus as well as Mount Edziza and the Big Raven Plateau to the north. The mountain range is drained on all sides by streams within the Stikine River watershed and, unlike Mount Edziza to the north, contains relatively small separate glaciers. Mount Edziza Provincial Park is the main protected area surrounding the Spectrum Range.

Hoodoo Butte is a cinder cone butte in the Cascade Range of northern Oregon, located near Santiam Pass. Immediately to the east lies Hayrick Butte, a prime example of a tuya; the two mountains' names were likely mistaken for each other, but stuck with them over time. The area has been subjected to a number of historic fires. Hoodoo is sometimes considered a subfeature of the Mount Washington shield volcano, and it forms part of the Sisters Reach, which extends from South Cinder Peak to Crane Prairie Reservoir, running for 56 miles (90 km). This region has a high vent density, with many mafic volcanoes of Pleistocene to Holocene age, such as Hoodoo. While Hoodoo has an intact summit crater that was blocked from erosion by glaciers, it has an irregular topography, giving it an open appearance.

Hayrick Butte is a tuya, a type of subglacial volcano, in Linn County, Oregon. Located in the Willamette National Forest near Santiam Pass, it lies adjacent to the cinder cone Hoodoo Butte, which has a ski area. Hayrick Butte likely formed when lava erupted underneath an overlying glacier or ice sheet, producing the flat top with near-vertical walls along the ice-contact margin as the lava cooled and hardened. Hayrick Butte has a nearly flat plateau about 0.5 miles (0.80 km) across and steep walls rising about 700 feet (0.21 km) above its surroundings. A cartographer accidentally switched the names for nearby Hoodoo Butte and Hayrick Butte; the word "hoodoo" usually refers to rock piles and pinnacles like those observed at Hayrick Butte.

Hogg Rock is a tuya volcano and lava dome in the Cascade Range of northern Oregon, United States, located close to Santiam Pass. Produced by magma with an intermediate andesite composition, it has steep slopes and thick glassy margins. Hogg Rock exhibits normal magnetic polarity and is probably about 80,000 years old.

The volcanic history of the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province presents a record of volcanic activity in northwestern British Columbia, central Yukon and the U.S. state of easternmost Alaska. The volcanic activity lies in the northern part of the Western Cordillera of the Pacific Northwest region of North America. Extensional cracking of the North American Plate in this part of North America has existed for millions of years. Continuation of this continental rifting has fed scores of volcanoes throughout the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province over at least the past 20 million years and occasionally continued into geologically recent times.

The Canadian Cascade Arc, also called the Canadian Cascades, is the Canadian segment of the North American Cascade Volcanic Arc. Located entirely within the Canadian province of British Columbia, it extends from the Cascade Mountains in the south to the Coast Mountains in the north. Specifically, the southern end of the Canadian Cascades begin at the Canada–United States border. However, the specific boundaries of the northern end are not precisely known and the geology in this part of the volcanic arc is poorly understood. It is widely accepted by geologists that the Canadian Cascade Arc extends through the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains. However, others have expressed concern that the volcanic arc possibly extends further north into the Kitimat Ranges, another subdivision of the Coast Mountains, and even as far north as Haida Gwaii.

The Mount Cayley volcanic field (MCVF) is a remote volcanic zone on the South Coast of British Columbia, Canada, stretching 31 km (19 mi) from the Pemberton Icefield to the Squamish River. It forms a segment of the Garibaldi Volcanic Belt, the Canadian portion of the Cascade Volcanic Arc, which extends from Northern California to southwestern British Columbia. Most of the MCVF volcanoes were formed during periods of volcanism under sheets of glacial ice throughout the last glacial period. These subglacial eruptions formed steep, flat-topped volcanoes and subglacial lava domes, most of which have been entirely exposed by deglaciation. However, at least two volcanoes predate the last glacial period and both are highly eroded. The field gets its name from Mount Cayley, a volcanic peak located at the southern end of the Powder Mountain Icefield. This icefield covers much of the central portion of the volcanic field and is one of the several glacial fields in the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains.