A Linux distribution is an operating system made from a software collection that includes the Linux kernel and often a package management system. They are often obtained from the website of each distribution, which are available for a wide variety of systems ranging from embedded devices and personal computers to servers and powerful supercomputers.

Scanner Access Now Easy (SANE) is an open-source application programming interface (API) that provides standardized access to any raster image scanner hardware. The SANE API is public domain. It is commonly used on Linux.
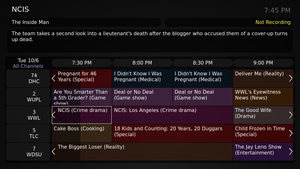
MythTV is a free and open-source home entertainment application with a simplified "10-foot user interface" design for the living room TV. It turns a computer with the necessary hardware into a network streaming digital video recorder, a digital multimedia home entertainment system, or home theater personal computer. It can be considered a free and open-source alternative to TiVo or Windows Media Center. It runs on various operating systems, primarily Linux, macOS, and FreeBSD.

Ubuntu is a Linux distribution derived from Debian and composed mostly of free and open-source software. Ubuntu is officially released in multiple editions: Desktop, Server, and Core for Internet of things devices and robots. The operating system is developed by the British company Canonical and a community of other developers, under a meritocratic governance model. As of April 2024, the most-recent long-term support release is 24.04.
Linux adoption is the adoption of Linux computer operating systems (OS) by households, nonprofit organizations, businesses, and governments.

NetworkManager is a daemon that sits on top of libudev and other Linux kernel interfaces and provides a high-level interface for the configuration of the network interfaces.
The Linutop is a small, light, environmentally friendly nettop computer containing a metal case and no moving parts, that runs the Linutop OS. It is sold by Linutop SAS of Paris, France. Linutop Kiosk software and Linutop Tv server offer a full Digital signage solution. A variety of QT applications oriented towards secure web browsing and digital signage are available in the Operating system. Linutop is multimedia-capable and offers line-out/mic-in for sound. The device can be configured easily into a LTSP thin client. Linutop is suited for use in internet cafés, public libraries and schools.

Oracle VM VirtualBox is a hosted hypervisor for x86 virtualization developed by Oracle Corporation. VirtualBox was originally created by InnoTek Systemberatung GmbH, which was acquired by Sun Microsystems in 2008, which was in turn acquired by Oracle in 2010.
Microsoft Application Virtualization is an application virtualization and application streaming solution from Microsoft. It was originally developed by Softricity, a company based in Boston, Massachusetts, acquired by Microsoft on July 17, 2006. App-V represents Microsoft's entry to the application virtualization market, alongside their other virtualization technologies such as Hyper-V, Microsoft User Environment Virtualization (UE-V), Remote Desktop Services, and System Center Virtual Machine Manager.

Microsoft Hyper-V, codenamed Viridian, and briefly known before its release as Windows Server Virtualization, is a native hypervisor; it can create virtual machines on x86-64 systems running Windows. Starting with Windows 8, Hyper-V superseded Windows Virtual PC as the hardware virtualization component of the client editions of Windows NT. A server computer running Hyper-V can be configured to expose individual virtual machines to one or more networks. Hyper-V was first released with Windows Server 2008, and has been available without additional charge since Windows Server 2012 and Windows 8. A standalone Windows Hyper-V Server is free, but has a command-line interface only. The last version of free Hyper-V Server is Hyper-V Server 2019, which is based on Windows Server 2019.

Ubuntu releases are made semiannually by Canonical Ltd, its developers, using the year and month of the release as a version number. The first Ubuntu release, for example, was Ubuntu 4.10 and was released on 20 October 2004. Consequently, version numbers for future versions are provisional; if the release is delayed until a different month than planned, the version number will change accordingly.

Ubiquity is the default installer for Ubuntu and its derivatives. It is run from the Live CD or USB and can be triggered to run from the options on the device or on the desktop of the Live mode. It was first introduced in Ubuntu 6.06 LTS "Dapper Drake". At program start, it allows the user to change the language to a local language if they prefer. It is designed to be easy to use.

Smuxi is a cross-platform IRC client for the GNOME desktop inspired by Irssi. It pioneered the concept of separating the frontend client from the backend engine which manages connections to IRC servers inside a single graphical application.

Unity is a graphical shell for the GNOME desktop environment originally developed by Canonical Ltd. for its Ubuntu operating system. It debuted in 2010 in the netbook edition of Ubuntu 10.10 and was used until Ubuntu 17.10. Since 2017, its development was taken over by the Unity7 Maintainers (Unity7) and UBports.
LinHES is a Linux distribution designed for use on Home Theater PCs (HTPCs). Before version 6, it was called KnoppMyth. The most recent release (R8), for 64-bit machines only, is based on Arch Linux, though previous versions were based on Knoppix and Debian.
Besides the Linux distributions designed for general-purpose use on desktops and servers, distributions may be specialized for different purposes including computer architecture support, embedded systems, stability, security, localization to a specific region or language, targeting of specific user groups, support for real-time applications, or commitment to a given desktop environment. Furthermore, some distributions deliberately include only free software. As of 2015, over four hundred Linux distributions are actively developed, with about a dozen distributions being most popular for general-purpose use.

GNOME Software is a utility for installing applications and updates on Linux. It is part of the GNOME Core Applications, and was introduced in GNOME 3.10.
Ubuntu is a Debian-based Linux distribution for personal computers, tablets and smartphones, where the Ubuntu Touch edition is used; and also runs network servers, usually with the Ubuntu Server edition, either on physical or virtual servers or with containers, that is with enterprise-class features.

Foliate is a free e-book reading application for desktop Linux systems. The name refers to leaves, meaning "(getting) leafy" or "…-leaved".