The Owyhee River is a tributary of the Snake River located in northern Nevada, southwestern Idaho and southeastern Oregon in the Western United States and its Pacific Northwest region. It is 280 miles (450 km) long. The river's drainage basin is 11,049 square miles (28,620 km2) in area, one of the largest subbasins of the Columbia River Basin with its major waterways of the Columbia River and Snake River. The mean annual discharge is 995 cubic feet per second (28.2 m3/s), with a maximum of 50,000 cu ft/s (1,400 m3/s) recorded in 1993 and a minimum of 42 cu ft/s (1.2 m3/s) in 1954.

The San Bernardino Mountains are a high and rugged mountain range in Southern California in the United States. Situated north and northeast of San Bernardino and spanning two California counties, the range tops out at 11,503 feet (3,506 m) at San Gorgonio Mountain – the tallest peak in Southern California. The San Bernardinos form a significant region of wilderness and are popular for hiking and skiing.

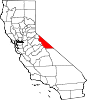
The Feather River is the principal tributary of the Sacramento River, in the Sacramento Valley of Northern California. The river's main stem is about 73 miles (117 km) long. Its length to its most distant headwater tributary is just over 210 miles (340 km). The main stem Feather River begins in Lake Oroville, where its four long tributary forks join—the South Fork, Middle Fork, North Fork, and West Branch Feather Rivers. These and other tributaries drain part of the northern Sierra Nevada, and the extreme southern Cascades, as well as a small portion of the Sacramento Valley. The total drainage basin is about 6,200 square miles (16,000 km2), with approximately 3,604 square miles (9,330 km2) above Lake Oroville.
Canyon, formerly known as Sequoya, is an unincorporated community located near the border of Contra Costa and Alameda counties, in the U.S. state of California. It is situated between Oakland and Moraga in the San Francisco Bay Area. The community is named for its location in the upper canyon of San Leandro Creek along the eastern slope of the Berkeley Hills. Canyon lies at an elevation of 1138 feet.

The Cosumnes River is a river in northern California in the United States. It rises on the western slope of the Sierra Nevada and flows approximately 52.5 miles (84.5 km) into the Central Valley, emptying into the Mokelumne River in the Sacramento-San Joaquin Delta.

Discovery Bay is an unincorporated community in Jefferson County, Washington. The community of Discovery Bay is an area near the intersection of U.S. Route 101 and State Route 20, at the foot of Discovery Bay – roughly midway between the larger communities of Port Townsend to the northeast and Sequim to the northwest. It is a mix of residential areas and commercial enterprises, including crabbing, oystering, clamming, timbering, security training and gravel extraction. A few restaurants and stores on US 101 near SR 20 primarily serve drivers and truckers along US 101.

The Kaweah River is a river draining the southern Sierra Nevada in Tulare County, California in the United States. Fed primarily by high elevation snowmelt along the Great Western Divide, the Kaweah begins as four forks in Sequoia National Park, where the watershed is noted for its alpine scenery and its dense concentrations of giant sequoias, the largest trees on Earth. It then flows in a southwest direction to Lake Kaweah – the only major reservoir on the river – and into the San Joaquin Valley, where it diverges into multiple channels across an alluvial plain around Visalia. With its Middle Fork headwaters starting at almost 13,000 feet (4,000 m) above sea level, the river has a vertical drop of nearly two and a half miles (4.0 km) on its short run to the San Joaquin Valley, making it one of the steepest river drainages in the United States. Although the main stem of the Kaweah is only 33.6 miles (54.1 km) long, its total length including headwaters and lower branches is nearly 100 miles (160 km).

The San Jacinto River is a 42-mile-long (68 km) river in Riverside County, California. The river's headwaters are in Santa Rosa and San Jacinto Mountains National Monument. The lower portion of the 765-square-mile (1,980 km2) watershed is urban and agricultural land. As a partially endorheic watershed that is contiguous with other Great Basin watersheds, the western side of the San Jacinto Basin is a portion of the Great Basin Divide.

Glenbrook is a census-designated place (CDP) on the east shore of Lake Tahoe in Douglas County, Nevada, United States. The population was 215 at the 2010 census. Beach and Bay are for residents and renters living in Glenbrook's gated community. There is no public access to the beach or bay.
Pulga is an unincorporated community in Butte County, California. It is located along the west slope of the Feather River canyon. A variant name for the community is Big Bar.
Sausal Creek, 3.1 miles (5.0 km) long, is one of the principal creeks in Oakland, California.

Havilah was an unincorporated community in Kern County, California that was completely destroyed by the 2024 Borel Fire. The land is located in the mountains between Walker Basin and the Kern River Valley, 5 miles (8.0 km) south-southwest of Bodfish at an elevation of 3,136 feet (956 m).
Toadtown is an unincorporated community in Butte County, California. It lies at an elevation of 2782 feet.

Casa Diablo Hot Springs is a hot springs and active geothermal location, near Mammoth Lakes and the Eastern Sierra Nevada, in Mono County, eastern California.

Forest Falls is an unincorporated community in San Bernardino County, California, 75 miles (121 km) due east of Los Angeles. The community has a population of 1,102 and contains 712 houses. Forest Falls is best known for the waterfalls on Vivian and Falls creeks and as a point of access for recreation in the San Bernardino National Forest, particularly the San Gorgonio Wilderness Area, which lies directly north of the community.

Mill Creek is a 14.5-mile-long (23.3 km) perennial stream that flows east from the Sierra Nevada Mountain Range into Mono Lake, in Mono County, California. It courses through Lundy Canyon and Lundy Lake, before passing through Mono City, California on its way to Mono Lake.

El Dorado Canyon is a canyon in southern Clark County, Nevada famed for its rich silver and gold mines. The canyon was named in 1857 by steamboat entrepreneur Captain George Alonzo Johnson when gold and silver was discovered here. It drains into the Colorado River at the former site of Nelson's Landing.

Swansboro Country; a subdivision within the community of Mosquito, is a residential area northeast of Placerville, the county seat of El Dorado County, California. The population was approximately 1,000 at the 2010 census. It is part of the Sacramento–Arden-Arcade–Roseville Metropolitan Statistical Area.

Mount Scowden is an 11,182-foot-elevation (3,408 meter) summit located in the Sierra Nevada mountain range, in Mono County of northern California, United States. The mountain is set less than three miles east of the Sierra crest, within the Hoover Wilderness, on land managed by Inyo National Forest. Mount Scowden is situated in Lundy Canyon, one mile north of line parent Tioga Crest, 1.6 miles (2.6 km) west of Gilcrest Peak, and 2.5 miles (4.0 km) southeast of Black Mountain. Topographic relief is significant as the summit rises 2,900 feet above Mill Creek in one mile. Precipitation runoff from this mountain drains to Mill Creek, and ultimately Mono Lake. The mountain's toponym has been officially adopted by the United States Board on Geographic Names and has been in publications since at least 1882. Leo A. Scowden was a mining engineer and United States deputy mineral surveyor for California who resided in Bodie, Mono County. There were several mining claims on Mt. Scowden in the 1800s which gave rise to the gold rush camp of Lundy.