Longford An Longfort (Irish) | |
|---|---|
 Baronies of County Longford. Longford is shaded pale green. | |
| Sovereign state | Ireland |
| County | Longford |
| Area | |
| • Total | 231.65 km2 (89.44 sq mi) |
Longford (Irish : An Longfort) is a barony in County Longford, Ireland.
Longford An Longfort (Irish) | |
|---|---|
 Baronies of County Longford. Longford is shaded pale green. | |
| Sovereign state | Ireland |
| County | Longford |
| Area | |
| • Total | 231.65 km2 (89.44 sq mi) |
Longford (Irish : An Longfort) is a barony in County Longford, Ireland.
Longford barony derives its name from the town of Longford (from Irish Longphort Uí Fhearghail, "O'Fergal's riverside camp". [1]
Longford barony is located in northwestern County Longford: east of the River Shannon, north of the River Camlin, south of the Rinn River and Black River, and west of the Longford Hills.
Carn Clonhugh was a ritual centre for the Clan Hugh (Clann Aoidh). [2]
Below is a list of settlements in Longford barony:

County Longford is a county in Ireland. It is in the province of Leinster. It is named after the town of Longford. Longford County Council is the local authority for the county. The population of the county was 46,634 at the 2022 census. The county is based on the historic Gaelic territory of Annaly (Anghaile), formerly known as Teffia (Teathbha).

Longford is the county town of County Longford in Ireland. It had a population of 10,952 at the 2022 census. It is the biggest town in the county and about one third of the county's population lives there. Longford lies at the meeting of Ireland's N4 and N5 National Primary Route roads, which means that traffic travelling between Dublin and County Mayo, or north County Roscommon passes around the town. Longford railway station, on the Dublin-Sligo line, is used heavily by commuters.

The Longford County Board of the Gaelic Athletic Association (GAA) or Longford GAA is one of the 32 county boards of the GAA in Ireland, and is responsible for Gaelic games in County Longford. The county board is also responsible for the Longford county teams.
A longphort is a term used in Ireland for a Viking ship enclosure or shore fortress. Although these longphorts were used as bases for Viking raids, the term had additional meanings and these sites had multiple purposes. The reason it cannot be assumed that longphorts were solely for military purposes as that would assume that there were always large numbers of Vikings at these settlements, which is not true. These camps were fortified areas along rivers, usually at a tributary where both sides were protected such that the Vikings could port ships. The sites were easily defended, sheltered, and gave immediate access to the sea. These camps would be of great importance to the Vikings during their raids of Ireland, which included attacks on many churches and monasteries located on the coast. It can be assumed that the purpose of these sites was to ease travel and trade within the region. Longphorts were essential to the economic prosperity of the Vikings. For example, it is clear that the earliest settlements became major trading centers throughout Ireland. Archeological evidence shows that imports and exports included textiles, animal skins, amber, and glass from England. During this time, the Vikings were able to begin a period of extremely profitable trade. Overall, the longphort settlements were essential in establishing the presence of the Vikings in Ireland during the ninth and tenth centuries.

Crossdoney is a village and townland in County Cavan, Ireland. The village is on the R154 regional road where it terminates at a junction with the R198. Peculiarly, all buildings in the village sit on one side of the road, and this gives rise to the widely used local expression: "All to one side like Crossdoney".

Fore is a barony in northern County Westmeath, Ireland. It was formed by 1672.

Carrigallen is a barony in County Leitrim, Ireland.

Corkaree is a barony in north County Westmeath, Ireland. It was formed by 1672. It is bordered by three other baronies: Fore, Moyashel and Magheradernon and Moygoish.

Moygoish is a barony in north County Westmeath, in Ireland, formed by 1672. It is bordered by County Longford to the west and four other Westmeath baronies: Corkaree, Fore, Moyashel and Magheradernon and Rathconrath to the south–west.

Moyashel and Magheradernon is a barony in the centre of County Westmeath, in Ireland, formed by 1672. It is bordered by eight other baronies: Corkaree and Fore, Delvin and Farbill, Fartullagh and Moycashel and Rathconrath and Moygoish.

Kilkenny West, previously Maherquirke or Dillons country, is a barony in west County Westmeath, Ireland. It was formed by 1542. It is bordered by County Longford to the west; it is also bordered by three other Westmeath baronies: Rathconrath, Brawny and Clonlonan. The largest centre of population in the barony is the village of Glassan.

Farbill is a barony in east County Westmeath, in Ireland. It was formed by 1672. It is bordered by County Meath to the south and east and three other baronies: Fartullagh, Moyashel and Magheradernon and Delvin. The largest centre of population in the barony is the town of Kinnegad.

Delvin is a barony in north-east County Westmeath, in Ireland. It was formed by 1672. It is bordered by County Meath to the east and three other baronies: Fore, Moyashel and Magheradernon and Farbill. The largest centre of population is Delvin.
Kilmacnevan is a civil parish in County Westmeath, Ireland. It is located about 15.81 kilometres (10 mi) west–north–west of Mullingar.
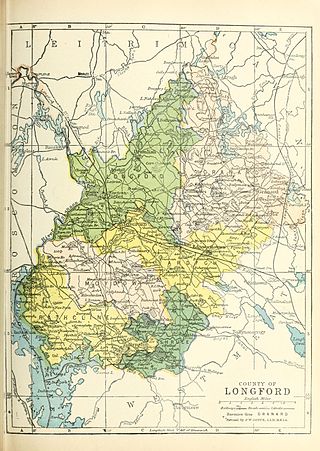
Moydow is a barony in County Longford, Ireland.
Street is a civil parish in County Westmeath, Ireland. It is located about 19.39 kilometres (12 mi) north-north-west of Mullingar.

Rathcline is a barony in County Longford, Ireland.

Shrule, sometimes called Abbeyshrule, is a barony in County Longford, Ireland.
Leitrim is a barony in Ireland that lies partly in County Galway and partly in County Clare. It is located in the south-eastern corner of County Galway and the north-eastern corner of County Clare. Prior to 1898, the entire barony was contained in County Galway. The Local Government (Ireland) Act 1898 split the barony: part of the barony was transferred to County Clare. Leitrim is bounded, clockwise from the southwest, by the Clare baronies of Tulla Upper and Tulla Lower; the Galway baronies of Loughrea to the west, Kilconnell to the north, and Longford to the east; and by Lough Derg to the south and southeast. It measures 20 miles (32 km) from north to south and 9.5 miles (15.3 km) from east to west.