
Ammonoids are a group of extinct marine mollusc animals in the subclass Ammonoidea of the class Cephalopoda. These molluscs, commonly referred to as ammonites, are more closely related to living coleoids than they are to shelled nautiloids such as the living Nautilus species. The earliest ammonites appeared during the Devonian, and the last species either vanished in the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, or shortly after during the Danian epoch of the Paleocene.

Tropaeum is an extinct genus of ammonites found throughout the oceans of the world during the Early Cretaceous. As with many other members of the family Ancyloceratidae, there was a trend among species within this genus to uncoil somewhat, in a very similar manner to the genus Lytoceras. The largest species, T. imperator of Australia, had a shell a little over one meter in diameter.

The Blockade of Callao was a military operation that occurred during the War of the Pacific or the Salitre War and that consisted of the Chilean squadron preventing the entry of ships to the port of Callao and the neighboring coves between 10 April 1880 and 17 January 1881.

Ammonoceratites is an extinct genus of ammonoid cephalopod known from the Albian of British Columbia, Madagascar, New Zealand, and Japan, included in the Lytoceratidae.
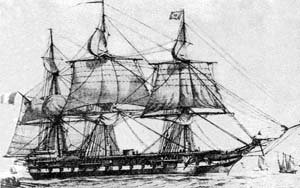
Apurímac was the second steam frigate of the Peruvian Navy, built in England in 1855 along with the steamers Loa and Tumbes as a part of a major built-up of the Navy during the government of President José Rufino Echenique. A veteran of two wars and many internal conflicts, due to her age she served as training ship in Callao port from 1873 until January 17, 1881, when she was scuttled along with the rest of the Peruvian Navy to prevent capture by Chilean troops who had occupied the port after the defeat of the Peruvian Army in the battles of San Juan and Miraflores.

Lytoceratidae is a taxonomic family of ammonoid cephalopods belonging to the suborder Lytoceratina, characterized by very evolute shells that generally enlarge rapidly, having whorls in contact but mostly overlapping very sightly, or not at all.

Lytoceras is an ammonite genus that was extant during most of the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods, and is the type genus for the family Lytoceratidae. These cephalopods were fast-moving nektonic carnivores.

Lytoceratinae is a subfamily of ammonoid cephalopods that make up part of the family Lytoceratidae.
Ptycholytoceras is a genus of fast-moving nektonic ammonoid carnivores included in the Lytoceratinae in which the shell has round inner and depressed outer whorls and sides with dorso-ventrally sloping folds that do not pass onto the venter.

Lytoceras batesi is an ammonite species belonging to the family Lytoceratidae. These cephalopods were fast-moving nektonic carnivores. They lived in the Cretaceous period.

Lytoceras cornucopia is an ammonite species belonging to the family Lytoceratidae. These cephalopods were fast-moving nektonic carnivores. They lived in the Jurassic period.

Lytoceras fimbriatum is an ammonite species belonging to the family Lytoceratidae. These cephalopods were fast-moving nektonic carnivores. They lived in the Jurassic period.

Lytoceras eudesianum is an ammonite species belonging to the family Lytoceratidae. These fast-moving nektonic carnivores lived from the Bajocian age to the Bathonian age of the Middle Jurassic.

The Forbes Shale is a geologic formation in the Sacramento Valley of northern California, United States. It is found in the Sutter Buttes area of Sutter County, California. It preserves fossils dating back to the Coniacian stage of the Late Cretaceous period.

Padillasaurus is an extinct genus of titanosauriform sauropod known from the Early Cretaceous Paja Formation in Colombia. It contains a single species, Padillasaurus leivaensis, known only from a single partial axial skeleton. Initially described as a brachiosaurid, it was considered to be the first South American brachiosaurid ever discovered and named. Before its discovery, the only known brachiosaurid material on the continent was very fragmentary and from the Jurassic period. However, a more recent study finds it to be a basal somphospondylan.
Georges Le Mesle was a French geologist. He is best known for his work on the geology of northern and southern Tunisia, which he undertook between 1887 and 1891.

Camisería Burgos, commonly known as Burgos, is a gentleman's bespoke shirtmaker founded in 1906 in Madrid. The store has been located at Calle Cedaceros 2 since its opening, and until 1949, had another shop at Boulevard des Capucines in Paris. Their most popular products are bespoke shirts, guayaberas, pyjamas and Teba jackets.

Fundación Huésped is a nonprofit foundation in Argentina. It was created in 1989 for the purpose of fighting HIV/AIDS, with a specific focus on creating a social environment that would allow the disease to be overcome. Since October 2015, the foundation has maintained a free testing center which allows rapid diagnosis of HIV/AIDS.















