
Medicago is a genus of flowering plants, commonly known as medick or burclover, in the legume family (Fabaceae). It contains at least 87 species and is distributed mainly around the Mediterranean basin. The best-known member of the genus is alfalfa, an important forage crop, and the genus name is based on the Latin name for that plant, medica, from Greek: μηδική (πόα) Median (grass). Most members of the genus are low, creeping herbs, resembling clover, but with burs. However, alfalfa grows to a height of 1 meter, and tree medick is a shrub. Members of the genus are known to produce bioactive compounds such as medicarpin and medicagenic acid. Chromosome numbers in Medicago range from 2n = 14 to 48.

Forage is a plant material eaten by grazing livestock. Historically, the term forage has meant only plants eaten by the animals directly as pasture, crop residue, or immature cereal crops, but it is also used more loosely to include similar plants cut for fodder and carried to the animals, especially as hay or silage.

Medicago truncatula, the barrelclover, strong-spined medick, barrel medic, or barrel medick, is a small annual legume native to the Mediterranean region that is used in genomic research. It is a low-growing, clover-like plant 10–60 centimetres (3.9–23.6 in) tall with trifoliate leaves. Each leaflet is rounded, 1–2 centimetres (0.39–0.79 in) long, often with a dark spot in the center. The flowers are yellow, produced singly or in a small inflorescence of two to five together; the fruit is a small, spiny pod.

Root nodules are found on the roots of plants, primarily legumes, that form a symbiosis with nitrogen-fixing bacteria. Under nitrogen-limiting conditions, capable plants form a symbiotic relationship with a host-specific strain of bacteria known as rhizobia. This process has evolved multiple times within the legumes, as well as in other species found within the Rosid clade. Legume crops include beans, peas, and soybeans.
NVC community CG7 is one of the calcicolous grassland communities in the British National Vegetation Classification system. It is one of three short-sward communities associated with heavy grazing, within the lowland calcicolous grassland group, and is regarded as the eastern counterpart of "typical" chalk grassland.

Colias croceus, clouded yellow, is a small butterfly of the family Pieridae, that is, the yellows and whites.

Medicago lupulina, commonly known as black medick, nonesuch, or hop clover, is a plant of dry grassland belonging to the legume or clover family. Plants of the genus Medicago, or bur clovers, are closely related to the true clovers (Trifolium) and sweet clover (Melilotus). Like the true clovers, black medick has three leaflets and a small, yellow flower closely resembling those of lesser trefoil. Black medick belongs to the same genus as alfalfa.

Medicago polymorpha is a plant species of the genus Medicago. It is native to the Mediterranean basin but is found throughout the world. It forms a symbiotic relationship with the bacterium Sinorhizobium medicae, which is capable of nitrogen fixation. Common names include California burclover, toothed bur clover, toothed medick and burr medic.

Medicago arborea is a flowering plant species in the pea and bean family Fabaceae. Common names include moon trefoil, shrub medick, alfalfa arborea, and tree medick. It is found throughout Europe and especially in the Mediterranean basin, primarily on rocky shores among shrubby vegetation. It forms a symbiotic relationship with the bacterium Sinorhizobium meliloti, which is capable of nitrogen fixation. It is the only member of the genus Medicago which is used as an ornamental. M. arborea is sometimes misidentified as Cytisus, which it resembles.

Medicago falcata is a plant species of the genus Medicago. It is native to much of Europe and Asia, but is found throughout the world. It forms a symbiotic relationship with the bacterium Sinorhizobium meliloti, which is capable of nitrogen fixation. Its common names include yellow lucerne, sickle alfalfa, yellow-flowered alfalfa, yellow alfalfa, sickle medick and yellow medick.

Medicago littoralis is a plant species of the genus Medicago. It is found primarily in the Mediterranean basin. It forms a symbiotic relationship with the bacterium Sinorhizobium meliloti, which is capable of nitrogen fixation. Common names include shore medick, water medick, coastal medick, and strand medick.

Medicago turbinata, the Southern medick, is a plant species of the genus Medicago It is found throughout the Mediterranean basin. It forms a symbiotic relationship with the bacterium Sinorhizobium medicae, which is capable of nitrogen fixation. An unidentified lectin isolated from M. turbinata has shown limited usefulness as a phytohaemagglutinin. The seed weight is 4.66 pounds.

Nomophila noctuella, the rush veneer, is a species of moth of the family Crambidae.

Vermiculation is a surface pattern of dense but irregular lines, so called from the Latin vermiculus meaning "little worm" because the shapes resemble worms, worm-casts, or worm tracks in mud or wet sand. The word may be used in a number of contexts for patterns that have little in common. The adjective vermiculated is more often used than the noun.

Medicarpin is a pterocarpan, a derivative of isoflavonoids.

Mirificarma eburnella is a moth of the family Gelechiidae. It is found in western, central and southern Europe and extends to North Africa, the Middle East and Russia. It is also found in California, United States, where it is presumed to have been introduced.
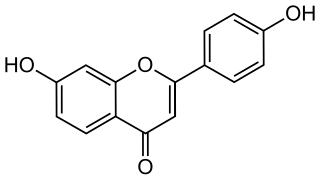
4′,7-Dihydroxyflavone is a flavone. It is found in Medicago truncatula in relation with the root nodulation symbiont Sinorhizobium meliloti or in seeds of Sophora viciifolia.

Medicago Inc. was a Canadian biotechnology company focused on the discovery, development, and commercialization of virus-like particles using plants as bioreactors to produce proteins, candidate vaccines, and medications. By using live plant leaves as hosts in the discovery and manufacturing process, the Medicago "Proficia" technology intended to create a rapid, high-yield system for its product candidates. Privately owned by a subsidiary of Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Medicago and its product development programs were terminated by Mitsubishi in February 2023.

CoVLP was a COVID-19 vaccine developed by Medicago in Canada and GlaxoSmithKline (GSK). The product and Medicago, Inc. were owned by Mitsubishi who terminated the company and program in February 2023 due to high international market competition for COVID-19 vaccines.

Medicago rigidula, the Tifton burclover, is a species of annual herb in the family Fabaceae. They have a self-supporting growth form and compound, broad leaves. Individuals can grow to 0.50m tall. It is a secondary wild relative of the cultivated crop Barrel Clover, and a tertiary wild relative of cultivated Alfalfa.

















