
The South Bay is a region of the Los Angeles metropolitan area, located in the southwest corner of Los Angeles County. The name stems from its geographic location stretching along the southern shore of Santa Monica Bay. The South Bay contains sixteen cities plus portions of the City of Los Angeles and unincorporated portions of the county. The area is bounded by the Pacific Ocean on the south and west and generally by the City of Los Angeles on the north and east.

The Pacific Electric Railway Company, nicknamed the Red Cars, was a privately owned mass transit system in Southern California consisting of electrically powered streetcars, interurban cars, and buses and was the largest electric railway system in the world in the 1920s. Organized around the city centers of Los Angeles and San Bernardino, it connected cities in Los Angeles County, Orange County, San Bernardino County and Riverside County.

The Balboa Peninsula is a neighborhood of the city of Newport Beach, Orange County, California. It is named after Spanish explorer Vasco Núñez de Balboa, the first European to sight the Pacific from the Americas. Balboa is primarily residential with some commercial areas.

The Port of Los Angeles is a seaport managed by the Los Angeles Harbor Department, a unit of the City of Los Angeles. It occupies 7,500 acres (3,000 ha) of land and water with 43 miles (69 km) of waterfront and adjoins the separate Port of Long Beach. Promoted as "America's Port", the port is located in San Pedro Bay in the San Pedro and Wilmington neighborhoods of Los Angeles, approximately 20 miles (32 km) south of downtown.
The history of Santa Monica, California, covers the significant events and movements in Santa Monica's past.
The Free Harbor Fight refers to the legal battle in the late nineteenth century on the West Coast of the United States, around Los Angeles Area Chamber of Commerce against Huntington and the Southern Pacific. US Senator Stephen M. White failed to cave in to the pressure of the railroad baron Collis Huntington and his congressional allies, which resulted in the Port of Los Angeles being located in San Pedro, instead of Santa Monica, as Huntington had wanted.

San Pedro Bay is an inlet on the Pacific Ocean coast of southern California, United States. It is the site of the Port of Los Angeles and the Port of Long Beach, which together form the fifth-busiest port facility in the world and the busiest in the Americas. The Los Angeles community of San Pedro borders a small portion of the western side of the bay. The city of Long Beach borders the port on the eastern side of the bay. The northern part of the bay, which is the largest part of the port, is bordered by the Los Angeles neighborhood of Wilmington.

The Oakland Long Wharf was an 11,000-foot railroad wharf and ferry pier along the east shore of San Francisco Bay located at the foot of Seventh Street in West Oakland. The Oakland Long Wharf was built, beginning 1868, by the Central Pacific Railroad on what was previously Oakland Point. Beginning November 8, 1869, it served as the west coast terminus of the First transcontinental railroad. In the 1880s, Southern Pacific Railroad took over the CPRR, extending it and creating a new ferry terminal building with the official station name Oakland Pier. The entire structure became commonly and popularly called the Oakland Mole. Portions of the Wharf lasted until the 1960s. The site is now part of the facilities of the Port of Oakland, while passenger train service operates at the nearby Jack London Square/Dellums Station and another nearby station in Emeryville.
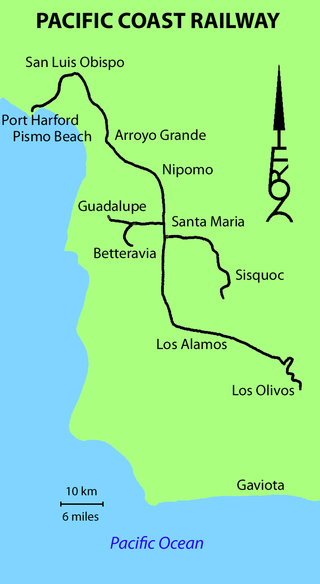
The Pacific Coast Railway was a 3 ft narrow gauge railway on the Central Coast of California. The original 10-mile (16 km) link from San Luis Obispo to Avila Beach and Port Harford was later built southward to Santa Maria and Los Olivos, with branches to Sisquoc and Guadalupe.

The Los Angeles and Independence Railroad, opened on October 17, 1875, was a steam-powered rail line which ran between the Santa Monica Long Wharf and 5th and San Pedro streets in downtown Los Angeles.

The Port of Los Angeles Waterfront Red Car Line was a 1.5-mile (2.4 km) heritage streetcar line for public transit along the waterfront in San Pedro, at the Port of Los Angeles in Los Angeles, California. The line operated between July 2003 and September 2015, when service was discontinued due to major construction projects that resulted in the demolition of a portion of the route.

The Santa Monica Air Line was an interurban railroad operated by the Pacific Electric between Santa Monica and downtown Los Angeles. Electric passenger service operated over the line between 1908 and 1953. After abandonment as a freight railroad, most of the route was converted to light rail for use by the Metro E Line.

San Pedro via Dominguez was a 25.39-mile (40.86 km) interurban transport route, part of the Pacific Electric system in Greater Los Angeles. Its termini were the Pacific Electric Building in Downtown Los Angeles and San Pedro in the south.
Streetcars in Los Angeles over history have included horse-drawn streetcars and cable cars, and later extensive electric streetcar networks of the Los Angeles Railway and Pacific Electric Railway and their predecessors. Also included are modern light rail lines.

The California Central Railway was incorporated on April 23, 1887, with headquarters in San Bernardino, California. George O. Manchester was the President of the corporation.

The Los Angeles Pacific Railroad (1896−1911) (LAP) was an electric public transit and freight railway system in Los Angeles County, California. At its peak it had 230 miles (370 km) of track extending from Downtown Los Angeles to the Westside, Santa Monica, and the South Bay towns along Santa Monica Bay.

Port Ballona is an archaic place name for an area near the center of Santa Monica Bay in coastal Los Angeles County, where Playa Del Rey and Del Rey Lagoon are located today. Port Ballona was a planned harbor and town site from circa 1859 to 1903. The name comes from the Rancho La Ballona Mexican land grant.

The place of McFadden Wharf was designated a California Historic Landmark (No.794) on July 3, 1964.

Naval Base San Pedro and San Pedro Submarine Base were United States Navy bases at the Port of San Pedro, California officially founded in 1919. While commissioned in 1919, the Navy started operating out of the port in 1910, by renting dock space at the City of San Pedro's Dock No. 1 in 1914. The Navy had vessels stationed at the port starting in 1913. The San Pedro Submarine Base closed in 1923, with the end of World War I. Naval Base San Pedro became part of Naval Operating Base Terminal Island on 25 September 1941, which closed in 1947.





















