Related Research Articles

The Mohicans are an Eastern Algonquian Native American tribe that historically spoke an Algonquian language. As part of the Eastern Algonquian family of tribes, they are related to the neighboring Lenape, whose indigenous territory was to the south as far as the Atlantic coast. The Mohican lived in the upper tidal Hudson River Valley, including the confluence of the Mohawk River and into western New England centered on the upper Housatonic River watershed. After 1680, due to conflicts with the powerful Mohawk to the west during the Beaver Wars, many were driven southeastward across the present-day Massachusetts western border and the Taconic Mountains to Berkshire County around Stockbridge, Massachusetts.

The Powhatan people may refer to any of the Indigenous Algonquian people that are traditionally from eastern Virginia. All of the Powhatan groups descend from the Powhatan Confederacy. In some instances, The Powhatan may refer to one of the leaders of the people. This is most commonly the case in historical records from English colonial accounts. The Powhatans have also been known as Virginia Algonquians, as the Powhatan language is an eastern-Algonquian language, also known as Virginia Algonquian. It is estimated that there were about 14,000–21,000 Powhatan people in eastern Virginia when English colonists established Jamestown in 1607.

The Susquehannock, also known as the Conestoga, were an Iroquoian people who lived in the Susquehanna River watershed in what is now Pennsylvania. Their name means “people of the muddy river.”

Kent Island is the largest island in the Chesapeake Bay and a historic place in Maryland. To the east, a narrow channel known as the Kent Narrows barely separates the island from the Delmarva Peninsula, and on the other side, the island is separated from Sandy Point, an area near Annapolis, by roughly four miles (6.4 km) of water. At only four miles wide, the main waterway of the bay is at its narrowest at this point and is spanned here by the Chesapeake Bay Bridge. The Chester River runs to the north of the island and empties into the Chesapeake Bay at Kent Island's Love Point. To the south of the island lies Eastern Bay. The United States Census Bureau reports that the island has 31.62 square miles (81.90 km2) of land area.

Maryland Route 8 is a state highway in the U.S. state of Maryland. Known for most of its length as Romancoke Road, the state highway runs 8.37 miles (13.47 km) from Romancoke Pier in Romancoke north to MD 18 in Stevensville. MD 8 is the main north–south highway of Kent Island in western Queen Anne's County. The state highway is also the first highway encountered on U.S. Route 50 /US 301 east of the Chesapeake Bay Bridge. South of Matapeake, MD 8 is paralleled by the Kent Island South Trail.
The English word squaw is an ethnic and sexual slur, historically used for Indigenous North American women. Contemporary use of the term, especially by non-Natives, is considered derogatory, misogynist, and racist.

The Piscataway Indian Nation, also called Piscatawa, is a state-recognized tribe in Maryland that is descended from the historic Piscataway people. At the time of European encounter, the Piscataway was one of the most populous and powerful Native polities of the Chesapeake Bay region, with a territory on the north side of the Potomac River. By the early seventeenth century, the Piscataway had come to exercise hegemony over other Algonquian-speaking Native American groups on the north bank of the river. The Piscataway nation declined dramatically before the nineteenth century, under the influence of colonization, infectious disease, and intertribal and colonial warfare.

The Montaukett ("Metoac"), more commonly known as Montauk are an Algonquian-speaking Native American people from the eastern and central sections of Long Island, New York.

The Piscataway or Piscatawa, are Native Americans. They spoke Algonquian Piscataway, a dialect of Nanticoke. One of their neighboring tribes, with whom they merged after a massive decline of population following two centuries of interactions with European settlers, called them the Conoy.
Matapeake is an unincorporated community located south of Stevensville on Kent Island, Maryland, United States.

Matapeake State Park is a public recreation area on Chesapeake Bay occupying the site of a former ferry landing in Matapeake, Kent Island, Maryland. The landing served the state-owned Chesapeake Bay Ferry System before the Chesapeake Bay Bridge opened. The park is leased and managed by Queen Anne's County.

Christ Church refers to both an Episcopal parish currently located in Matapeake, Maryland and the historic church building located in the Stevensville Historic District in Stevensville, Maryland, which the parish occupied from 1880 to 1995, and that is now a Lutheran church. Christ Church Parish was one of the original 30 Anglican parishes in the Province of Maryland.
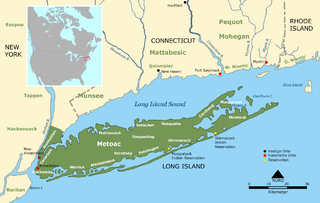
Metoac is an erroneous term used by some to group together the Munsee-speaking Lenape (west), Quiripi-speaking Unquachog (center) and Pequot-speaking Montaukett (east) American Indians on what is now Long Island in New York state. The term was invented by amateur anthropologist and U.S. Congressman Silas Wood in the mistaken belief that the various native settlements on the island each comprised distinct tribes.
Kent Fort was a fort and settlement located near 38.84°N 76.37°W on southern Kent Island in colonial Virginia and later Maryland, and was the first English settlement within the boundaries of present-day Maryland and the fourth oldest permanent English settlement in the United States, after Jamestown, Virginia (1607), Hampton, Virginia (1609–10), and Plymouth, Massachusetts (1620). The fort was established by William Claiborne in 1631, and was a central part of early Kent Island. Claiborne made Kent Fort into a trading post with the Matapeake people, the Indigenous tribe of the island. Beads imported from Italy were given to the Matapeake people in exchange for furs. By the end of the century, however, activity had shifted northward to the port town of Broad Creek.
The Nacotchtank were an indigenous Algonquian people who lived in the area of what is now Washington, D.C., during the 17th century. The Nacotchtank village was within the modern borders of the District of Columbia along the intersection of the Potomac and the Anacostia river.
The Accokeek were a group of Native Americans living in Southern Maryland at the time of English colonization. They lived along the Potomac River in present-day Prince George's County, Maryland. They were an Algonquian-language tribe and were related to the Piscataway, another Algonquian-language tribe.
The history of Native Americans in Baltimore and what is now Baltimore dates back at least 12,000 years. As of 2014, Baltimore is home to a small Native American population, centered in East Baltimore. The majority of Native Americans now living in Baltimore belong to the Lumbee, Piscataway, and Cherokee nations. The Piscataway people are indigenous to Southern Maryland, living in the area for centuries prior to European colonization, and are recognized as a tribe by the state of Maryland. The Lumbee and Cherokee are indigenous to North Carolina and neighboring states of the Southeastern United States. Many of the Lumbee and Cherokee migrated to Baltimore during the mid-20th century along with other migrants from the Southern United States, such as African-Americans and white Appalachians.
The Ozinie, also known as the Wicomiss, were a group of Native Americans living near modern-day Rock Hall, in Kent County, Maryland. They were hunter-gatherers and fished.
References
- ↑ "Waterman talks about history of Kent Island". The Star Democrat . Retrieved 2023-08-13.
- ↑ Scharf, John Thomas (1879). History of Maryland from the Earliest Period to the Present Day. Baltimore, MD: John B. Piet. pp. 137.
matapeake.
- ↑ "Kent Island: Third Oldest US Settlement - 2002-02-19". Voice of America . Retrieved 2023-08-13.
- ↑ "People, Tribes, & Bands". Maryland State Archives . Retrieved 2023-08-13.
- ↑ "History of Kent Island". Kent Island Heritage Society. Retrieved 2023-08-13.