Lytoceras is an ammonite genus that was extant during most of the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods, and is the type genus for the family Lytoceratidae. These cephalopods were fast-moving nektonic carnivores.
Lytoceras is an ammonite genus that was extant during most of the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods, and is the type genus for the family Lytoceratidae. These cephalopods were fast-moving nektonic carnivores.

Shells of Lytoceras are evolute, round or quadrate in section, covered with crinkled growth lines or riblets, and may have slight constrictions on internal molds. Some have fine striations, (parallel grooves running longitudinally along the flanks).
Fossils of species within this genus have been found in the Jurassic and Cretaceous rocks all over the world, particularly in Western Europe, Morocco, Madagascar, South Africa and United States. [2]

Neoceratodus is a genus of lungfish in the family Neoceratodontidae. The extant Australian lungfish is the only surviving member of this genus, but it was formerly much more widespread, being distributed throughout Africa, Australia, and South America. Species were also much more diverse in body plan; for example, the Cretaceous species Neoceratodus africanus was a gigantic species that coexisted with Spinosaurus in what is now the Kem Kem Formation of Morocco. The earliest fossils from this genus are of Neoceratodus potkooroki from the mid Cretaceous (Albian-Cenomanian) Griman Creek Formation of Australia; remains from the Late Jurassic of Uruguay assigned to this genus probably do not belong to the genus.

The Brachiosauridae are a family or clade of herbivorous, quadrupedal sauropod dinosaurs. Brachiosaurids had long necks that enabled them to access the leaves of tall trees that other sauropods would have been unable to reach. In addition, they possessed thick spoon-shaped teeth which helped them to consume tough plants more efficiently than other sauropods. They have also been characterized by a few unique traits or synapomorphies; dorsal vertebrae with 'rod-like' transverse processes and an ischium with an abbreviated pubic peduncle.

Goniopholis is an extinct genus of goniopholidid crocodyliform that lived in Europe and North America during the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous. Like other goniopholidids, it resembled living crocodilians, and probably had a similar ecology as semi-aquatic ambush predators.

Lycoptera is an extinct genus of fish that lived from Lower Cretaceous, Barremian to Aptian in present-day China, North Korea, Mongolia and Siberia. Although there is record from Jurassic Formation in Siberia, its age remains questionable. It is known from abundant fossils representing sixteen species, which serve as important index fossil used to date geologic formations in China. Along with the genus Peipiaosteus, Lycoptera has been considered a defining member of the Jehol Biota, a prehistoric ecosystem famous for its feathered dinosaurs, which flourished for 20 million years during the Early Cretaceous, where it occurs abundantly in often monospecific beds, where they are thought to have died in seasonal mass death events. Lycoptera is a crown group teleost belonging to an early diverging lineage of the Osteoglossomorpha, which contains living mooneyes, arapaima, arowana, elephantfish and knifefish/featherbacks.

Berriasella is a discoidal evolute perisphinctacean ammonite, and type genus for the neocomitid subfamily Berriasellinae. Its ribbing is distinct, consisting of both simple and bifurcated ribs that extend from the umbilical seam across the venter; its whorl section generally compressed, the venter more or less narrowly rounded. The species Berriasella jacobi traditionally has been regarded an index fossil defining the base of the Cretaceous, however since 2016 this had been replaced by the first occurrence of Calpionella alpina. Some authors regard B. jacobi as instead belonging to the genus Strambergella.

Ceratodus is an extinct genus of lungfish. It has been described as a "catch all", and a "form genus" used to refer to the remains of a variety of lungfish belonging to the extinct family Ceratodontidae. Fossil evidence dates back to the Early Triassic. A wide range of fossil species from different time periods have been found around the world in places such as the United States, Argentina, Greenland, England, Germany, Egypt, Madagascar, China, and Australia. Ceratodus is believed to have become extinct sometime around the beginning of the Eocene Epoch.

Mawsonia is an extinct genus of prehistoric coelacanth fish. It is amongst the largest of all coelacanths, with one quadrate specimen possibly belonging to an individual measuring 5.3 metres in length. It lived in freshwater and brackish environments from the late Jurassic to the mid-Cretaceous of South America, eastern North America, and Africa. Mawsonia was first described by British paleontologist Arthur Smith Woodward in 1907.

Baptanodon is an ichthyosaur of the Late Jurassic period, named for its supposed lack of teeth. It had a graceful 3.5 m (11 ft) long dolphin-shaped body, and its jaws were well adapted for catching squid. Major fossil finds of this genus have been recorded in North America. The type species, Sauranodon natans, was originally included under Sauranodon in 1879, but this name was preoccupied.

Ptychoceratodus is an extinct genus of lungfish living from Early Triassic to Middle Jurassic. It was established by Otto Jaekel for one species, transferred from Ceratodus genus. Type species is P. serratus from the Middle Triassic of Switzerland and Germany. Ptychoceratodus had two pairs of massive dental plates, bearing 4-6 acute ridges. Its skull roof was composed from massive, plate-like bones. In the central part of skull roof was localized an unossified fenestra. Most of the Ptychoceratodus findings are isolated dental plates, some associated with jaws. Other parts of skull or postcranial skeleton are relatively rarely found as fossils. The anatomy of skull is the best recognized in P. serratus, whereas less complete cranial material is available also for P. concinuus, P. phillipsi, and P. rectangulus. Although Ptychoceratodus is known exclusively from the Triassic and Jurassic, there were also Cretaceous specimens referred to this genus. However, they are more often regarded as representants of Metaceratodus. Ptychoceratodus is the only member of the family Ptychoceratodontidae. The first named species is P. phillipsi by Louis Agassiz in 1837 as a species of Ceratodus and later moved to the genus Ptychoceratodus. Occurrences of Ptychoceratodus come mainly from Europe. However, occurrences from other continents suggest it was dispersed globally during the Triassic. After 2010, the new fossil material behind the Europe was reported from South America, India, and Greenland
Lusitanisuchus is an extinct genus of mesoeucrocodylian crocodyliform. Mostly fragmentary fossils have been found from several localities in Portugal and are Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous in age.

