
Magnesium is a chemical element; it has symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals it occurs naturally only in combination with other elements and it almost always has an oxidation state of +2. It reacts readily with air to form a thin passivation coating of magnesium oxide that inhibits further corrosion of the metal. The free metal burns with a brilliant-white light. The metal is obtained mainly by electrolysis of magnesium salts obtained from brine. It is less dense than aluminium and is used primarily as a component in strong and lightweight alloys that contain aluminium.

Magnesium oxide (MgO), or magnesia, is a white hygroscopic solid mineral that occurs naturally as periclase and is a source of magnesium (see also oxide). It has an empirical formula of MgO and consists of a lattice of Mg2+ ions and O2− ions held together by ionic bonding. Magnesium hydroxide forms in the presence of water (MgO + H2O → Mg(OH)2), but it can be reversed by heating it to remove moisture.

Magnesium sulfate or magnesium sulphate is a chemical compound, a salt with the formula MgSO4, consisting of magnesium cations Mg2+ (20.19% by mass) and sulfate anions SO2−4. It is a white crystalline solid, soluble in water but not in ethanol.

Pyruvate carboxylase (PC) encoded by the gene PC is an enzyme of the ligase class that catalyzes the physiologically irreversible carboxylation of pyruvate to form oxaloacetate (OAA).
PubChem is a database of chemical molecules and their activities against biological assays. The system is maintained by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), a component of the National Library of Medicine, which is part of the United States National Institutes of Health (NIH). PubChem can be accessed for free through a web user interface. Millions of compound structures and descriptive datasets can be freely downloaded via FTP. PubChem contains multiple substance descriptions and small molecules with fewer than 100 atoms and 1,000 bonds. More than 80 database vendors contribute to the growing PubChem database.
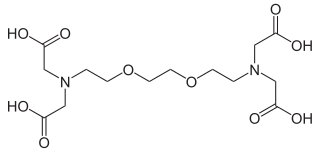
EGTA, also known as egtazic acid, is an aminopolycarboxylic acid, a chelating agent. It is a white solid that is related to the better known EDTA. Compared to EDTA, it has a lower affinity for magnesium, making it more selective for calcium ions. It is useful in buffer solutions that resemble the environment in living cells where calcium ions are usually at least a thousandfold less concentrated than magnesium.

Fumarase is an enzyme that catalyzes the reversible hydration/dehydration of fumarate to malate. Fumarase comes in two forms: mitochondrial and cytosolic. The mitochondrial isoenzyme is involved in the Krebs cycle and the cytosolic isoenzyme is involved in the metabolism of amino acids and fumarate. Subcellular localization is established by the presence of a signal sequence on the amino terminus in the mitochondrial form, while subcellular localization in the cytosolic form is established by the absence of the signal sequence found in the mitochondrial variety.
The Boord olefin synthesis is an organic reaction forming alkenes from ethers carrying a halogen atom 2 carbons removed from the oxygen atom (β-halo-ethers) using a metal such as magnesium or zinc. The reaction, discovered by Cecil E. Boord in 1930 is a classic named reaction with high yields and broad scope.
Magnesium aspartate is a magnesium salt of aspartic acid. It is used as a mineral supplement, and as an ingredient in manufacturing of cosmetics and household products.
Malate dehydrogenase (decarboxylating) (EC 1.1.1.39) or NAD-malic enzyme (NAD-ME) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a malate dehydrogenase (NADP+) (EC 1.1.1.82) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a malate dehydrogenase (oxaloacetate-decarboxylating) (EC 1.1.1.38) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction below
In enzymology, a malate dehydrogenase (quinone) (EC 1.1.5.4), formerly malate dehydrogenase (acceptor) (EC 1.1.99.16), is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a malate synthase (EC 2.3.3.9) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Mitochondrial 2-oxoglutarate/malate carrier protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC25A11 gene. Inactivating mutations in this gene predispose to metastasic paraganglioma.

Malate dehydrogenase, mitochondrial also known as malate dehydrogenase 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MDH2 gene.
Magnesium cyanide is a chemical compound with the formula Mg(CN)2. It is a toxic white solid. Unlike calcium isocyanide, the cyanide ligands prefer to coordinate at carbon, with a 0.3‑kcal/mol isomerization barrier. When this salt is heated to 500 °C, it decomposes to magnesium nitride.

The citrate-malate shuttle is a series of chemical reactions, commonly referred to as a biochemical cycle or system, that transports acetyl-CoA in the mitochondrial matrix across the inner and outer mitochondrial membranes for fatty acid synthesis. Mitochondria are enclosed in a double membrane. As the inner mitochondrial membrane is impermeable to acetyl-CoA, the shuttle system is essential to fatty acid synthesis in the cytosol. It plays an important role in the generation of lipids in the liver.
Alkali citrate is an inhibitor of kidney stones. It is used to increase urine citrate levels - this prevents calcium oxalate stones by binding to calcium and inhibiting its binding to oxalate. It is also used to increase urine pH - this prevents uric acid stones and cystine stones.












