
Miletus symethus, the great brownie, is a small butterfly found in India that belongs to the lycaenids or blues family. The species was first described by Pieter Cramer in 1777.

Kaniska canace, the blue admiral, is a nymphalid butterfly, the only species of the genus Kaniska. It is found in south and southeast Asia.

Nacaduba kurava, the transparent six-line blue, is a species of butterfly in the family Lycaenidae found in Asia and Australia. The species was first described by Frederic Moore in 1857.

Athyma nefte, the colour sergeant, is a species of brush-footed butterfly found in tropical South and Southeast Asia.

The Indian fritillary is a species of butterfly of the nymphalid or brush-footed family. It is usually found from south and southeast Asia to Australia.

Catochrysops strabo, the forget-me-not, is a small butterfly found in Asia that belongs to the lycaenids or blues family. The species was first described by Johan Christian Fabricius in 1793. It is found in Sri Lanka, India, from Sikkim to Indochina and in Sundaland, Sulawesi and the Philippines.

Spilosoma clava is a species of moth of the family Erebidae. It was described by Alfred Ernest Wileman in 1910. It is found in Taiwan.

Spilosoma wilemani is a species of moth of the family Erebidae. It was described by Walter Rothschild in 1914. It is found in Taiwan and Japan's southern Ryukyu Islands.

Spilosoma fumida is a species of moth of the family Erebidae. It was described by Alfred Ernest Wileman in 1910. It is found in Taiwan.
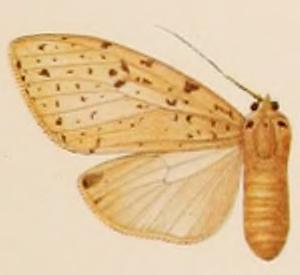
Lophocampa albescens is a moth of the family Erebidae. It was described by Walter Rothschild in 1909. It is found in French Guiana, Suriname and Venezuela.

Spilosoma eldorado is a moth of the family Erebidae. It was described by Walter Rothschild in 1910. It is found in eastern India and Sri Lanka.

Spilosoma semperi is a moth of the family Erebidae. It was described by Walter Rothschild in 1910. It is found on Sumatra and Peninsular Malaysia.

Spilosoma roseata is a moth of the family Erebidae. It was described by Walter Rothschild in 1910. It is found on Java in Indonesia.

Spilosoma fraterna is a moth of the family Erebidae first described by Walter Rothschild in 1910. It is found on Papua New Guinea.

Spilosoma batesi is a moth of the family Erebidae. It was described by Walter Rothschild in 1910. It is found in Nigeria, Cameroon, Congo and Zaire.
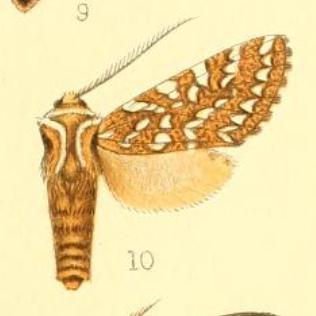
Lophocampa andensis is a moth in the family Erebidae. It was described by Schaus in 1896. It is found in Colombia.

Lophocampa dognini, the Rothschild's marbled tiger, is a moth of the family Erebidae. It was described by Walter Rothschild in 1910. It is found in Peru.

Lophocampa endrolepia is a moth of the family Erebidae. It was described by Paul Dognin in 1908. It is found in Ecuador.

Spilosoma buryi is a moth in the family Erebidae. It was described by Walter Rothschild in 1910. It is found in Ghana and Nigeria.

Spilosoma gynephaea is a moth in the family Erebidae. It was described by George Hampson in 1901. It is found in South Africa and Zimbabwe.
















