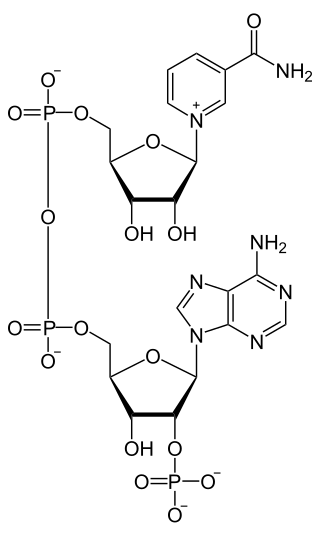
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, abbreviated NADP+ or, in older notation, TPN (triphosphopyridine nucleotide), is a cofactor used in anabolic reactions, such as the Calvin cycle and lipid and nucleic acid syntheses, which require NADPH as a reducing agent ('hydrogen source'). It is used by all forms of cellular life.

GTP cyclohydrolase I (GTPCH) (EC 3.5.4.16) is a member of the GTP cyclohydrolase family of enzymes. GTPCH is part of the folate and biopterin biosynthesis pathways. It is responsible for the hydrolysis of guanosine triphosphate (GTP) to form 7,8-dihydroneopterin triphosphate (7,8-DHNP-3'-TP, 7,8-NH2-3'-TP).

Bifunctional purine biosynthesis protein PURH is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ATIC gene.

10-Formyltetrahydrofolate (10-CHO-THF) is a form of tetrahydrofolate that acts as a donor of formyl groups in anabolism. In these reactions 10-CHO-THF is used as a substrate in formyltransferase reactions.

3-Methylglutaconyl-CoA hydratase, also known as MG-CoA hydratase and AUH, is an enzyme encoded by the AUH gene on chromosome 19. It is a member of the enoyl-CoA hydratase/isomerase superfamily, but it is the only member of that family that is able to bind to RNA. Not only does it bind to RNA, AUH has also been observed to be involved in the metabolic enzymatic activity, making it a dual-role protein. Mutations of this gene have been found to cause a disease called 3-Methylglutaconic Acuduria Type 1.

In enzymology, a methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase (NADP+) (EC 1.5.1.5) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a formate—tetrahydrofolate ligase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Methionine synthase reductase, also known as MSR, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MTRR gene.

MTHFD1 is a gene located in humans on chromosome 14 that encodes for a protein with three distinct enzymatic activities. C-1-tetrahydrofolate synthase, cytoplasmic also known as C1-THF synthase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MTHFD1 gene.

Isocitrate dehydrogenase [NADP], mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the IDH2 gene.

Isocitrate dehydrogenase [NAD] subunit gamma, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the IDH3G gene.

Isocitrate dehydrogenase [NAD] subunit beta, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the IDH3B gene.

Bifunctional methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase/cyclohydrolase, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MTHFD2 gene.

L-2-hydroxyglutarate dehydrogenase, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the L2HGDH gene, also known as C14orf160, on chromosome 14.

Alpha-aminoadipic semialdehyde synthase is an enzyme encoded by the AASS gene in humans and is involved in their major lysine degradation pathway. It is similar to the separate enzymes coded for by the LYS1 and LYS9 genes in yeast, and related to, although not similar in structure, the bifunctional enzyme found in plants. In humans, mutations in the AASS gene, and the corresponding alpha-aminoadipic semialdehyde synthase enzyme are associated with familial hyperlysinemia. This condition is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern and is not considered a particularly negative condition, thus making it a rare disease.

10-formyltetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ALDH1L1 gene.

5,10-Methenyltetrahydrofolate (5,10-CH=THF) is a form of tetrahydrofolate that is an intermediate in metabolism. 5,10-CH=THF is a coenzyme that accepts and donates methenyl (CH=) groups.

Monofunctional C1-tetrahydrofolate synthase, mitochondrial also known as formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MTHFD1L gene.

Retinol dehydrogenase 13 (all-trans/9-cis) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RDH13 gene. This gene encodes a mitochondrial short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase, which catalyzes the reduction and oxidation of retinoids. The encoded enzyme may function in retinoic acid production and may also protect the mitochondria against oxidative stress. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described.
Riboflavin-responsive exercise intolerance is a rare disorder caused by mutations of the SLC25A32 gene that encodes the mitochondrial folate transporter. Patients suffer from exercise intolerance and may have disrupted motor function.






















