This article needs additional citations for verification .(October 2009) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
Madalag | |
|---|---|
| Municipality of Madalag | |
 Aklan River in Madalag | |
| Motto(s): Madalagnon Ako Banwa Ko Amligan Ko | |
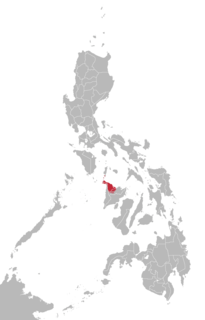
 Map of Aklan with Madalag highlighted | |
Location within the Philippines | |
| Coordinates: 11°31′N122°18′E / 11.52°N 122.3°E Coordinates: 11°31′N122°18′E / 11.52°N 122.3°E | |
| Country | |
| Region | Western Visayas (Region VI) |
| Province | Aklan |
| District | Lone district |
| Founded | 1948 |
| Barangays | 25 (see Barangays) |
| Government | |
| • Type | Sangguniang Bayan |
| • Mayor | Alfonso 'Dindo' A. Gubatina |
| • Electorate | 11,322 voters (2016) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 269.6 km2 (104.1 sq mi) |
| Population (2015 census) [3] | |
| • Total | 18,389 |
| • Density | 68/km2 (180/sq mi) |
| Demonym(s) | Madalagnon |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (PST) |
| ZIP code | 5603 |
| PSGC | |
| IDD : area code | +63 (0)36 |
| Climate type | Tropical climate |
| Income class | 4th municipal income class |
| Revenue (₱) | 84.1 million (2016) |
| Native languages | Aklan language Tagalog |
| Website | elgu |
Madalag, officially the Municipality of Madalag, (Aklanon: Banwa it Madalag; Hiligaynon: Banwa sang Madalag; Tagalog : Bayan ng Madalag), is a 4th class municipality in the province of Aklan, Philippines. According to the 2015 census, it has a population of 18,389 people. [3]
Aklanon (Akeanon), also known as Aklan, is a regional Visayan language spoken in the province of Aklan on the island of Panay in the Philippines. Its unique feature among other Visayan languages is the close-mid back unrounded vowel [ɤ] occurring as part of diphthongs and traditionally written with the letter E such as in the name Akeanon (Aklanon). However, this phoneme is also present in sister Philippine languages, namely Itbayat, Isneg, Manobo, Samal and Sagada.

The Hiligaynon language, also often referred to by most of its speakers simply as Ilonggo, is an Austronesian regional language spoken in the Philippines by about 9.1 million people, mainly in Western Visayas and Soccsksargen, most of whom belong to the Visayan ethnic group, mainly the Hiligaynons. It is the second-most widely spoken language and a member of the so-named Visayan language family and is more distantly related to other Philippine languages.

Tagalog is an Austronesian language spoken as a first language by a quarter of the population of the Philippines and as a second language by the majority. Its standardized form, officially named Filipino, is the national language of the Philippines, and is one of two official languages alongside English.
Contents
- Geography
- Climate
- Soil
- Land Use
- Barangays
- Demographics
- Economy
- Agriculture
- Industry
- Transportation
- Utilities
- Water supply system
- Communication
- Power facilities
- Health
- Education
- References
Madalag was formerly an arrabal and part of Libacao. In 1948, it was separated and constituted as a separate town, with the following barrios: Logohon, Singay, Balactasan, Cabangahan, Cabilawan, Pangitan, San Jose, Talimagao, Talangban, Alaminos, Catabana, Bakyang, Calicia, Mercedes, Maria Cristina, Dit-ana, Guinato-an, Tigbauan, Alas-as, Mamba, Medina, Panikyason, and Paningayan. [4]

A suburb is a mixed-use or residential area, existing either as part of a city or urban area or as a separate residential community within commuting distance of a city. In most English-speaking countries, suburban areas are defined in contrast to central or inner-city areas, but in Australian English and South African English, suburb has become largely synonymous with what is called a "neighborhood" in other countries and the term extends to inner-city areas. In some areas, such as Australia, India, China, New Zealand, the United Kingdom, and a few U.S. states, new suburbs are routinely annexed by adjacent cities. In others, such as Saudi Arabia, Canada, France, and much of the United States, many suburbs remain separate municipalities or are governed as part of a larger local government area such as a county.