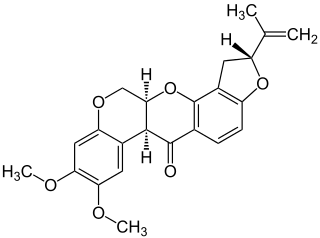
Rotenone is an odorless, colorless, crystalline isoflavone used as a broad-spectrum insecticide, piscicide, and pesticide. It occurs naturally in the seeds and stems of several plants, such as the jicama vine, and in the roots of several other members of the Fabaceae. It was the first-described member of the family of chemical compounds known as rotenoids.

David Edward Crombie is a Canadian former academic and politician who served as the 56th mayor of Toronto from 1972 to 1978. Crombie was elected to Parliament following his tenure as mayor. A member of the Progressive Conservative (PC) Party, he served as minister of national health and welfare from 1979 to 1980, minister of Indian affairs and northern development from 1984 to 1986, and secretary of state for Canada from 1986 to 1988.

Crombie 1805 Ltd., formerly known as J&J Crombie Ltd., is a Scottish fashion company, producing high-end clothing and accessories under the Crombie brand name. Crombie is most famous for its luxury coats; so much so that the word 'Crombie' is sometimes used by other companies to refer to their own coats produced in the style of Crombie's most famous three-quarter length overcoats, although the Crombie company has been known to take legal action to prevent this trademark word from being used generically.

Indigofera tinctoria, also called true indigo, is a species of plant from the bean family that was one of the original sources of indigo dye.
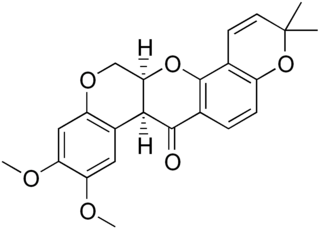
Deguelin is a derivative of rotenone. Both are compounds classified as rotenoids of the flavonoid family and are naturally occurring insecticides. They can be produced by extraction from several plant species belonging to three genera of the legume family, Fabaceae: Lonchocarpus, Derris, or Tephrosia.
Lonchocarpus is a plant genus in the legume family (Fabaceae). The species are called lancepods due to their fruit resembling an ornate lance tip or a few beads on a string.
Lonchocarpus retifer is a species of legume in the family Fabaceae. It is native to Central America: Costa Rica, El Salvador, Honduras and Nicaragua. Its scientific name has also been spelt Lonchocarpus retiferus.

Tephrosin is rotenoid. It is a natural fish poison found in the leaves and seeds of Tephrosia purpurea and T. vogelii.

Amorpha fruticosa is a species of flowering plant in the legume family Fabaceae, known by several common names, including desert false indigo, false indigo-bush, and bastard indigobush. It is native to North America.
Philenoptera laxiflora, synonym Lonchocarpus laxiflorus, is a species of legume in the family Fabaceae. The tree grows to 4–8 meters in height, has grey or yellowish bark and compound leaves. New leaves are accompanied by purple flowers on multi-branched panicles. The fruit is a glabrous papery pod, usually containing one seed. Ph. laxiflorus is widely distributed in West Africa, Central Africa, the African Great Lakes, and Northeast Africa. It is found in savanna woodlands and dry forested areas, particularly fringing forest near water courses.

Millettia pachycarpa is a perennial climbing shrub belonging to the genus Millettia. It is one of the most well known among ~150 species of Millettia, as it is widely used in traditional practices, such as for poisoning fish, agricultural pesticide, blood tonic, and treatments of cancer and infertility. The bark fiber is used for making strong ropes.

Barbigerone is one of a few pyranoisoflavones among several groups of isoflavones. It was first isolated from the seed of a leguminous plant Tephrosia barbigera; hence the name "barbigerone". Members of the genus Millettia are now known to be rich in barbigerone, including M. dielsiena, M. ferruginea, M. usaramensis, and M. pachycarpa. It has also been isolated from the medicinal plant Sarcolobus globosus. Barbigerone from S. globosus is validated to have significant antioxidant property. Barbigerone exhibits profound antiplasmodial activity against the malarial parasite Plasmodium falciparum. It is also demonstrated that it has anti-cancer potential as it causes apoptosis of murine lung-cancer cells.

Sarcolobus globosus is a twining shrub native to tropical regions of Asia including India, China, Thailand, Malaysia, Myanmar-Burma, the Philippines and Indonesia.

The tribe Millettieae is one of the subdivisions of the plant family Fabaceae.

Rotenoids are naturally occurring substances containing a cis-fused tetrahydrochromeno[3,4-b]chromene nucleus. Many have insecticidal activity, such as the prototypical member of the family, rotenone. Rotenoids are related to the isoflavones.

Derris trifoliata is a plant species in the genus Derris, Family - Leguminosae It is known as "Karanjvel" in Marathi - local language of Maharashtra, India.

Clitoria fairchildiana, the sombreiro, is a flowering plant species in the genus Clitoria found in Campina Grande, Brazil.
L. salvadorensis may refer to:
Meizonyx is an extinct genus of megalonychid ground sloth from the Pleistocene of El Salvador and southern Mexico. The type and only species, Meizonyx salvadorensis, was described in 1985 from a mandible found in Barranca del Sisimico and other remains found at Rio Tomayate in El Salvador considered to be Middle Pleistocene in age. Later, in 2021, additional remains were described from Late Pleistocene aged deposits in Sistema Huautla, Oxaca, Mexico. It is considered closely related to Xibalbaonyx. It is thought to be comparable in size to Megalonyx and it inhabited relatively mountainous areas.














