
Plantago is a genus of about 200 species of flowering plants in the family Plantaginaceae, commonly called plantains or fleaworts. The common name plantain is shared with the unrelated cooking plantain. Most are herbaceous plants, though a few are subshrubs growing to 60 centimetres tall.

Cunninghamia is a genus of one or two living species of evergreen coniferous trees in the cypress family Cupressaceae. They are native to China, northern Vietnam and Laos, and perhaps also Cambodia. They may reach 50 m (160 ft) in height. In vernacular use, it is most often known as Cunninghamia, but is also sometimes called "China-fir". The genus name Cunninghamia honours Dr. James Cunningham, a British doctor who introduced this species into cultivation in 1702 and botanist Allan Cunningham.

A midge is any small fly, including species in several families of non-mosquito nematoceran Diptera. Midges are found on practically every land area outside permanently arid deserts and the frigid zones. Some midges, such as many Phlebotominae and Simuliidae, are vectors of various diseases. Many others play useful roles as prey for insectivores, such as various frogs and swallows. Others are important as detritivores, and form part of various nutrient cycles. The habits of midges vary greatly from species to species, though within any particular family, midges commonly have similar ecological roles.

Plantago lanceolata is a species of flowering plant in the plantain family Plantaginaceae. It is known by the common names ribwort plantain, narrowleaf plantain, English plantain, ribleaf, lamb's tongue, and buckhorn. It is a common weed on cultivated or disturbed land.

Psychodidae, also called drain flies, sink flies, filter flies, sewer flies, or sewer gnats, is a family of true flies. Some genera have short, hairy bodies and wings, giving them a "furry" moth-like appearance, hence one of their common names, moth flies. Members of the sub-family Phlebotominae, which are hematophagous, may be called sand flies in some countries, although this term is also used for other unrelated flies.

Tasmannia lanceolata, commonly known as pepper tree, native pepper, mountain pepper or mountain pepperbush, is a species of flowering plant in the family Winteraceae, and is endemic to south-eastern Australia. It is a dioecious bushy shrub to small tree with lance-shaped or narrowly ellipic leaves, male and female flowers on separate plants, the flowers with 3 to 9 petals, and the fruit a deep maroon to glossy black berry.

The Phlebotominae are a subfamily of the family Psychodidae. In several countries, their common name is sandfly, but that name is also applied to other flies. The Phlebotominae include many genera of blood-feeding (hematophagous) flies, including the primary vectors of leishmaniasis, bartonellosis and pappataci fever.

Pithecellobium dulce, commonly known as Manila tamarind, Madras thorn, monkeypod tree or camachile, is a species of flowering plant in the pea family, Fabaceae, that is native to the Pacific Coast and adjacent highlands of Mexico, Central America, and northern South America. It is also sometimes known as monkeypod, but that name is also used for several other plants, including Samanea saman. It is an introduced species and extensively naturalized in the Caribbean and Florida, as well as the Philippines and Guam via the Manila galleons. It has also been introduced to Cambodia, Thailand and South Asia, It is considered an invasive species in Hawaii.

Cuphea viscosissima, also known as blue waxweed, clammy cuphea or (ambiguously) as "tarweed", is an herbaceous plant in the loosestrife family. It native to the eastern United States, where it is most often found in open, rocky calcareous areas. It is the most common and widespread Cuphea in the U.S.

The Psychodinae are the nominate subfamily of moth flies (Psychodidae), also known as drain flies. Like most of their relatives, they are usually found in damp habitats; some occur in caves. The small larvae are aquatic or semi-terrestrial; the adults are winged and capable of flight. Psychodinae are found worldwide, including some subantarctic islands.

Cunninghamia konishii is an endangered species of tree in the cypress family, Cupressaceae. It is native to southeast China (Fujian), Taiwan, Laos and Vietnam.

Cunninghamia lanceolata is a species of tree in the cypress family, Cupressaceae. It is native to south-central and southeast China. Ornamentally C. lanceolata is commonly planted as a specimen tree in temperate zones.

Arnica lanceolata is a North American species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae, known by the common name clasping arnica or lanceleaf arnica. It has a disjunct (discontinuous) distribution in western North America and northeastern North America.

Clogmia albipunctata is a species of drain fly, a member of the family Psychodidae commonly known as the bathroom moth midge, bathroom moth fly or drain fly.
Boreofairchildia nearctica, the sugarfoot moth-fly, is a species of nematoceran flies in the family Psychodidae. It is endemic to the United States.
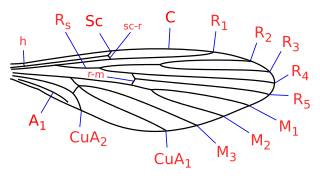
Nemopalpus is a genus of moth fly in the family Psychodidae, in the subfamily Bruchomyiinae. Recently (2018) a number of similar species have been transferred to the genera: Alexanderia, Boreofairchildia, Laurenceomyia and Notofairchildia. In Macquart's original publication, the genus name was spelled both as Nemopalpus and Nemapalpus, but Macquart corrected the error in 1839.
Pericoma is a genus of moth flies in the family Psychodidae. There are at least 190 described species in Pericoma.
Maruina is a genus of moth flies in the family Psychodidae. There are at least 30 described species in Maruina. marui, diminutive for a fly.

Psychoda alternata is a species of moth fly in the family Psychodidae, commonly known as the trickling filter fly or drain fly. The larva is semiaquatic and lives in the gelatinous ooze associated with leaks of sewage effluent, drains, and in trickling filter systems.

The subfamily Bruchomyiinae contains genera of moth flies in the order Diptera, was originally described by the American entomologist Charles Paul Alexander.
















