Related Research Articles
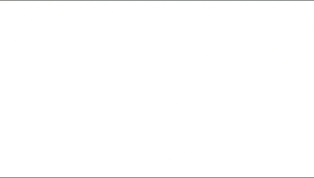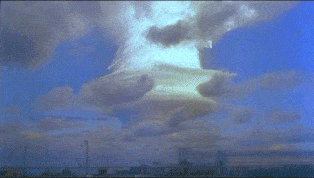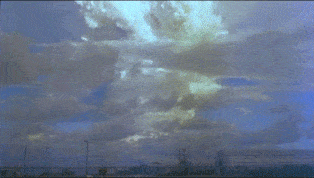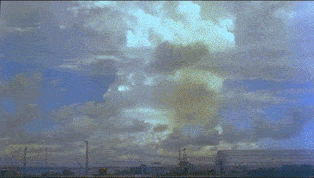
Operation Ivy was the eighth series of American nuclear tests, coming after Tumbler-Snapper and before Upshot–Knothole. The two explosions were staged in late 1952 at Enewetak Atoll in the Pacific Proving Ground in the Marshall Islands.

Operation Castle was a United States series of high-yield (high-energy) nuclear tests by Joint Task Force 7 (JTF-7) at Bikini Atoll beginning in March 1954. It followed Operation Upshot–Knothole and preceded Operation Teapot.

Castle Bravo was the first in a series of high-yield thermonuclear weapon design tests conducted by the United States at Bikini Atoll, Marshall Islands, as part of Operation Castle. Detonated on March 1, 1954, the device remains the most powerful nuclear device ever detonated by the United States and the first lithium deuteride-fueled thermonuclear weapon tested using the Teller-Ulam design. Castle Bravo's yield was 15 megatons of TNT [Mt] (63 PJ), 2.5 times the predicted 6 Mt (25 PJ), due to unforeseen additional reactions involving lithium-7, which led to radioactive contamination in the surrounding area.
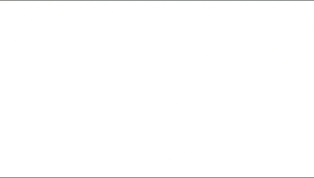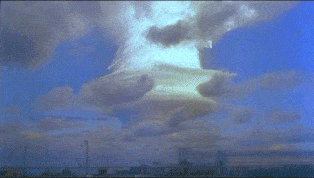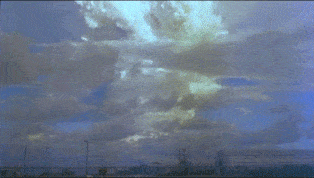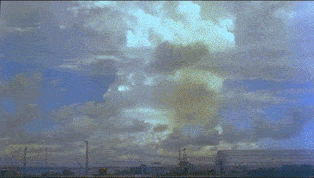
Ivy Mike was the codename given to the first full-scale test of a thermonuclear device, in which part of the explosive yield comes from nuclear fusion. Ivy Mike was detonated on November 1, 1952, by the United States on the island of Elugelab in Enewetak Atoll, in the now independent island nation of the Marshall Islands, as part of Operation Ivy. It was the first full test of the Teller–Ulam design, a staged fusion device.
RDS-6s was the first Soviet attempted test of a thermonuclear weapon that occurred on August 12, 1953, that detonated with a force equivalent to 400 kilotons of TNT.
RDS-37 was the Soviet Union's first two-stage hydrogen bomb, first tested on 22 November 1955. The weapon had a nominal yield of approximately 3 megatons. It was scaled down to 1.6 megatons for the live test.

Castle Yankee was the code name given to one of the tests in the Operation Castle series of American tests of thermonuclear bombs. It was originally intended as a test of a TX-16/EC-16 Jughead bomb, but the design became obsolete after the Castle Bravo test was successful. The test device was replaced with a TX-24/EC-24 Runt II bomb which was detonated on May 5, 1954, at Bikini Atoll. It released energy equivalent to 13.5 megatons of TNT, the second-largest yield ever in a U.S. fusion weapon test.

Castle Romeo was the code name given to one of the tests in the Operation Castle series of U.S. nuclear tests. It was the first test of the TX-17 thermonuclear weapon, the first deployed thermonuclear bomb.

