Related Research Articles

An analog computer or analogue computer is a type of computer that uses the continuous variation aspect of physical phenomena such as electrical, mechanical, or hydraulic quantities to model the problem being solved. In contrast, digital computers represent varying quantities symbolically and by discrete values of both time and amplitude.

Nokia Bell Labs, originally named Bell Telephone Laboratories (1925–1984), then AT&T Bell Laboratories (1984–1996) and Bell Labs Innovations (1996–2007), is an American industrial research and scientific development company owned by Finnish company Nokia. With headquarters located in Murray Hill, New Jersey, the company operates several laboratories in the United States and around the world.

Digital electronics is a field of electronics involving the study of digital signals and the engineering of devices that use or produce them. This is in contrast to analog electronics and analog signals.

Automatic test equipment or automated test equipment (ATE) is any apparatus that performs tests on a device, known as the device under test (DUT), equipment under test (EUT) or unit under test (UUT), using automation to quickly perform measurements and evaluate the test results. An ATE can be a simple computer-controlled digital multimeter, or a complicated system containing dozens of complex test instruments capable of automatically testing and diagnosing faults in sophisticated electronic packaged parts or on wafer testing, including system on chips and integrated circuits.

A fire-control system (FCS) is a number of components working together, usually a gun data computer, a director, and radar, which is designed to assist a ranged weapon system to target, track, and hit a target. It performs the same task as a human gunner firing a weapon, but attempts to do so faster and more accurately.

Elliott Brothers (London) Ltd was an early computer company of the 1950s–60s in the United Kingdom. It traced its descent from a firm of instrument makers founded by William Elliott in London around 1804. The research laboratories were originally set up in 1946 at Borehamwood and the first Elliott 152 computer appeared in 1950.

The SCR-584 was an automatic-tracking microwave radar developed by the MIT Radiation Laboratory during World War II. It was one of the most advanced ground-based radars of its era, and became one of the primary gun laying radars used worldwide well into the 1950s. A trailer-mounted mobile version was the SCR-784.

The Mark 4 nuclear bomb was an American implosion-type nuclear bomb based on the earlier Mark 3 Fat Man design, used in the Trinity test and the bombing of Nagasaki. With the Mark 3 needing each individual component to be hand-assembled by only highly trained technicians under closely controlled conditions, the purpose of the Mark 4 was to produce an atomic weapon as a practical piece of ordnance. The Mark 4 Mod 0 entered the stockpile starting March 19, 1949 and was in use until 1953. With over 500 units procured, the Mark 4 was the first mass-produced nuclear weapon.

The W58 was an American thermonuclear warhead used on the Polaris A-3 submarine-launched ballistic missile. Three W58 warheads were fitted as multiple warheads on each Polaris A-3 missile.

High Angle Control System (HACS) was a British anti-aircraft fire-control system employed by the Royal Navy from 1931 and used widely during World War II. HACS calculated the necessary deflection required to place an explosive shell in the location of a target flying at a known height, bearing and speed.

Rangekeepers were electromechanical fire control computers used primarily during the early part of the 20th century. They were sophisticated analog computers whose development reached its zenith following World War II, specifically the Computer Mk 47 in the Mk 68 Gun Fire Control system. During World War II, rangekeepers directed gunfire on land, sea, and in the air. While rangekeepers were widely deployed, the most sophisticated rangekeepers were mounted on warships to direct the fire of long-range guns.
In naval gunnery, when long-range guns became available, an enemy ship would move some distance after the shells were fired. It became necessary to figure out where the enemy ship, the target, was going to be when the shells arrived. The process of keeping track of where the ship was likely to be was called rangekeeping, because the distance to the target—the range—was a very important factor in aiming the guns accurately. As time passed, train, the direction to the target, also became part of rangekeeping, but tradition kept the term alive.

A computer is a machine that can be programmed to carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as programs. These programs enable computers to perform a wide range of tasks. A computer system is a nominally complete computer that includes the hardware, operating system, and peripheral equipment needed and used for full operation. This term may also refer to a group of computers that are linked and function together, such as a computer network or computer cluster.
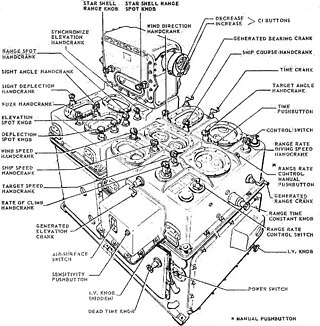
The Mark 1, and later the Mark 1A, Fire Control Computer was a component of the Mark 37 Gun Fire Control System deployed by the United States Navy during World War II and up to 1991 and possibly later. It was originally developed by Hannibal C. Ford of the Ford Instrument Company. and William Newell. It was used on a variety of ships, ranging from destroyers to battleships. The Mark 37 system used tachymetric target motion prediction to compute a fire control solution. It contained a target simulator which was updated by further target tracking until it matched.

The Iowa-class battleships are the most heavily armed gunships the United States Navy has ever put to sea, due to the continual development of their onboard weaponry. The first Iowa-class ship was laid down in June 1940; in their World War II configuration, each of the Iowa-class battleships had a main battery of 16-inch (406 mm) guns that could hit targets nearly 20 statute miles (32 km) away with a variety of artillery shells designed for anti-ship or bombardment work. The secondary battery of 5-inch (127 mm) guns could hit targets nearly 9 statute miles (14 km) away with solid projectiles or proximity fuzed shells, and was effective in an anti-aircraft role as well. Each of the four battleships carried a wide array of 20 mm and 40 mm anti-aircraft guns for defense against enemy aircraft.

A director, also called an auxiliary predictor, is a mechanical or electronic computer that continuously calculates trigonometric firing solutions for use against a moving target, and transmits targeting data to direct the weapon firing crew.

The Mark 92 Fire Control System is a US-built medium-range anti-aircraft missile and gun fire control system. It was developed for the FFG-7 Oliver Hazard Perry class guided missile frigates. The system is a licensed USN version of the Thales Nederland WM-25 fire control system. The Mark 92 fire control system was approved for service use in 1975. Introduction to the fleet and follow-on test and evaluation began in 1978.

Ship gun fire-control systems (GFCS) are analogue fire-control systems that were used aboard naval warships prior to modern electronic computerized systems, to control targeting of guns against surface ships, aircraft, and shore targets, with either optical or radar sighting. Most US ships that are destroyers or larger employed gun fire-control systems for 5-inch (127 mm) and larger guns, up to battleships, such as Iowa class.

The Torpedo Data Computer (TDC) was an early electromechanical analog computer used for torpedo fire-control on American submarines during World War II. Britain, Germany, and Japan also developed automated torpedo fire control equipment, but none were as advanced as the US Navy's TDC, as it was able to automatically track the target rather than simply offering an instantaneous firing solution. This unique capability of the TDC set the standard for submarine torpedo fire control during World War II.
The Vickers Main Battle Tank Mk. 4 later known as the Vickers Valiant was a main battle tank developed as a private venture by British company Vickers for export. Its development began in 1976 and ended in January 1984. Although the Valiant did not enter production, its development provided valuable experience in the production of an aluminium-hulled, Chobham-armoured tank in the 40 tonnes weight range. A further development of its turret was later used for the Vickers Mk. 7 MBT.
References
- W.H.C. Higgins; B.D. Holbrook; J.W. Emling (July–September 1982). "Electrical Computers for Fire Control" . Annals of the History of Computing. IEEE. 4 (3): 218–244. doi:10.1109/MAHC.1982.10026. S2CID 18464927.