
Melicope is a genus of about 240 species of shrubs and trees in the family Rutaceae, occurring from the Hawaiian Islands across the Pacific Ocean to tropical Asia, Australia and New Zealand. Plants in the genus Melicope have simple or trifoliate leaves arranged in opposite pairs, flowers arranged in panicles, with four sepals, four petals and four or eight stamens and fruit composed of up to four follicles.

β-Carboline (9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole) represents the basic chemical structure for more than one hundred alkaloids and synthetic compounds. The effects of these substances depend on their respective substituent. Natural β-carbolines primarily influence brain functions but can also exhibit antioxidant effects. Synthetically designed β-carboline derivatives have recently been shown to have neuroprotective, cognitive enhancing and anti-cancer properties.

Harmala alkaloids are several alkaloids that act as monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs). These alkaloids are found in the seeds of Peganum harmala, as well as Banisteriopsis caapi (ayahuasca), leaves of tobacco and coffee beans. The alkaloids include harmine, harmaline, harmalol, and their derivatives, which have similar chemical structures, hence the name "harmala alkaloids". These alkaloids are of interest for their use in Amazonian shamanism, where they are derived from other plants. Harmine, once known as telepathine and banisterine, is a naturally occurring beta-carboline alkaloid that is structurally related to harmaline, and also found in the vine Banisteriopsis caapi. Tetrahydroharmine is also found in B. caapi and P. harmala. Dr. Alexander Shulgin has suggested that harmine may be a breakdown product of harmaline. Harmine and harmaline are reversible inhibitors of monoamine oxidase A (RIMAs). They can stimulate the central nervous system by inhibiting the metabolism of monoamine compounds such as serotonin and norepinephrine.

Sida cordifolia is a perennial subshrub of the mallow family Malvaceae native to India. It has naturalized throughout the world, and is considered an invasive weed in Africa, Australia, the southern United States, Hawaiian Islands, New Guinea, and French Polynesia. The specific name, cordifolia, refers to the heart-shaped leaf.

Asparagus racemosus is a species of asparagus native from Africa through southern Asia, including the Indian subcontinent, to northern Australia. It grows 1–2 m tall and prefers to take root in gravelly, rocky soils high up in piedmont plains, at 1,300–1,400 m (4,300–4,600 ft) elevation. It was botanically described in 1799. Because of its multiple uses, the demand for Asparagus racemosus is constantly on the rise. Due to destructive harvesting, combined with habitat destruction, and deforestation, the plant is now considered "endangered" in its natural habitat.

Medicosma is a genus of shrubs and trees in the family Rutaceae, all native to New Guinea, Australia or New Caledonia. They usually have simple leaves arranged in opposite pairs, flowers arranged in cymes with four sepals, four petals and eight stamens. The fruit is a follicle fused at the base in groups of up to four, each containing one or two brown or black seeds.
Thomas Gordon Hartley was an American botanist.
Platydesma is a formerly recognized genus of plants in family Rutaceae. Evidence from 2009 indicated that Platydesma is nested within the genus Melicope and is sister to all Hawaiian Melicope species, and it is now placed within that genus. The other Melicope species are dioecious, whereas the flowers of species formerly placed in Platydesma are hermaphroditic, suggesting a rare evolutionary reversion away from dioecy. Species included:

Sarcomelicope is a genus of about ten species of flowering plants in the family Rutaceae that are endemic to the South Pacific.
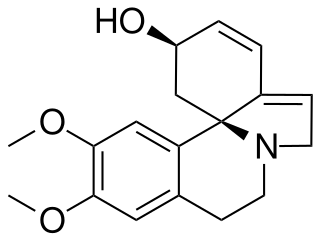
Erythravine is a tetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloid found in the plant Erythrina mulungu and other species of the genus Erythrina.

Evoxine (haploperine) is a furoquinoline alkaloid with hypnotic and sedative effects. It is found naturally in a variety of Australian and African plants including Evodia xanthoxyloides and Teclea gerrardii.

Zanthoxylum zanthoxyloides, also called Senegal prickly-ash or artar root, is a plant species in the genus Zanthoxylum.

Furoquinoline alkaloids are a group of alkaloids with simple structure. Distribution of this group of alkaloids is essentially limited to plant family Rutaceae. The simplest member of this group is dictamnine and most widespread member is skimmianine.

Akuammicine is a monoterpene indole alkaloid of the Vinca sub-group. It is found in the Apocynaceae family of plants including Picralima nitida, Vinca minor and the Aspidosperma.

Tabernaemontanine is a naturally occurring monoterpene indole alkaloid found in several species in the genus Tabernaemontana including Tabernaemontana divaricata.

Medicosma fareana, commonly known as white aspen, is a species of rainforest small tree in the family Rutaceae and is endemic to north Queensland. It has elliptical leaves and white or cream-coloured flowers borne singly or in small groups in leaf axils.

Medicosma glandulosa is a species of shrub or small tree in the family Rutaceae and is endemic to far north Queensland. It has elliptical to egg-shaped leaves and flowers that are white with red tips or cream-coloured, borne singly or in small groups in leaf axils.

Medicosma sessiliflora is a species of shrub or small tree in the family Rutaceae and is endemic to far north Queensland. It has simple elliptical to egg-shaped leaves with the narrower end towards the base and cream-coloured flowers borne singly or in small groups in leaf axils.

Zanthoxyloideae is a subfamily of the family Rutaceae. Its most notable member is probably Sichuan pepper.

















