
A poppy is a flowering plant in the subfamily Papaveroideae of the family Papaveraceae. Poppies are herbaceous plants, often grown for their colourful flowers. One species of poppy, Papaver somniferum, is the source of the narcotic drug mixture opium which contains powerful medicinal alkaloids such as morphine and has been used since ancient times as an analgesic and narcotic medicinal and recreational drug. It also produces edible seeds. Following the trench warfare in the poppy fields of Flanders, Belgium during World War I, poppies have become a symbol of remembrance of soldiers who have died during wartime, especially in the UK, Canada, Australia, New Zealand and other Commonwealth realms.

Papaver is a genus of 70–100 species of frost-tolerant annuals, biennials, and perennials native to temperate and cold regions of Eurasia, Africa and North America. It is the type genus of the poppy family, Papaveraceae.

The Papaveraceae are an economically important family of about 42 genera and approximately 775 known species of flowering plants in the order Ranunculales, informally known as the poppy family. The family is cosmopolitan, occurring in temperate and subtropical climates, but almost unknown in the tropics. Most are herbaceous plants, but a few are shrubs and small trees. The family currently includes two groups that have been considered to be separate families: Fumariaceae and Pteridophyllaceae.

Meconopsis is a genus of flowering plants in the poppy family Papaveraceae. It was created by French botanist Viguier in 1814 for the species known by the common name Welsh poppy, which Carl Linnaeus had described as Papaver cambricum. The genus name means "poppy-like". Himalayan species discovered later were also placed in Meconopsis. In the 21st century, it was discovered that the Himalayan species were less closely related to the Welsh poppy, which has been restored to Papaver. All species now placed in Meconopsis are native to the Himalayas and surrounding regions. They have attractive, usually blue flowers.

Papaver cambricum, synonym Meconopsis cambrica, the Welsh poppy, is a perennial flowering plant in the poppy family Papaveraceae. It has yellow to orange flowers and is widely grown as a garden plant. It is a native of damp, rocky sites in upland areas of Western Europe from the British Isles to the Iberian Peninsula. It has been used since 2006 as the basis for the logo of the political party Plaid Cymru.

Meconopsis betonicifolia, the Himalayan blue poppy, is a species of flowering plant in the family Papaveraceae. It was first formally named for western science in 1912 by the British officer Lt. Col. Frederick Marshman Bailey.

Meconopsis simplicifolia is a perennial in the poppy family, sometimes monocarpic, with a taproot, rosette of leaves with bristly hairs, and blue or purple flowers on leafless stems, native to altitudes of 3,450–5,450 metres (11,300–17,900 ft) in central Nepal and southeastern Tibet.
Meconopsis villosa, the Himalayan woodland-poppy, is an ornamental poppy, which is native of Nepal. The species was placed in the genus Cathcartia erected by J.D. Hooker to honour J.F. Cathcart, an Indian civil servant and amateur botanist who collected and hired native artists to illustrate the flowers of the Himalayas. It was transferred to Meconopsis by George Taylor in 1934. In 2017, it was suggested that the genus Cathcartia should be revived, and this species again treated as Cathcartia villosa.

Wildlife diversity is a notable feature of Nepal. Because of the variance in climate, from tropical to arctic, Nepal has a large variety of plants and animals. Wildlife tourism is a major source of tourism in the country. There are some animal species which are unique to Nepal, such as the spiny babbler. Nepal is also host to many rhododendron species. Nepal has numerous national parks and reserves to protect its diverse fauna. Nepal is a biodiversity hot spot with ecoregions broadly comprising the mountainous ecoregion, the savanna and grasslands ecoregion of the terai (foothills), and the Rara Lake ecoregion.
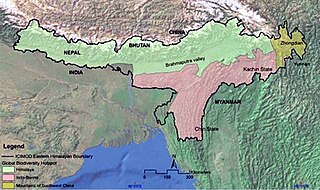
The Eastern Himalayas extend from eastern Nepal across Northeast India, Bhutan, the Tibet Autonomous Region to Yunnan in China and northern Myanmar. The climate of this region is influenced by the monsoon of South Asia from June to September. It is a biodiversity hotspot, with notable biocultural diversity.

Meconopsis grandis, the Himalayan blue poppy, is a species of flowering plant in the poppy family Papaveraceae, native to China (Yunnan), Bhutan, North East India and Nepal.

Meconopsis autumnalis, the Nepalese autumn poppy, is a yellow-flowered Himalayan poppy belonging to series Robustae, and is endemic to the Ganesh Himal range of central Nepal, where it was discovered in 2008 on a research expedition from the University of Aberdeen. In addition to several morphological features, the species is characterised by its late flowering period, which has more than likely resulted in a barrier to gene flow and subsequent evolutionary divergence from the closely related and sympatric species Meconopsis paniculata.

Meconopsis manasluensis is a red-flowered Himalayan poppy belonging to Meconopsis subg. Discogyne, which forms a natural grouping of 6 or 7 species within the genus all characterised by a stylar disc surmounting the ovary. As reflected by the species etymology, M. manasluensis is endemic to the vicinity of the Manaslu Himal of Gorkha district, central Nepal, where it grows at high elevation and so far remains known only from its type collection locality.

Clematis napaulensis, the Nepal clematis, is a species of flowering plant in the buttercup family Ranunculaceae. It is native to China and the Indian subcontinent, including Nepal, whence the specific epithet napaulensis.
Meconopsis bella is commonly known as the pretty blue poppy. M. bella is a species of the genus Meconopsis which is found from central Nepal to southeastern Tibet. It is a herbaceous flowering plant and is a part of the poppy family Papaveraceae. This plant is also referred to as Meconopsis bella prain, since it was aptly names by the botanist Prain.

Meconopsis horridula, the prickly blue poppy, is a flowering plant from the family Papaveraceae. It is an endangered species that grows in high altitudes. The height of the plant varies from 20 cm to 1m. It is a monocarpic, dicot plant.
Meconopsis lancifolia is a plant species in the genus Meconopsis, in the family Papaveraceae. M. lancifolia is monocarpic, meaning that it flowers only once before dying.

Meconopsis gakyidiana is a species of blue poppy native to Eastern Bhutan, Western Arunachal Pradesh of India and Southern Xizang of China. It is the national flower of Bhutan.
Cathcartia is a small genus of flowering plants in the family Papaveraceae, native to China, Nepal, the eastern Himalayas, and northern Myanmar. Chloroplast DNA evidence supports a split of Cathcartia from the blue poppy genus Meconopsis in an effort to resolve longstanding taxonomic difficulties in the Himalayan poppies.

Oreomecon is a genus in the poppy family Papaveraceae. It was established in 2022 for what was previously treated as Papaver sect. Meconella in order to ensure that the genus Papaver was monophyletic. As of June 2023, names in the genus Oreomecon had only been published for better known and phylogenetically understood species present in Europe, either as natives or aliens.
















