A reverse transcriptase (RT) is an enzyme used to generate complementary DNA (cDNA) from an RNA template, a process termed reverse transcription. Reverse transcriptases are used by certain viruses such as HIV and the hepatitis B virus to replicate their genomes, by retrotransposon mobile genetic elements to proliferate within the host genome, and by eukaryotic cells to extend the telomeres at the ends of their linear chromosomes. Contrary to a widely held belief, the process does not violate the flows of genetic information as described by the classical central dogma, as transfers of information from RNA to DNA are explicitly held possible.

RecBCD is an enzyme of the E. coli bacterium that initiates recombinational repair from potentially lethal double strand breaks in DNA which may result from ionizing radiation, replication errors, endonucleases, oxidative damage, and a host of other factors. The RecBCD enzyme is both a helicase that unwinds, or separates the strands of DNA, and a nuclease that makes single-stranded nicks in DNA.
A molecular lesion, or a point lesion, is damage to the structure of a biological molecule such as DNA, RNA, or protein. This damage may result in the reduction or absence of normal function, and in rare cases the gain of a new function. Lesions in DNA may consist of breaks or other changes in chemical structure of the helix, ultimately preventing transcription. Meanwhile, lesions in proteins consist of both broken bonds and improper folding of the amino acid chain. While many nucleic acid lesions are general across DNA and RNA, some are specific to one, such as thymine dimers being found exclusively in DNA. Several cellular repair mechanisms exist, ranging from global to specific, in order to prevent lasting damage resulting from lesions.

Lipid peroxidation is the oxidative degradation of lipids. It is the process in which free radicals "steal" electrons from the lipids in cell membranes, resulting in cell damage. This process proceeds by a free radical chain reaction mechanism. It most often affects polyunsaturated fatty acids, because they contain multiple double bonds in between which lie methylene bridges (-CH2-) that possess especially reactive hydrogen atoms. As with any radical reaction, the reaction consists of three major steps: initiation, propagation, and termination. The chemical products of this oxidation are known as lipid peroxides or lipid oxidation products (LOPs).

4-Hydroxynonenal, or 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal or 4-HNE or HNE, (C9H16O2), is an α,β-unsaturated hydroxyalkenal that is produced by lipid peroxidation in cells. 4-HNE is the primary alpha,beta-unsaturated hydroxyalkenal formed in this process.

Malondialdehyde (MDA) is the organic compound with the nominal formula CH2(CHO)2. A colorless liquid, malondialdehyde is a highly reactive compound that occurs as the enol. It occurs naturally and is a marker for oxidative stress.

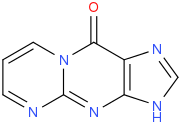
Pyrimidine dimers are molecular lesions formed from thymine or cytosine bases in DNA via photochemical reactions. Ultraviolet light (UV) induces the formation of covalent linkages between consecutive bases along the nucleotide chain in the vicinity of their carbon–carbon double bonds. The dimerization reaction can also occur among pyrimidine bases in dsRNA —uracil or cytosine. Two common UV products are cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPDs) and 6–4 photoproducts. These premutagenic lesions alter the structure and possibly the base-pairing. Up to 50–100 such reactions per second might occur in a skin cell during exposure to sunlight, but are usually corrected within seconds by photolyase reactivation or nucleotide excision repair. Uncorrected lesions can inhibit polymerases, cause misreading during transcription or replication, or lead to arrest of replication. Pyrimidine dimers are the primary cause of melanomas in humans.

In genetics, crosslinking of DNA occurs when various exogenous or endogenous agents react with two nucleotides of DNA, forming a covalent linkage between them. This crosslink can occur within the same strand (intrastrand) or between opposite strands of double-stranded DNA (interstrand). These adducts interfere with cellular metabolism, such as DNA replication and transcription, triggering cell death. These crosslinks can, however, be repaired through excision or recombination pathways.

In molecular genetics, a DNA adduct is a segment of DNA bound to a cancer-causing chemical. This process could be the start of a cancerous cell, or carcinogenesis. DNA adducts in scientific experiments are used as biomarkers of exposure and as such are themselves measured to reflect quantitatively, for comparison, the amount of carcinogen exposure to the subject organism, for example rats or other living animals. Under experimental conditions for study, such DNA adducts are induced by known carcinogens, of which commonly used is DMBA. For example, the term "DMBA-DNA adduct" in a scientific journal refers to a piece of DNA that has DMBA attached to it. The presence of such an adduct indicates prior exposure to a potential carcinogen, but does not by itself indicate the presence of cancer in the subject animal.

ERCC2, or XPD is a protein involved in transcription-coupled nucleotide excision repair.
Thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) are formed as a byproduct of lipid peroxidation which can be detected by the TBARS assay using thiobarbituric acid as a reagent. TBARS can be upregulated, for example, by heart attack or by certain kinds of stroke.

Nucleotidyltransferases are transferase enzymes of phosphorus-containing groups, e.g., substituents of nucleotidylic acids or simply nucleoside monophosphates. The general reaction of transferring a nucleoside monophosphate moiety from A to B, can be written as:

DNA excision repair protein ERCC-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ERCC1 gene. Together with ERCC4, ERCC1 forms the ERCC1-XPF enzyme complex that participates in DNA repair and DNA recombination.

Glutathione peroxidase 4, also known as GPX4, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GPX4 gene. GPX4 is a phospholipid hydroperoxidase that protects cells against membrane lipid peroxidation.

Xeroderma pigmentosum, complementation group C, also known as XPC, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the XPC gene. XPC is involved in the recognition of bulky DNA adducts in nucleotide excision repair. It is located on chromosome 3.

DNA repair protein complementing XP-G cells is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ERCC5 gene.

Aldehyde dehydrogenase, dimeric NADP-preferring is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ALDH3A1 gene.

Inhibitor of growth protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ING2 gene.
DNA damage is distinctly different from mutation, although both are types of error in DNA. DNA damage is an abnormal chemical structure in DNA, while a mutation is a change in the sequence of standard base pairs. DNA damages cause changes in the structure of the genetic material and prevents the replication mechanism from functioning and performing properly.

3-Dimethylaminoacrolein is an organic compound with the formula Me2NC(H)=CHCHO. It is a pale yellow water-soluble liquid. The compound has a number of useful and unusual properties, e.g. it "causes a reversal of the hypnotic effect of morphine in mice" and has a "stimulating effect in humans".