Related Research Articles
A Linux distribution is an operating system made from a software collection that is based upon the Linux kernel and, often, a package management system. Linux users usually obtain their operating system by downloading one of the Linux distributions, which are available for a wide variety of systems ranging from embedded devices and personal computers to powerful supercomputers.
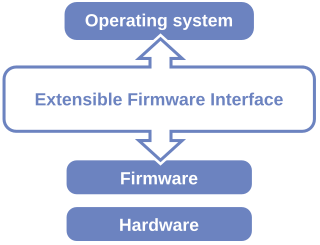
The Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) is a specification that defines a software interface between an operating system and platform firmware. UEFI replaces the legacy Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) firmware interface originally present in all IBM PC-compatible personal computers, with most UEFI firmware implementations providing support for legacy BIOS services. UEFI can support remote diagnostics and repair of computers, even with no operating system installed.

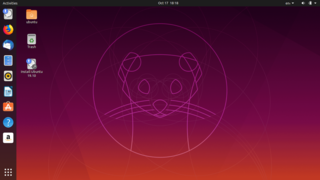
Ubuntu is a free and open-source Linux distribution based on Debian. Ubuntu is officially released in three editions: Desktop, Server, and Core for the internet of things devices and robots. All the editions can run on the computer alone, or in a virtual machine. Ubuntu is a popular operating system for cloud computing, with support for OpenStack.

Xubuntu is a Canonical Ltd.–recognized, community-maintained derivative of the Ubuntu operating system. The name Xubuntu is a portmanteau of Xfce and Ubuntu, as it uses the Xfce desktop environment, instead of Ubuntu's GNOME desktop.
In computing, initrd is a scheme for loading a temporary root file system into memory, which may be used as part of the Linux startup process. initrd and initramfs refer to two different methods of achieving this. Both are commonly used to make preparations before the real root file system can be mounted.

A multiseat, multi-station or multiterminal configuration is a single computer which supports multiple independent local users at the same time.

A bootsplash, also known as a bootscreen, is a graphical representation of the boot process of the operating system.

Linux Mint is a community-driven Linux distribution based on Ubuntu or Debian that strives to be a 'modern, elegant and comfortable operating system which is both powerful and easy to use'. Linux Mint provides full out-of-the-box multimedia support by including some proprietary software, such as multimedia codecs, and comes bundled with a variety of free and open-source applications.
The Linutop is a small, light, environmentally friendly Nettop computer containing a metal case and no moving parts, that runs the Linutop OS . Linutop Kiosk software and Linutop Tv server offer a full Digital signage solution. A variety of QT applications oriented towards secure web browsing and digital signage are available in the Operating system. Linutop is multimedia-capable and offers line-out/mic-in for sound. The device can be configured easily into a LTSP thin client. Linutop is suited for use in internet cafés, public libraries and schools.
Linux startup process is the multi-stage initialization process performed during booting a Linux installation. It is in many ways similar to the BSD and other Unix-style boot processes, from which it derives.

Splashtop OS is a discontinued proprietary Linux distribution intended to serve as instant-on environment for personal computers. The original concept of Splashtop was that it was intended to be integrated on a read-only device and shipped with the hardware, rather than installed by the user. It did not prevent the installation of another operating system for dual booting. It was an instant-on commercial Linux distribution targeting PC motherboard vendors and other device manufacturers. The first OEM partner for the original Splashtop was ASUS, and their first joint product was called Express Gate. Later, other computer manufacturers also built Splashtop into certain models and re-branded it under different names. The aspects below detailing these events are retained verbatim from past articles, for historical reference.

Usplash is a software project in the Ubuntu community. Historically, scrolling text "verbose mode" has typically appeared on Linux computers during boot. Usplash replaces the scrolling-text screens with a graphical splash screen. It was designed to replace Bootsplash, which did the same thing on the kernel space level. Since usplash operates in user space, it can be updated without recompiling the kernel.

Moblin, short for 'mobile Linux', is a discontinued open source operating system and application stack for Mobile Internet Devices (MIDs), netbooks, nettops and embedded devices.
Acer Aspire One is a line of netbooks first released in July 2008 by Acer Inc.

Ubuntu releases are made semiannually by Canonical Ltd, the developers of the Ubuntu operating system, using the year and month of the release as a version number. The first Ubuntu release, for example, was Ubuntu 4.10 and was released on 20 October 2004. Consequently, version numbers for future versions are provisional; if the release is delayed until a different month to that planned, the version number will change accordingly.
Netbooks are small laptops, with screen sizes between approximately 7 and 12 inches and low power consumption. They use either an SSD or a HDD for storage, have up to 2 gigabytes of RAM, lack an optical disk drive, and usually have USB, Ethernet, WiFi and often Bluetooth connectivity. The name emphasizes their use as portable Internet appliances.

Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) is a compatibility layer for running Linux binary executables natively on Windows 10 and Windows Server 2019.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Ubuntu:
References
- ↑ "Making a Splash". Netsplit.com. Archived from the original on October 8, 2009. Retrieved 2009-10-31.