Castle Union was the code name given to one of the tests in the Operation Castle series of United States nuclear tests. It was the first test of the TX-14 thermonuclear weapon, one of the first deployed U.S. thermonuclear bombs.
A thermonuclear weapon, fusion weapon or hydrogen bomb (H bomb) is a second-generation nuclear weapon design. Its greater sophistication affords it vastly greater destructive power than first-generation nuclear bombs, a more compact size, a lower mass, or a combination of these benefits. Characteristics of nuclear fusion reactions make possible the use of non-fissile depleted uranium as the weapon's main fuel, thus allowing more efficient use of scarce fissile material such as uranium-235 or plutonium-239. The first full-scale thermonuclear test was carried out by the United States in 1952, and the concept has since been employed by most of the world's nuclear powers in the design of their weapons.
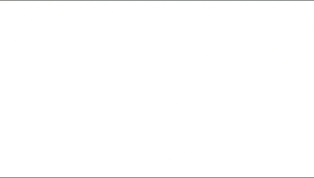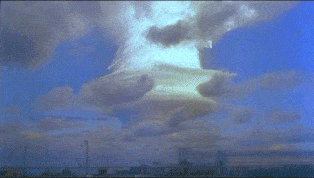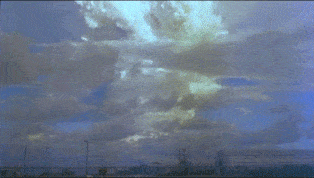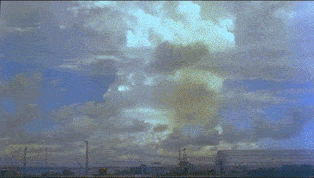
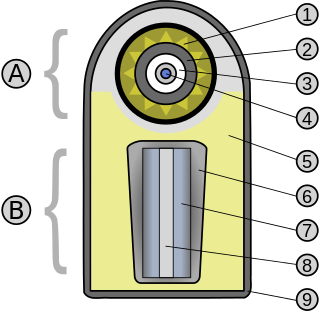
The Teller–Ulam design is a technical concept behind modern thermonuclear weapons, also known as hydrogen bombs. The design – the details of which are military secrets and known to only a handful of major nations – is believed to be used in virtually all modern nuclear weapons that make up the arsenals of the major nuclear powers.
The B46 nuclear bomb was an American high-yield thermonuclear bomb which was designed and tested in the late 1950s. It was never deployed. Though originally intended to be a production design, the B46 ended up being only an intermediate prototype of the B-53 and was test fired several times. These prototypes were known as TX-46 units (Test/Experimental).

The Mark 24 nuclear bomb was an American thermonuclear bomb design, based on the third American thermonuclear bomb test, Castle Yankee. The Mark 24 bomb was tied as the largest weight and size nuclear bomb ever deployed by the United States, with the same size and weight as the Mark 17 nuclear bomb which used a very similar design concept but unenriched lithium.

The Mark 14 nuclear bomb was a 1950s strategic thermonuclear weapon, the first deployed solid-fuel hydrogen bomb. It was an experimental design, and only five units were produced in early 1954. It was tested in April 1954 during the Castle Union nuclear test and had a yield of 6.9 Mt. The bomb is often listed as the TX-14 or EC-14. It has also been referred to as the "Alarm Clock" device though it has nothing to do with the design by the same name proposed earlier by Edward Teller and known as the Sloika in the Soviet Union.
RACER IV was a component of some of the first hydrogen bombs made by the United States during the 1950s. The RACER was developed in 1953 at Los Alamos National Laboratory.

The Mark 17 and Mark 24 were the first mass-produced hydrogen bombs deployed by the United States. The two differed in their "primary" stages. They entered service in 1954, and were phased out by 1957.

The Mark 21 nuclear bomb was a United States thermonuclear gravity bomb first produced in 1955. It was based on the TX 21 "Shrimp" prototype that had been detonated during the Castle Bravo test in March 1954. While most of the Operation Castle tests were intended to evaluate weapons intended for immediate stockpile, or which were already available for use as part of the Emergency Capability Program, Castle Bravo was intended to test a design which would drastically reduce the size and costs of the first generation of air-droppable atomic weapons.
The Mark 22 nuclear bomb (Mk-22) was the first thermonuclear device test by the University of California Radiation Lab (UCRL). The test was part of the Koon shot of Operation Castle. The Mk-22 failed to achieve anything like its intended yield due to premature heating of the secondary from exposure to neutrons. As the other UCRL test planned for the Castle series, the liquid-fueled "Ramrod" device had the same basic design flaw, that test was canceled. Within a month of the bomb's failure, the Mk-22 was terminated because the United States Atomic Energy Commission realized there was nothing that could be done to salvage the design.

The Mk 36 was a heavy high-yield nuclear bomb developed by the United States during the 1950s. It was a thermonuclear, using a multi-stage fusion secondary system to generate yields up to about 10 megatons TNT equivalent.
References
- 1 2 Allbombs.html at the Nuclear Weapon Archive, accessed 2 October 2006
- ↑ Historical United States Nuclear Weapons at Globalsecurity.org (see also Globalsecurity.org), accessed 2 October 2006
- Hansen, Chuck, "Swords of Armageddon: U.S. Nuclear Weapons Development since 1945" (CD-ROM & download available). PDF-2.67 Mb. 2,600 pages, Sunnyvale, California, Chucklea Publications, 1995, 2007. ISBN 978-0-9791915-0-3 (2nd Ed.)
- O'Keefe, Bernard J. "Nuclear Hostages," Boston, Houghton Mifflin Company, 1983, ISBN 0-395-34072-1.