EAC-C2C is a submarine telecommunications cable system interconnecting several countries in Asia, the Pacific, and the United States. It is a merger of the former EAC (East Asia Crossing) and C2C cable systems. [1] The merger occurred in 2007 by Asia Netcom, and the cable system is now owned/operated by Pacnet. [2] Pacnet was acquired by the Australian telecommunications company Telstra in 2015.
Contents

The EAC portion of the cable system includes:
- Changi, Singapore
- Tseung Kwan O, Hong Kong
- Qingdao, China (later extension)
- Bali, Taiwan
- Capepisa, The Philippines
- Taean, South Korea
- Shima, Japan
- Ajigaura, Hitachinaka, Ibaraki, Japan
Length: 19,500 kilometers
Capacity: 160 Gbit/s - upgradeable to 2.5 Tbit/s
Technology: DWDM (dense wavelength-division multiplex)
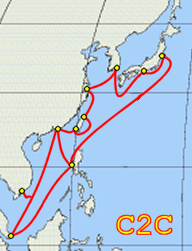
The C2C portion of the cable system comprises three rings:
- C2C North Ring
- C2C South Ring
The landing points on each ring are as follows:

