Related Research Articles

Appendicitis is inflammation of the appendix. Symptoms commonly include right lower abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and decreased appetite. However, approximately 40% of people do not have these typical symptoms. Severe complications of a ruptured appendix include widespread, painful inflammation of the inner lining of the abdominal wall and sepsis.

Peritonitis is inflammation of the localized or generalized peritoneum, the lining of the inner wall of the abdomen and cover of the abdominal organs. Symptoms may include severe pain, swelling of the abdomen, fever, or weight loss. One part or the entire abdomen may be tender. Complications may include shock and acute respiratory distress syndrome.

An appendectomy, also termed appendicectomy, is a surgical operation in which the vermiform appendix is removed. Appendectomy is normally performed as an urgent or emergency procedure to treat complicated acute appendicitis.

McBurney's point is the name given to the point over the right side of the abdomen that is one-third of the distance from the anterior superior iliac spine to the umbilicus (navel). This is near the most common location of the appendix.

Abdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom associated with both non-serious and serious medical issues.
Rovsing's sign, named after the Danish surgeon Niels Thorkild Rovsing (1862–1927), is a sign of appendicitis. If palpation of the left lower quadrant of a person's abdomen increases the pain felt in the right lower quadrant, the patient is said to have a positive Rovsing's sign and may have appendicitis. The phenomenon was first described by Swedish surgeon Emil Samuel Perman (1856-1945) writing in the journal Hygiea in 1904.
Blumberg's sign is a clinical sign in which there is pain upon removal of pressure rather than application of pressure to the abdomen. It is indicative of peritonitis. It was named after German surgeon Jacob Moritz Blumberg.
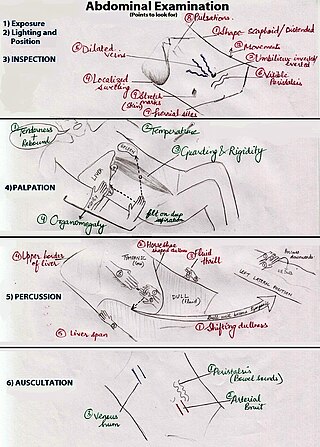
An abdominal examination is a portion of the physical examination which a physician or nurse uses to clinically observe the abdomen of a patient for signs of disease. The physical examination typically occurs after a thorough medical history is taken, that is, after the physician asks the patient the course of their symptoms. The abdominal examination is conventionally split into four different stages: first, inspection of the patient and the visible characteristics of their abdomen. Auscultation (listening) of the abdomen with a stethoscope. Palpation of the patient's abdomen. Finally, percussion (tapping) of the patient's abdomen and abdominal organs. Depending on the need to test for specific diseases such as ascites, special tests may be performed as a part of the physical examination. An abdominal examination may be performed because the physician suspects a disease of the organs inside the abdominal cavity, or simply as a part of a complete physical examination for other conditions. In a complete physical examination, the abdominal exam classically follows the respiratory examination and cardiovascular examination.
In medicine, Murphy's sign is a maneuver during a physical examination as part of the abdominal examination. It is useful for differentiating pain in the right upper quadrant. Typically, it is positive in cholecystitis, but negative in choledocholithiasis, pyelonephritis, and ascending cholangitis.

The psoas sign, also known as Cope's sign or Obraztsova's sign, is a medical sign that indicates irritation to the iliopsoas group of hip flexors in the abdomen, and consequently indicates that the inflamed appendix is retrocaecal in orientation.

Costovertebral angle (CVA) tenderness is pain that results from touching the region inside of the costovertebral angle. The CVA is formed by the 12th rib and the spine. Assessing for CVA tenderness is part of the abdominal exam, and CVA tenderness often indicates kidney pathology.
Valentino's syndrome is pain presenting in the right lower quadrant of the abdomen caused by a duodenal ulcer with perforation through the retroperitoneum.

The obturator sign, also called Cope's obturator test, is an indicator of irritation to the obturator internus muscle.
An acute abdomen refers to a sudden, severe abdominal pain. It is in many cases a medical emergency, requiring urgent and specific diagnosis. Several causes need immediate surgical treatment.

Epiploic appendagitis (EA) is an uncommon, benign, self-limiting inflammatory process of the epiploic appendices. Other, older terms for the process include appendicitis epiploica and appendagitis, but these terms are used less now in order to avoid confusion with acute appendicitis.
The Alvarado score is a clinical scoring system used in the diagnosis of appendicitis. Alvarado scoring has largely been superseded as a clinical prediction tool by the Appendicitis Inflammatory Response score.
In medicine, Carnett's sign is a finding on clinical examination in which (acute) abdominal pain remains unchanged or increases when the muscles of the abdominal wall are tensed. For this part of the abdominal examination, the patient can be asked to lift the head and shoulders from the examination table to tense the abdominal muscles. An alternative is to ask the patient to raise both legs with straight knees.
Lépine's sign is one of the medical signs of gallbladder disease. It is positive when effleurage with crooked third finger at the point of the gallbladder projection to anterior abdominal wall elicits pain. It is not to be confused with the following:
Heel tap sign, also called heel-jar or jar tenderness, is a clinical sign to identify appendicitis. It is found in patients with localized peritonitis. With the patient supine the right heel is elevated by 10-20 degrees is hit firmly with palm of the examiner's hand.
Intra-abdominal infection is a group of infections that occur within the abdominal cavity. They vary from appendicitis to fecal peritonitis. Risk of death despite treatment is often high.
References
- ↑ Acute appendicitis on Medscape
- ↑ Richard F. LeBlond, Richard L. DeGowin, Elmer Louis DeGowin, Jim Abel. DeGowin's Diagnostic Examination, page 481. McGraw Hill Professional, 2008. ISBN 978-0-07-147898-4. Google books
- ↑ Markle, George B. (1973). "A simple test for intraperitoneal inflammation". The American Journal of Surgery. 125 (6): 721–722. doi:10.1016/0002-9610(73)90171-2. PMID 4710195.