
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit. Electrodes are essential parts of batteries that can consist of a variety of materials (chemicals) depending on the type of battery.

Lithium is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the least dense solid element. Like all alkali metals, lithium is highly reactive and flammable, and must be stored in vacuum, inert atmosphere, or inert liquid such as purified kerosene or mineral oil. It exhibits a metallic luster. It corrodes quickly in air to a dull silvery gray, then black tarnish. It does not occur freely in nature, but occurs mainly as pegmatitic minerals, which were once the main source of lithium. Due to its solubility as an ion, it is present in ocean water and is commonly obtained from brines. Lithium metal is isolated electrolytically from a mixture of lithium chloride and potassium chloride.

Lithium carbonate is an inorganic compound, the lithium salt of carbonic acid with the formula Li
2CO
3. This white salt is widely used in processing metal oxides. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines for its efficacy in the treatment of mood disorders such as bipolar disorder.

Genus is a taxonomic rank above species and below family as used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus.

A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery that uses the reversible intercalation of Li+ ions into electronically conducting solids to store energy. In comparison with other commercial rechargeable batteries, Li-ion batteries are characterized by higher specific energy, higher energy density, higher energy efficiency, a longer cycle life, and a longer calendar life. Also noteworthy is a dramatic improvement in lithium-ion battery properties after their market introduction in 1991: over the following 30 years, their volumetric energy density increased threefold while their cost dropped tenfold.

A lithium polymer battery, or more correctly, lithium-ion polymer battery, is a rechargeable battery of lithium-ion technology using a polymer electrolyte instead of a liquid electrolyte. Highly conductive semisolid (gel) polymers form this electrolyte. These batteries provide higher specific energy than other lithium battery types. They are used in applications where weight is critical, such as mobile devices, radio-controlled aircraft, and some electric vehicles.

In organometallic chemistry, organolithium reagents are chemical compounds that contain carbon–lithium (C–Li) bonds. These reagents are important in organic synthesis, and are frequently used to transfer the organic group or the lithium atom to the substrates in synthetic steps, through nucleophilic addition or simple deprotonation. Organolithium reagents are used in industry as an initiator for anionic polymerization, which leads to the production of various elastomers. They have also been applied in asymmetric synthesis in the pharmaceutical industry. Due to the large difference in electronegativity between the carbon atom and the lithium atom, the C−Li bond is highly ionic. Owing to the polar nature of the C−Li bond, organolithium reagents are good nucleophiles and strong bases. For laboratory organic synthesis, many organolithium reagents are commercially available in solution form. These reagents are highly reactive, and are sometimes pyrophoric.
Lithium is a chemical element with symbol Li and atomic number 3.
The Corey–House synthesis (also called the Corey–Posner–Whitesides–House reaction and other permutations) is an organic reaction that involves the reaction of a lithium diorganylcuprate () with an organic halide or pseudohalide () to form a new alkane, as well as an ill-defined organocopper species and lithium (pseudo)halide as byproducts.

Lithium hydride is an inorganic compound with the formula LiH. This alkali metal hydride is a colorless solid, although commercial samples are grey. Characteristic of a salt-like (ionic) hydride, it has a high melting point, and it is not soluble but reactive with all protic organic solvents. It is soluble and nonreactive with certain molten salts such as lithium fluoride, lithium borohydride, and sodium hydride. With a molar mass of 7.95 g/mol, it is the lightest ionic compound.
Naturally occurring lithium (3Li) is composed of two stable isotopes, lithium-6 (6Li) and lithium-7 (7Li), with the latter being far more abundant on Earth. Both of the natural isotopes have an unexpectedly low nuclear binding energy per nucleon when compared with the adjacent lighter and heavier elements, helium and beryllium. The longest-lived radioisotope of lithium is 8Li, which has a half-life of just 838.7(3) milliseconds. 9Li has a half-life of 178.2(4) ms, and 11Li has a half-life of 8.75(6) ms. All of the remaining isotopes of lithium have half-lives that are shorter than 10 nanoseconds. The shortest-lived known isotope of lithium is 4Li, which decays by proton emission with a half-life of about 91(9) yoctoseconds, although the half-life of 3Li is yet to be determined, and is likely to be much shorter, like 2He which undergoes proton emission within 10−9 s.

Lithium bromide (LiBr) is a chemical compound of lithium and bromine. Its extreme hygroscopic character makes LiBr useful as a desiccant in certain air conditioning systems.

The McMurry reaction is an organic reaction in which two ketone or aldehyde groups are coupled to form an alkene using a titanium chloride compound such as titanium(III) chloride and a reducing agent. The reaction is named after its co-discoverer, John E. McMurry. The McMurry reaction originally involved the use of a mixture TiCl3 and LiAlH4, which produces the active reagents. Related species have been developed involving the combination of TiCl3 or TiCl4 with various other reducing agents, including potassium, zinc, and magnesium. This reaction is related to the Pinacol coupling reaction which also proceeds by reductive coupling of carbonyl compounds.

Lithium amide or lithium azanide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula LiNH2. It is a white solid with a tetragonal crystal structure. Lithium amide can be made by treating lithium metal with liquid ammonia:
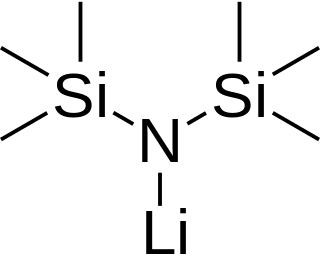
Lithium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide is a lithiated organosilicon compound with the formula LiN(Si(CH3)3)2. It is commonly abbreviated as LiHMDS or Li(HMDS) (lithium hexamethyldisilazide - a reference to its conjugate acid HMDS) and is primarily used as a strong non-nucleophilic base and as a ligand. Like many lithium reagents, it has a tendency to aggregate and will form a cyclic trimer in the absence of coordinating species.
Lithium superoxide is an unstable inorganic salt with formula LiO2. A radical compound, it can be produced at low temperature in matrix isolation experiments, or in certain nonpolar, non-protic solvents. Lithium superoxide is also a transient species during the reduction of oxygen in a lithium–air galvanic cell, and serves as a main constraint on possible solvents for such a battery. For this reason, it has been investigated thoroughly using a variety of methods, both theoretical and spectroscopic.
Lithium carbide, Li2C2, often known as dilithium acetylide, is a chemical compound of lithium and carbon, an acetylide. It is an intermediate compound produced during radiocarbon dating procedures. Li2C2 is one of an extensive range of lithium-carbon compounds which include the lithium-rich Li4C, Li6C2, Li8C3, Li6C3, Li4C3, Li4C5, and the graphite intercalation compounds LiC6, LiC12, and LiC18.
Lithium burning is a nucleosynthetic process in which lithium is depleted in a star. Lithium is generally present in brown dwarfs and not in older low-mass stars. Stars, which by definition must achieve the high temperature (2.5 × 106 K) necessary for fusing hydrogen, rapidly deplete their lithium.

Certain lithium compounds, also known as lithium salts, are used as psychiatric medication, primarily for bipolar disorder and for major depressive disorder. Lithium is taken orally.
Lithium battery may refer to:











