| Developer(s) | various |
|---|---|
| Stable release | 67 |
| Platform | Ubuntu (Linux) |
| Available in | English |
| License | Various (Ubuntu MOTU Developers) |
| Website | Ubuntu wiki RestrictedFormats |
Ubuntu Restricted Extras is a software package for the computer operating system Ubuntu that allows the user to install essential software which is not already included due to legal or copyright reasons.
It is a meta-package that installs:
The software in this package is not included in Ubuntu by default, as Ubuntu maintainers wish to include only completely free software in out-of-the-box installations. Included packages may be closed-source, encumbered by software patents, or otherwise restricted. For example, the Adobe Flash plugin is a closed-source piece of software. Additionally, many multimedia formats such as MP3 and H.264 are patented. In countries where these patents apply, legally distributing software that use these formats may require paying licensing fees to the patent owners. [1]
The Ubuntu Restricted Extras is a metapackage and has the following dependencies: [2]
Starting with Ubuntu 10.10, several of these dependencies are included indirectly via another meta-package ubuntu-restricted-addons which is included by default.
Due to the legal status of the software included in Ubuntu Restricted Extras, the package is not included by default on any Ubuntu CDs. [3] [4] [5]

GNOME Evolution is the official personal information manager for GNOME. It has been an official part of GNOME since Evolution 2.0 was included with the GNOME 2.8 release in September 2004. It combines e-mail, address book, calendar, task list and note-taking features. Its user interface and functionality is similar to Microsoft Outlook. Evolution is free software licensed under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL).
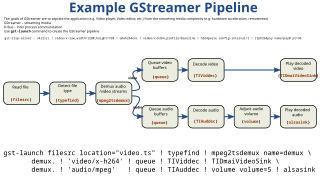
GStreamer is a pipeline-based multimedia framework that links together a wide variety of media processing systems to complete complex workflows. For instance, GStreamer can be used to build a system that reads files in one format, processes them, and exports them in another. The formats and processes can be changed in a plug and play fashion.

Rhythmbox is a free and open-source audio player software, tag editor and music organizer for digital audio files on Linux and Unix-like systems.

Ubuntu is a Linux distribution based on Debian and composed mostly of free and open-source software. Ubuntu is officially released in three editions: Desktop, Server, and Core for Internet of things devices and robots. All of the editions can run on a computer alone, or in a virtual machine. Ubuntu is a popular operating system for cloud computing, with support for OpenStack. Ubuntu's default desktop changed back from the in-house Unity to GNOME after nearly 6.5 years in 2017 upon the release of version 17.10.
Maven is a build automation tool used primarily for Java projects. Maven can also be used to build and manage projects written in C#, Ruby, Scala, and other languages. The Maven project is hosted by the Apache Software Foundation, where it was formerly part of the Jakarta Project.
FAAC or Freeware Advanced Audio Coder is a software project which includes the AAC encoder FAAC and decoder FAAD2. It supports MPEG-2 AAC as well as MPEG-4 AAC. It supports several MPEG-4 Audio object types, file formats, multichannel and gapless encoding/decoding and MP4 metadata tags. The encoder and decoder is compatible with standard-compliant audio applications using one or more of these object types and facilities. It also supports Digital Radio Mondiale.

Maemo is a software platform originally developed by Nokia, now developed by the community, for smartphones and Internet tablets. The platform comprises both the Maemo operating system and SDK. Maemo played a key role in Nokia's strategy to compete with Apple and Android, and that strategy failed for complex, institutional and strategic reasons.

Gnash is a media player for playing SWF files. Gnash is available both as a standalone player for desktop computers and embedded devices, as well as a plugin for the browsers still supporting NPAPI. It is part of the GNU Project and is a free and open-source alternative to Adobe Flash Player. It was developed from the gameswf project.

Banshee is a cross-platform open-source media player, called Sonance until 2005. Built upon Mono and Gtk#, it used the GStreamer multimedia platform for encoding, and decoding various media formats, including Ogg Vorbis, MP3 and FLAC. Banshee can play and import audio CDs and supports many portable media players, including Apple's iPod, Android devices and Creative's ZEN players. Other features include Last.fm integration, album artwork fetching, smart playlists and podcast support. Banshee is released under the terms of the MIT License. Stable versions are available for many Linux distributions, as well as a beta preview for OS X and an alpha preview for Windows.

Compiz is a compositing window manager for the X Window System, using 3D graphics hardware to create fast compositing desktop effects for window management. Effects, such as a minimization animation or a cube workspace, are implemented as loadable plugins. Because it conforms to the ICCCM conventions, Compiz can be used as a substitute for the default Mutter or Metacity, when using GNOME Panel, or KWin in KDE Plasma Workspaces. Internally Compiz uses the OpenGL library as the interface to the graphics hardware.

Pitivi is a free and open-source non-linear video editor for Linux, developed by various contributors from free software community and the GNOME project, with support also available from Collabora. Pitivi is designed to be the default video editing software for the GNOME desktop environment. It is licensed under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License.
Automatix is a tool designed to automate the addition of applications, codecs, fonts and libraries not provided directly by the software repositories of Debian-based distributions.

Ubuntu Studio is a recognized flavor of the Ubuntu Linux distribution, which is geared to general multimedia production. The original version, based on Ubuntu 7.04, was released on 10 May 2007.
Medibuntu was a community-maintained repository of Debian packages that could not be included in the Ubuntu distribution for legal reasons.

Moonlight was a free and open source implementation for Linux and other Unix-based operating systems of the now deprecated Microsoft Silverlight application framework, developed and then abandoned by the Mono Project. Like Silverlight, Moonlight was a web application framework which provided capabilities similar to those of Adobe Flash, integrating multimedia, graphics, animations and interactivity into a single runtime environment.

Buzztrax is a free software project designed to create a clone of the Buzz music composer. Its functionality is to preserve the playability of the compositions made with Buzz. Songs are made by adding virtual sound generators and effects, connecting them, recording short musical phrases and arranging them in the sequencer. For distribution, songs can be exported to common audio formats such as OGG, MP3, WAV and many others.
Ultamatix was a tool to automate the addition of applications, codecs, fonts and libraries not provided directly by the software repositories of Debian-based distributions like Ubuntu.

Ubiquity is the default installer for Ubuntu and its derivatives. It is run from the Live CD or USB and can be triggered to run from the options on the device or on the desktop of the Live mode. It was first introduced in Ubuntu 6.06 LTS "Dapper Drake". At program start, it allows the user to change the language to a local language if they prefer. It is designed to be easy to use.
The HTML5 specification introduced the video element for the purpose of playing videos, partially replacing the object element. HTML5 video is intended by its creators to become the new standard way to show video on the web, instead of the previous de facto standard of using the proprietary Adobe Flash plugin, though early adoption was hampered by lack of agreement as to which video coding formats and audio coding formats should be supported in web browsers. As of 2020, HTML5 video is the only widely supported video playback technology in modern browsers, with the Flash plugin being phased out.

Zim is a graphical text editor designed to maintain a collection of locally stored wiki-pages, a personal wiki. Each wiki-page can contain things like text with simple formatting, links to other pages, attachments, and images. Additional plugins, such as an equation editor and spell-checker, are also available. The wiki-pages are stored in a folder structure in plain text files with wiki formatting. Zim can be used with the Getting Things Done method.