
Gaius Suetonius Paulinus was a Roman general best known as the commander who defeated Boudica and her army during the Boudican revolt.

The Fosse Way was a Roman road built in Britain during the first and second centuries AD that linked Isca Dumnoniorum (Exeter) in the southwest and Lindum Colonia (Lincoln) to the northeast, via Lindinis (Ilchester), Aquae Sulis (Bath), Corinium (Cirencester), and Ratae Corieltauvorum (Leicester).

Atherstone is a market town and civil parish in the North Warwickshire district of Warwickshire, England. Located in the far north of the county, Atherstone is on the A5 national route, and is adjacent to the border with Leicestershire which is here formed by the River Anker. It is situated between the towns of Tamworth and Nuneaton. Atherstone is the administrative centre of the North Warwickshire district, with the offices of North Warwickshire Borough Council located in the town.

Mancetter is a village and civil parish in North Warwickshire, England at the crossing of Watling Street over the River Anker. The population had reduced from 2,449 to 2,339 at the 2011 census. It is situated on the B4111 road towards Hartshill and Nuneaton. It adjoins the town of Atherstone.

Tripontium was a town in Roman Britain. It lay on the Roman road later called Watling Street at a site now chiefly within the civil parish of Churchover in the English county of Warwickshire and partly in Leicestershire, some 3.4 miles north-east of Rugby and 3.1 miles south of Lutterworth.

Viroconium or Uriconium, formally Viroconium Cornoviorum, was a Roman city, one corner of which is now occupied by Wroxeter, a small village in Shropshire, England, about 5 miles (8 km) east-south-east of Shrewsbury. At its peak, Viroconium is estimated to have been the 4th-largest Roman settlement in Britain, a civitas with a population of more than 15,000. The settlement probably lasted until the end of the 7th century or the beginning of the 8th. Extensive remains can still be seen.

Ambresbury Banks is the name given to the remains of an Iron Age hill fort in Epping Forest, Essex, England.

Letocetum is the ancient remains of a Roman settlement. It was an important military staging post and posting station near the junction of Watling Street, the Roman military road to north Wales, and Icknield Street. The site is now within the parish of Wall, Staffordshire, England. It is owned and run by the National Trust, under the name Letocetum Roman Baths Site & Museum. The site is in the guardianship of English Heritage as Wall Roman Site.
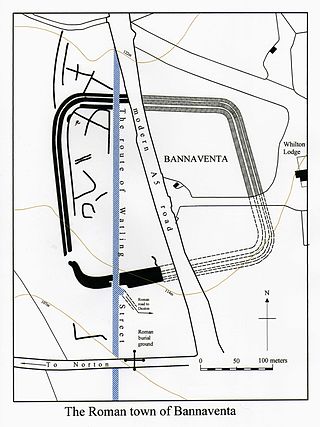
Bannaventa or Benaventa was a Romano-British fortified town which was on the Roman road later called Watling Street, which today is here, as in most places, the A5 road. Bannaventa straddles the boundaries of Norton and Whilton, Northamptonshire, England, villages highly clustered 1 kilometre (0.62 mi) and double that away, respectively.

This is about the history of the county Warwickshire situated in the English Midlands. Historically, bounded to the north-west by Staffordshire, by Leicestershire to the north-east, Northamptonshire to the east, Worcestershire to the west, Oxfordshire to the south and Gloucestershire to the south-west. Areas historically part of Warwickshire include Coventry, Solihull, Sutton Coldfield and much of central Birmingham including Aston and Edgbaston. These became part of the metropolitan county of West Midlands following local government re-organisation in 1974 after the passage of the Local Government Act 1972.

Fenny Drayton is a village and former civil parish, now in the parish of Witherley, in the Hinckley and Bosworth district of Leicestershire, England. It lies near the Warwickshire boundary, three miles south-east of Atherstone in the Coventry postcode area, just off the A444, the Roman Watling Street. Another Roman road crosses at the end of the scenic Fenn Lanes. The village is four miles from Stoke Golding, where Henry VII of England was crowned after the Battle of Bosworth in 1485. The reinterment of Richard III of England on 21 March 2015 started along Fenn Lanes, near the village. In 1931 the parish had a population of 125. On 1 April 1935 the parish was abolished and merged with Witherley, parts also went to Hartshill, Mancetter and Caldecote. The name means "farm/settlement for portage" or "farm/settlement used as a dragging place". "Fenny" reflects the fen-like ground along the Roman road.

Richborough Castle is a Roman Saxon Shore fort better known as Richborough Roman Fort. It is situated in Richborough near Sandwich, Kent. Substantial remains of the massive fort walls still stand to a height of several metres.

Hartshill is a large village and civil parish in North Warwickshire, England, adjoined with the much larger town of Nuneaton, the town centre of which is 2.5 miles to the south-east. The parish borders the district of Nuneaton and Bedworth at the south, the North Warwickshire district parishes of Ansley at the south-west, Mancetter at the north-west, and Caldecote at the east, and the parish of Witherley in Leicestershire to the north-east from which it is separated by the A5 road. The market town of Atherstone is 3.5 miles (6 km) to the north-west.

Blestium was a small fort and iron working centre in the Roman province of Britannia Superior, part of Roman Britain. It has been identified with the site of the later town of Monmouth in south east Wales, located adjoining the confluence of the River Monnow with the River Wye. A plaque on the local bank records its position.

The Cavarī or Cavarēs were a Gallic tribe dwelling in the western part of modern Vaucluse, around the present-day cities of Avignon, Orange and Cavaillon, during the Roman period. They were at the head of a confederation of tribes that included the Tricastini, Segovellauni and Memini, and whose territory stretched further north along the Rhône Valley up to the Isère river.

Isurium or Isurium of the Brigantes was a Roman fort and town in the province of Britannia at the site of present-day Aldborough in North Yorkshire, England, in the United Kingdom. Its remains—the Aldborough Roman Site—are in the care of English Heritage.
Lactodurum was a town in the Roman province of Britannia. Today it is known as Towcester, located in the English county of Northamptonshire.

The Derby Racecourse Roman settlement was the third settlement in Derby or Derventio which was a small town in the Roman province of Britannia. It lies 600m east of Derventio fort in Little Chester, on the outskirts of Derby, in the English county of Derbyshire. The Roman road from Derventio to Sawley on the River Trent passes the settlement. It is a scheduled National Monument.

The Boudican revolt was an armed uprising by native Celtic Britons against the Roman Empire during the Roman conquest of Britain. It took place circa AD 60–61 in the Roman province of Britain, and was led by Boudica, the Queen of the Iceni tribe. The uprising was motivated by the Romans' failure to honour an agreement they had made with Boudica's husband, Prasutagus, regarding the succession of his kingdom upon his death, and by the brutal mistreatment of Boudica and her daughters by the occupying Romans.

Oldbury is a hamlet and former civil parish about 2 miles from Atherstone, now in the parish of Hartshill, in the North Warwickshire district, in the county of Warwickshire, England. In 1961 the parish had a population of 82.





















