Related Research Articles

Goniurosaurus is a genus of geckos, containing 24 species. Members are known by various names including ground geckos, tiger geckos, leopard geckos, and cave geckos Members of this genus are found in China, Japan, and Vietnam. For this reason they are known commonly as Asian geckos. They belong to the family Eublepharidae.

Rhizobium is a genus of Gram-negative soil bacteria that fix nitrogen. Rhizobium species form an endosymbiotic nitrogen-fixing association with roots of (primarily) legumes and other flowering plants.

Thermus is a genus of thermophilic bacteria. It is one of several bacteria belonging to the Deinococcus–Thermus group. Thermus species can be distinguished from other genera in the family Thermaceae as well as all other bacteria by the presence of eight conserved signature indels (CSIs) found in proteins such as adenylate kinase and replicative DNA helicase as well as 14 conserved signature proteins (CSPs) that are exclusively shared by members of this genus.
The Gemmatimonadetes are a phylum of bacteria established in 2003. The phylum contains two classes Gemmatimonadetes and Longimicrobia.
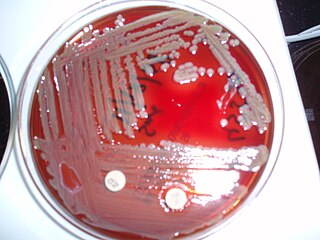
The family Flavobacteriaceae is composed of environmental bacteria. Most species are aerobic, while some are microaerobic to anaerobic; for example Capnocytophaga and Coenonia.
Paracoccus is a genus of bacteria in the family Rhodobacteraceae.
Novosphingobium is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria that includes N. taihuense, which can degrade aromatic compounds such as phenol, aniline, nitrobenzene and phenanthrene. The species N. aromativorans, which was first found in Ulsan Bay, similarly degrades aromatic molecules of two to five rings.
The Chloroflexi or Chlorobacteria are a phylum of bacteria containing isolates with a diversity of phenotypes, including members that are aerobic thermophiles, which use oxygen and grow well in high temperatures; anoxygenic phototrophs, which use light for photosynthesis ; and anaerobic halorespirers, which uses halogenated organics as electron acceptors.
Kribbella is a genus of bacteria first discovered in 1999.

Deinococcus is in the monotypic family Deinococcaceae, and one genus of three in the order Deinococcales of the bacterial phylum Deinococcus-Thermus highly resistant to environmental hazards. These bacteria have thick cell walls that give them Gram-positive stains, but they include a second membrane and so are closer in structure to Gram-negative bacteria. Deinococcus survive when their DNA is exposed to high doses of gamma and UV radiation. Whereas other bacteria change their structure in the presence of radiation, such as by forming endospores, Deinococcus tolerate it without changing their cellular form and do not retreat into a hardened structure. They are also characterized by the presence of the carotenoid pigment deinoxanthin that give them their pink color. They are usually isolated according to these two criteria. In August 2020, scientists reported that bacteria from Earth, particularly Deinococcus bacteria, were found to survive for three years in outer space, based on studies conducted on the International Space Station. These findings support the notion of panspermia, the hypothesis that life exists throughout the Universe, distributed in various ways, including space dust, meteoroids, asteroids, comets, planetoids or contaminated spacecraft.
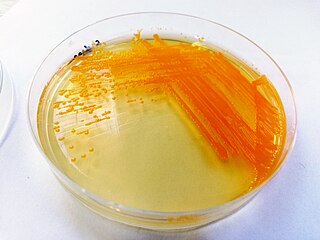
Chryseobacterium is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria. Chryseobacterium species are chemoorganotrophic, rod shape gram-negative bacteria. Chryseobacterium form typical yellow-orange color colonies due to flexirubin-type pigment. The genus contains more than 100 described species from diverse habitats, including freshwater sources, soil, marine fish, and human hosts.
Algoriphagus is a genus in the phylum Bacteroidetes (Bacteria).
Algibacter is a genus in the phylum Bacteroidetes (Bacteria).
Muricauda is a genus in the phylum "Bacteroidetes".
Roseivirga is a strictly aerobic genus from the phylum "Bacteroidetes'".
Echinicola is an aerobic and motile bacterial genus from the family of Cyclobacteriaceae.
Leeuwenhoekiella is a strictly aerobic bacterial genus from the family of Flavobacteriaceae.
Pontibacter is a strictly aerobic bacterial genus from the family of Cytophagaceae.
Mariniflexile is a genus in the phylum Bacteroidetes (Bacteria). The various species have been recovered from sea water, sea urchins, springs, brackish water, and an oyster.
Ulvibacter litoralis is a Gram-negative, aerobic, heterotrophic and non-motile bacterium from the genus of Ulvibacter which has been isolated from the alga Ulva fenestrata.
References
- 1 2 3 Nedashkovskaya OI, Kim SB, Han SK, Lysenko AM, Rohde M, Rhee MS, Frolova GM, Falsen E, Mikhailov VV, Bae KS. (2004). "Maribacter gen. nov., a new member of the family Flavobacteriaceae, isolated from marine habitats, containing the species Maribacter sedimenticola sp. nov., Maribacter aquivivus sp. nov., Maribacter orientalis sp. nov. and Maribacter ulvicola sp. nov". Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 54: 1017–1023.
- 1 2 Euzéby JP, Parte AC. "Maribacter". List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN). Retrieved June 30, 2021.