Dorsetisaurus is a genus of extinct lizard, known from the Late Jurassic of North America, and the Late Jurassic-earliest Cretaceous of Europe. The genus was first reported from the Early Cretaceous (Berriasian) Lulworth Formation of the Purbeck Group of Durlston Bay, in Dorset. It has also been reported from the Late Jurassic aged Alcobaça Formation of Portugal, the Aptian-Albian Dzunbain Formation of Mongolia, and the Morrison Formation of Western North America present in stratigraphic zones 2, 4, and 5. It is considered the oldest widely accepted member of Anguimorpha. based on the presence of 11 shared synapomorphies.
Compsemys is an extinct genus of prehistoric turtles from the Late Cretaceous and Paleocene of North America and possibly Europe. The type species C. victa, first described by Joseph Leidy from the Hell Creek Formation in Montana in 1856, and another probable species C. russelli, described in 2012, from Paleocene deposits in France. Its affinites have long been uncertain, but it has recently been considered to be the most basal member of Paracryptodira, despite the clade first appearing in the Late Jurassic, and is sometimes included in its own family, Compsemydidae. A revision in 2020 found Compsemydidae to be more expansive, also containing Riodevemys and Selenemys from the Late Jurassic of Europe, and Peltochelys from the Early Cretaceous of Europe.

Paleontology in Oregon refers to paleontological research occurring within or conducted by people from the U.S. state of Oregon. Oregon's geologic record extends back approximately 400 million years ago to the Devonian period, before which time the state's landmass was likely submerged under water. Sediment records show that Oregon remained mostly submerged until the Paleocene period. The state's earliest fossil record includes plants, corals, and conodonts. Oregon was covered by seaways and volcanic islands during the Mesozoic era. Fossils from this period include marine plants, invertebrates, ichthyosaurs, pterosaurs, and traces such as invertebrate burrows. During the Cenozoic, Oregon's climate gradually cooled and eventually yielded the environments now found in the state. The era's fossils include marine and terrestrial plants, invertebrates, fish, amphibians, turtles, birds, mammals, and traces such as eggs and animal tracks.

Lytoceratinae is a subfamily of ammonoid cephalopods that make up part of the family Lytoceratidae.

Nilssonia is a genus of fossil foliage traditionally assigned to the Cycadophyta either in Cycadales or their own order Nilssoniales, though the relationships of this genus with the Cycadales have been put into question on chemical grounds.

Padillasaurus is an extinct genus of titanosauriform sauropod known from the Early Cretaceous Paja Formation in Colombia. It contains a single species, Padillasaurus leivaensis, known only from a single partial axial skeleton. Initially described as a brachiosaurid, it was considered to be the first South American brachiosaurid ever discovered and named. Before its discovery, the only known brachiosaurid material on the continent was very fragmentary and from the Jurassic period. However, a more recent study finds it to be a basal somphospondylan.
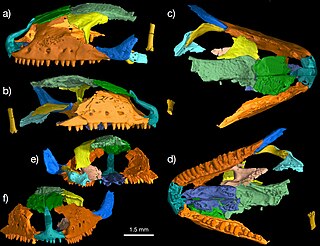
Paramacellodidae is an extinct family of lizards that first appeared in the Middle Jurassic around 170 million years ago (Ma) and became extinct at the end of the Cretaceous around 66 Ma. It was one of the earliest groups of lizards to have undergone an evolutionary radiation, with members found across the supercontinent Laurasia. The phylogenetic relationships and constituent species of Paramacellodidae are uncertain. Many studies regard them to be scincomorphs, a large group that includes skinks and their closest extinct relatives, and possibly also to Cordyoidea, a group that includes spinytail lizards and relatives. Like modern skinks, paramacelloidids had rectangular bony plates called osteoderms covering most of their bodies, including their backs, undersides, and tails. They also had short and robust limbs. Paramacellodids are distinguished from other lizards by the combination two traits in their dentition, the teeth are labiolingually expanded at their bases, and the tooth apices are lingually concave.
Tacuarembemys is an extinct genus of continental turtle from South America. It contains a single species, T. kusterae. The genus was described based on the external mold of a carapace and associated shell bone fragments found near the city of Tacuarembó, Uruguay. This fossil was found on the Tacuarembó Formation, whose estimated age ranges from late Jurassic to earliest Cretaceous.

Ctenis is a genus of fossil foliage attributable to the Cycadales, being one of the most common genera of cycad fossil leaves in the Mesozoic.

Aratasaurus is an extinct genus of basal coelurosaurian theropod dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous (Aptian) Romualdo Formation of Brazil. The genus contains a single species, A. museunacionali, known from a partial right leg. Aratasaurus represents the only tetrapod fossil known from the lower levels of the Romualdo Formation.
![]() Media related to Lytoceras at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Lytoceras at Wikimedia Commons