A Linux distribution is an operating system made from a software collection, which is based upon the Linux kernel and, often, a package management system. Linux users usually obtain their operating system by downloading one of the Linux distributions, which are available for a wide variety of systems ranging from embedded devices and personal computers to powerful supercomputers.

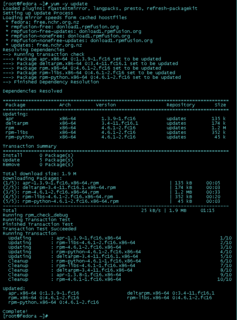
Advanced Package Tool, or APT, is a free-software user interface that works with core libraries to handle the installation and removal of software on Debian, Ubuntu, and related Linux distributions. APT simplifies the process of managing software on Unix-like computer systems by automating the retrieval, configuration and installation of software packages, either from precompiled files or by compiling source code.
The Yellowdog Updater, Modified (YUM) is a free and open-source command-line package-management utility for computers running the Linux operating system using the RPM Package Manager. Though YUM has a command-line interface, several other tools provide graphical user interfaces to YUM functionality.

Ubuntu is a free and open-source Linux distribution based on Debian. Ubuntu is officially released in three editions: Desktop, Server, and Core. Ubuntu is a popular operating system for cloud computing, with support for OpenStack.
libdvdcss is a free and open-source software library for accessing and unscrambling DVDs encrypted with the Content Scramble System (CSS). libdvdcss is part of the VideoLAN project and is used by VLC media player and other DVD player software packages, such as Ogle, xine-based players, and MPlayer.

LAMP is an archetypal model of web service stacks, named as an acronym of the names of its original four open-source components: the Linux operating system, the Apache HTTP Server, the MySQL relational database management system (RDBMS), and the PHP programming language. The LAMP components are largely interchangeable and not limited to the original selection. As a solution stack, LAMP is suitable for building dynamic web sites and web applications.
In 2006, a branding issue developed when Mike Connor, representing the Mozilla Corporation, requested that the Debian Project comply with Mozilla standards for use of the Thunderbird trademark when redistributing the Thunderbird software. At issue were modifications not approved by the Mozilla Foundation, when the name for the software remained the same.

gNewSense is a Linux distribution based on Debian, and developed with sponsorship from the Free Software Foundation. Its goal is user-friendliness, but with all proprietary and non-free software removed. The Free Software Foundation considers gNewSense to be composed entirely of free software.

Linux Mint is a community-driven Linux distribution based on Debian and Ubuntu that strives to be a "modern, elegant and comfortable operating system which is both powerful and easy to use." Linux Mint provides full out-of-the-box multimedia support by including some proprietary software and comes bundled with a variety of free and open-source applications.
In the 1950s and 1960s, computer operating software and compilers were delivered as a part of hardware purchases without separate fees. At the time, source code, the human-readable form of software, was generally distributed with the software providing the ability to fix bugs or add new functions. Universities were early adopters of computing technology. Many of the modifications developed by universities were openly shared, in keeping with the academic principles of sharing knowledge, and organizations sprung up to facilitate sharing. As large-scale operating systems matured, fewer organizations allowed modifications to the operating software, and eventually such operating systems were closed to modification. However, utilities and other added-function applications are still shared and new organizations have been formed to promote the sharing of software.

Fedora is a Linux distribution developed by the community-supported Fedora Project and sponsored by Red Hat. Fedora contains software distributed under various free and open-source licenses and aims to be on the leading edge of such technologies. Fedora is the upstream source of the commercial Red Hat Enterprise Linux distribution.

Free content, libre content, or free information, is any kind of functional work, work of art, or other creative content that meets the definition of a free cultural work.
Ubuntu Restricted Extras is a software package for the computer operating system Ubuntu that allows the user to install essential software which is not already included due to legal or copyright reasons.

A free-software license is a notice that grants the recipient of a piece of software extensive rights to modify and redistribute that software. These actions are usually prohibited by copyright law, but the rights-holder of a piece of software can remove these restrictions by accompanying the software with a software license which grants the recipient these rights. Software using such a license is free software as conferred by the copyright holder. Free-software licenses are applied to software in source code and also binary object-code form, as the copyright law recognizes both forms.
Proprietary software, also known as "closed-source software", is a non-free computer software for which the software's publisher or another person retains intellectual property rights—usually copyright of the source code, but sometimes patent rights.

Ubuntu Software Center or simply Software Center is a discontinued high-level graphical front end for the APT/dpkg package management system. It is free software written in Python, PyGTK/PyGObject based on GTK+.

Unity is a graphical shell for the GNOME desktop environment originally developed by Canonical Ltd. for its Ubuntu operating system. Unity debuted in the netbook edition of Ubuntu 10.10. It was initially designed to make more efficient use of space given the limited screen size of netbooks, including, for example, a vertical application switcher called the launcher, and a space-saving horizontal multipurpose top menu bar.
An app store is a type of digital distribution platform for computer software, often in a mobile context. Apps provide a specific set of functions which, by definition, do not include the running of the computer itself. Complex software designed for use on a personal computer, for example, may have a related app designed for use on a mobile device. Today apps are normally designed to run on a specific operating system, - such as the contemporary iOS, macOS, Windows or Android - but in the past mobile carriers had their own portals for apps and related media content.














