Related Research Articles
The Southern Cross Cable is a trans-Pacific network of telecommunications cables commissioned in 2000. The network is operated by the Bermuda-registered company Southern Cross Cables Limited. The network has 28,900 km (18,000 mi) of submarine and 1,600 km (990 mi) of terrestrial fiber optic cables, all which operate in a triple-ring configuration. Initially, each cable had a bandwidth capacity of 120 gigabit/s. Southern Cross offers capacity services from 100M/STM-1 to 100 Gbit/s OTU-4, including 1G, 10G and 40G Ethernet Private Line services.

Hibernia Networks, alternately known as Hibernia Atlantic, was a privately held, US-owned provider of telecommunication services. It operated global network routes on self-healing rings in North America, Europe and Asia including submarine communications cable systems in the North Atlantic Ocean which connected Canada, the United States, the Republic of Ireland, the United Kingdom and mainland Europe. Hibernia managed cable landing stations in Dublin, Republic of Ireland; Coleraine, Northern Ireland; Southport, England; Halifax, Canada; Lynn, Massachusetts, United States.
SEA-ME-WE3 or South-East Asia - Middle East - Western Europe 3 is an optical submarine telecommunications cable linking those regions and is the longest in the world. Completed in late 2000, it is led by France Telecom and China Telecom, and is administered by Singtel, a telecommunications operator owned by the Government of Singapore. The Consortium is formed by 92 other investors from the telecom industry. It was commissioned in March 2000.

South East Asia–Middle East–Western Europe 4 is an optical fibre submarine communications cable system that carries telecommunications between Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand, Bangladesh, India, Sri Lanka, Pakistan, United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, Egypt, Italy, Tunisia, Algeria and France. It is intended to be a complement to, rather than a replacement for, the SEA-ME-WE 3 cable.
APCN 2 or Asia-Pacific Cable Network 2 is a submarine telecommunications cable linking several countries in the Asia-Pacific region.

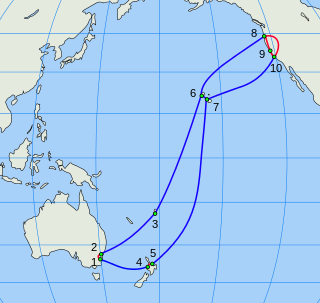
The Australia–Japan Cable, or AJC, is a 12,700 km submarine telecommunications cable system linking Australia and Japan via Guam that became operational in 2001. It had an original design capacity of 640 Gbit/s, but was initially equipped to use only 80 Gbit/s of this capacity. In April 2008 a capacity upgrade was completed, bringing equipped capacity to 240 Gbit/s. Design capacity was also increased to 1000 Gbit/s. Further upgrades will increase equipped capacity to meet increasing demand.
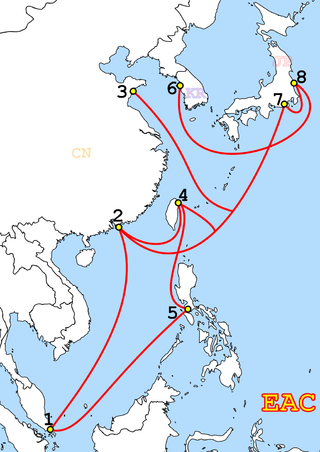
EAC-C2C is a submarine telecommunications cable system interconnecting several countries in Asia, the Pacific, and the United States. It is a merger of the former EAC and C2C cable systems. The merger occurred in 2007 by Asia Netcom, and the cable system is now owned/operated by Pacnet. Pacnet was acquired by the Australian telecommunications company Telstra in 2015.
APCN or Asia-Pacific Cable Network is a submarine telecommunications cable system linking nine Asian countries.
G-P is a submarine telecommunications cable system in the North Pacific Ocean linking the two named territories.

LEV is a submarine telecommunications cable system in the Mediterranean Sea linking Italy, Cyprus and Israel.
TIS (Thailand-Indonesia-Singapore) is a submarine telecommunications cable system in the South China Sea linking Thailand, Singapore, and Indonesia
SAm-1 is an optical submarine communications cable. It started operations in 2000, connecting the United States, Puerto Rico, Brazil, Argentina, Chile, Peru and Guatemala. In 2007, SAm-1 was extended to reach Ecuador and Colombia.
TGN Atlantic (TGN-A) previously VSNL Transatlantic and TGN Transatlantic, is a submarine telecommunications cable system transiting the Atlantic Ocean. The cable has been in operation since 2001.
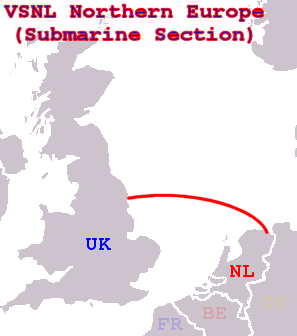
VSNL Northern Europe is a telecommunications cable system with both submarine and terrestrial parts, connecting England and the Netherlands.
JASURAUS was a 5.332 Gbit/s, 2,800 km optical submarine telecommunications cable that connected Port Hedland, Australia, to Jakarta, Indonesia, with a further interconnection to the APCN and which was decommissioned in 2012.
St. Maarten Puerto Rico-1 (SMPR-1) is an 8-pair non-repeated submarine telecommunications cable system of 375 km which uses wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) technology to link St. Maarten and Puerto Rico.
NorSea Com-1, now called Tampnet, is a submarine telecommunications cable system in the North Sea linking the UK and Norway, and connecting five off-shore platforms.

Greenland Connect is a submarine communications cable system that connects Canada, Greenland, and Iceland. The cable contains two fibre pairs specified for 128*10 Gbit/s wavelength each. Initial lit capacity is 1*10 Gbit/s for each fibre pair. Two additional 10 Gbit/s Wavelength were installed in the summer of 2010. The cable has cable landing points at:

PT Telekomunikasi Indonesia International or Telkom International, and commonly abbreviated as Telin, is an Indonesian carrier services and investment company and is a wholly owned subsidiary of Telkom Indonesia. It is an international telecommunication business serves as Telkom's business arms in managing and developing its business lines outside Indonesia.
References
- "Matrix Cable System Overview". Submarine Networks. 21 June 2011. Retrieved 1 May 2021.