Fibre-optic Link Around the Globe (FLAG) is a 28,000-kilometre-long fibre optic mostly-submarine communications cable that connects the United Kingdom, Japan, India, and many places in between. The cable is operated by Global Cloud Xchange, a subsidiary of RCOM. The system runs from the eastern coast of North America to Japan. Its Europe–Asia segment was the fourth longest cable in the world in 2008.
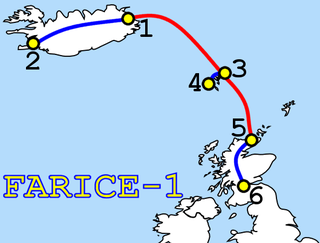
FARICE-1 is a submarine communications cable connecting Iceland, the Faroe Islands and Scotland. The cable has been in use since January 2004 and is 100% owned by the Icelandic state. The cable had an initial design capacity of 720 Gbit/s and is a two fibre pair design. The length of the cable is 1205 km for the direct route between Iceland and Scotland. The cable structure and repeaters were made by Pirelli and the terminal equipment was supplied by TYCO. In the year 2013 the terminal equipment was upgraded by Ciena bringing the total capacity of the submarine cable to 11 Tbit/s. The cable has service access points in Reykjavik and Keflavik Airport as well as in London Telehouse East. The company Farice ehf sells services over the FARICE-1 cable. FARICE-2 was never built. DANICE is the complementary submarine cable.
SEA-ME-WE3 or South-East Asia - Middle East - Western Europe 3 is an optical submarine telecommunications cable linking those regions and is the longest in the world. Completed in late 2000, it is led by France Telecom and China Telecom, and is administered by Singtel, a telecommunications operator owned by the Government of Singapore. The Consortium is formed by 92 other investors from the telecom industry. It was commissioned in March 2000.

South East Asia–Middle East–Western Europe 4 is an optical fibre submarine communications cable system that carries telecommunications between Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand, Bangladesh, India, Sri Lanka, Pakistan, United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, Egypt, Italy, Tunisia, Algeria and France. It is intended to be a complement to, rather than a replacement for, the SEA-ME-WE 3 cable.
APCN 2 or Asia-Pacific Cable Network 2 is a submarine telecommunications cable linking several countries in the Asia-Pacific region.

Yellow / AC-2 is a submarine telecommunications cable system linking the United States and the United Kingdom. The cable is wholly owned by CenturyLink in the US following its acquisition of Global Crossing. The original owners, which each owned two of the fibre pairs, gave this cable system different names, so it is known as both Yellow and AC-2. It has a capacity of 320 Gbit/s as of January 2007, upgradeable to 640 Gbit/s.
APCN or Asia-Pacific Cable Network is a submarine telecommunications cable system linking nine Asian countries.
Dumai-Malacca Cable System or DMCS is a submarine telecommunications cable system linking Indonesia and Malaysia across the Strait of Malacca
Japan-US is a submarine telecommunications cable system in the North Pacific Ocean linking the United States and Japan. It has landing points in:
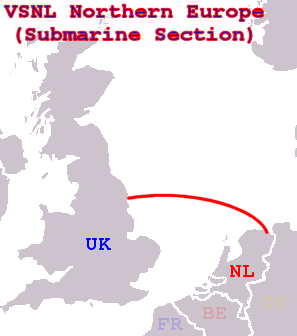
VSNL Northern Europe is a telecommunications cable system with both submarine and terrestrial parts, connecting England and the Netherlands.
JASURAUS was a 5.332 Gbit/s, 2,800 km optical submarine telecommunications cable that connected Port Hedland, Australia, to Jakarta, Indonesia, with a further interconnection to the APCN and which was decommissioned in 2012.
The ASEAN cable system was a submarine telecommunications cable system linking Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore, Thailand and the Philippines. It was completed in September 1983, but has since been decommissioned.

The 2000 AFF Championship, officially known as the 2000 Tiger Cup, was the third edition of the AFF Championship and was held in Thailand from 5 to 18 November 2000.
The Matrix Cable System (MCS) is a submarine telecommunications cable linking Indonesia and Singapore with a 2nd phase to Landing at Perth, Australia. It was constructed by Tyco.

Greenland Connect is a submarine communications cable system that connects Canada, Greenland, and Iceland. The cable contains two fibre pairs specified for 128*10 Gbit/s wavelength each. Initial lit capacity is 1*10 Gbit/s for each fibre pair. Two additional 10 Gbit/s Wavelength were installed in the summer of 2010. The cable has cable landing points at:
The Asia-America Gateway (AAG) is a 20,000-kilometre (12,000 mi) long submarine communications cable system, connecting South-East Asia with the mainland of the United States, across the Pacific Ocean via Guam and Hawaii.

Gulf Bridge International (GBI) is the Middle East's first privately owned submarine cable system linking the countries bordering the Persian Gulf on a self-healing ring to each other and onward to Europe, Africa and Asia. Gulf Bridge International (GBI), both owns and operates this submarine cable asset as a carrier's carrier as well as offering a full suite of wholesale transmission, IP capacity options, and Enterprise Services. Its main headquarters are located at the Qatar Science & Technology Park in Doha, Qatar.
Asia Pacific Gateway (APG) is a submarine communications cable system that connects Mainland China, Hong Kong, Japan, South Korea, Malaysia, Taiwan, Thailand, Vietnam and Singapore. It will be about 10,400 kilometres (6,500 mi) long. The capacity will be 54.8 terabits per second. The APG cable consortium includes Facebook, CAT Telecom, China Telecom, China Mobile International, China Unicom, Chunghwa Telecom, KT Corporation, LG Uplus, NTT Communications, StarHub, Global Transit, Viettel and VNPT. The APG cable system was scheduled to be ready for service in 2016.
South-East Asia Japan Cable System (SJC) is a pan-Asia submarine communications cable system connecting Japan, China, Hong Kong, the Philippines, Brunei, Thailand, Singapore and Indonesia in Asia. The SJC cable consists of 6 fiber pairs, with an initial design capacity of over 15 Tbit/s which can be upgraded to 23 Tbit/s. The SJC cable system utilizes the state-of-the-art advanced 40G SLTE and OADM Branching technologies. The SJC is operational on June 27, 2013.







